Anise
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Volatile Oils
Anise consists of dried ripe fruits of Pimpinella anisum Linn., belonging to family Umbelliferae.
ANISE
Synonyms
Anise, Anise fruits, Aniseed, Sweet cumin, Star anise,
Chinese anise.
Biological Source
Anise consists of dried ripe fruits of Pimpinella anisum Linn., belonging to family Umbelliferae.
Geographical Source
Anise is native of Egypt, Greece, Crete, and Asia Minor and
at present is cultivated in European countries like Spain, North Africa, Italy,
Malta, Russia, Germany, Bulgaria, and Mexico.
History
Anise has been in use since the fourteenth century, The
ancient Greeks, including Hippocrates, prescribed Anise for coughs. In Virgil’s
time, the Ancient Romans used Anise in a special cake (Mustacae) which prevents
indigestion.
Historically, Anise was used due to the flavor, its ability
to promote digestion; it acted as an aphrodisiac, for infant colic, etc. Early
English herbalists recommended Anise for hiccups, for promoting lactation, in
headache, as breath freshener, in asthma, bronchitis, insomnia, nausea, lice,
infant colic, cholera, and even in cancer. Anise is one of the herbs that were
supposed to avert the Evil Eye.
Cultivation and Collection
The prorogation is done using seeds; the seeds are sown in
dry, light soil, on a warm, sunny border during early April. The plant flowers
in July and ripen in autumn. Once the fruits are ripened the plants are cut
down and the seeds thrashed out.
Characteristics
Anise is a delicate, white-flowered umbelliferous annual
herb which grows to about 18 inches high, with secondary feather-like leaflets
of bright green colour. Anise is an entire cremocarp and the pedicel is
attached. It has greyish brown colour, ovoid-conical shape. The size of fruit
varies from 3 to 5 mm long and 1.5 to 2 mm broad. Due to the presence of short,
conical epidermal trichomes the fruits exhibit a rough texture. It has sweet
and aromatic odour and taste.

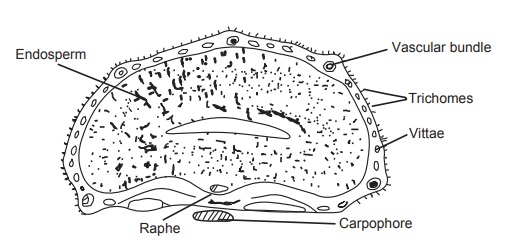
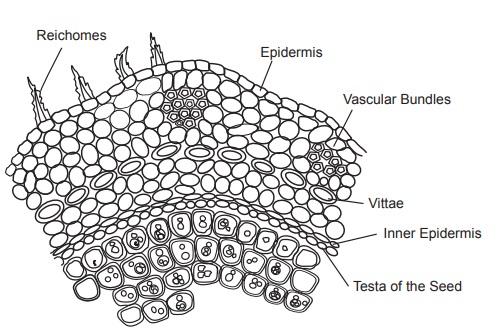
Microscopy
Anise has two vittae on the ventral surface and about 20 to
40 vittae on the dorsal surface. Below the primary ridges it has the vascular
strands, the epicarp consists of short, conical, epidermal trichomes. Mesocarp
has rounded parenchyma cells showing the parquetry arrangement. Testa is
single-layered cell with thin, brown-coloured cells, abundant oil globules, and
aleuron grains are present in the endosperm region.
Chemical Constituents
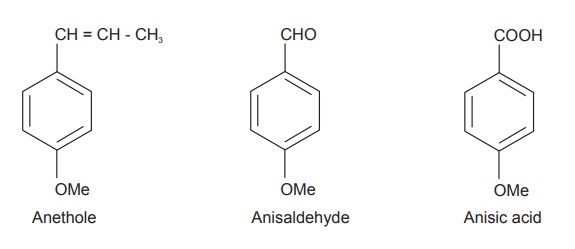
Anise fruit consist of 2.5 to 3.5% of a fragrant, syrupy,
volatile oil. The chief aromatic component of the essential oil is
trans-anethole, present to about 90% along with estragole, anisic acid,
anisaldehyde, anise ketone, β-caryophylline, linalool; polymers
of anethole, dianethole, and photoanet-hole. It consists of coumarins
(umbelliferone, scopoletin), flavonoid glycosides (rutin, isovitexin and
quercetin), and phenylpropanoids. Other constituents of the fruit are lipids,
fatty acids, sterols, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Uses
Anise is used as expectorant, carminative, aromatic,
antimicrobial, and antispasmodic. It can enhance the memory, increases
lactation, it is used in the treatment of bronchitis, asthma, relieves
menopausal discomforts, in whooping cough, externally in scabies, flatulent
colic of infants, overcomes nausea, and as a digestive.
