Tulsi
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Volatile Oils
Tulsi consists of fresh and dried leaves of Ocimum sanctum Linn., belonging to family Labiatae.
TULSI
Synonyms
Sacred basil, Holy basil.
Biological Source
Tulsi consists of fresh and dried leaves of Ocimum sanctum Linn., belonging to
family Labiatae.
Geographical Source
It is a herbaceous, much branched annual plant found
throughout India, it is considered as sacred by Hindus. The plant is commonly
cultivated in garden and also grown near temples. It is propagated by seeds.
Tulsi, nowadays, is cultivated commercially for its volatile oil.
Characteristics
It is much branched small herb and 30 to 75 cm in height.
All parts of tulsi are used in medicine, especially fresh and dried leaves.
Leaves are oblong, acute with entire or serrate margin, pubescent on both sides
and minutely gland-dotted, The leaves are green in colour with aromatic flavour
and slightly pungent taste. Flowers are purplish in colour in the form of
racemes. Nutlets are subglobose, slightly compressed, pale brown or red in
colour. Seeds are reddish-black and subglobose.
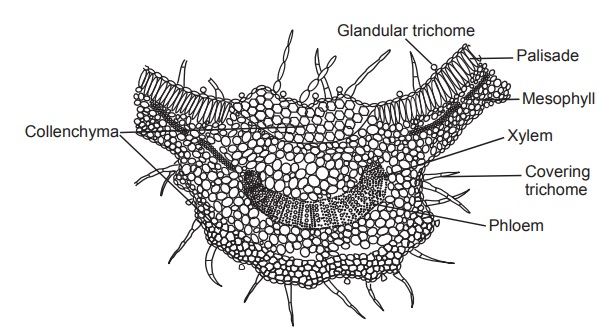
Microscopy
Tulsi leaf is dorsiventral. Stomata are of diacytic type,
par-ticularly abundant on lower surface. Epidermal cells are wavy walled with
thin cuticle. A single layer of elongated palisade cells is present below upper
epidermis. Mesophyll consists of four to six layers of spongy parenchymatous cells
with intercellular spaces and oil glands. Leaf bears both covering and
glandular trichomes; covering trichomes, uniseriate, multicellular and often
very long (100–400 μ). Glandular trichomes are sessile
with radiate head composed of eight cells with common cuticle forming a
bladder, typical labiate type trichomes. A few glandular trichomes with
unicellular stalk and a spherical unicellular head also occur. The midrib
region shows collenchymatous cells below both upper and lower epidermis. Xylem
bundles are arranged in an arc. The phloem is arranged on the dorsal side of
xylem.
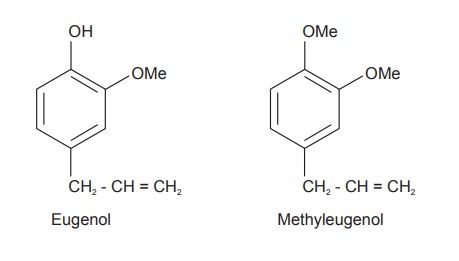
Chemical Constituents
Tulsi leaves contain bright, yellow coloured and pleas-ant
volatile oil (0.1 to 0.9%). The oil content of the drug varies depending upon
the type, the place of cultivation and season of its collection. The oil is
collected by steam distillation method from the leaves and flowering tops. It
contains approximately 70% eugenol, carvacrol (3%), and eugenol-methyl-ether
(20%). It also contains caryophyl-lin. Seeds contain fixed oil with good drying
properties. The plant is also reported to contain alkaloids, glycosides,
saponin, tannins, an appreciable amount of vitamin C and traces of maleic,
citric, and tartaric acid.
Uses
The fresh leaves, its juice and volatile oil are used for
various purposes. The oil is antibacterial and insecticidal. The leaves are
used as stimulant, aromatic, spasmolytic, and diaphoretic. The juice is used as
an antiperiodic and as a constituent of several preparations for skin diseases
and also to cure earache. Infusion of the leaves is used as a stomachic. The
drug is a good immunomodulatory agent.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparations known as
Abana, Diabecon, Diakof, Koflet (Himalaya Drug Company), Respinova (Lupin
Herbal Laboratory), Amulcure (Aimil Pharmaceuticals), Nomarks (Nyle Herbals),
Sualin (Hamdard), and Kofol syrup (Charak Pharma Pvt. Ltd.).
