Coca Leaves
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Alkaloids
Coca consists of the dried leaves of various species of Eryth-mxylon, that is, Erythroxylon coca Lam (Huanco or Bolivian coca) or Erythroxylon coca var. Spruceanum (Peruvian, Truxillo or Java coca) also known as Erythroxylon truxillense Rusby., belonging to family Erythroxylaceae.
COCA LEAVES
Synonyms
Coca, Cuca, Cocaine, Folium cocae, Peruvian coca, Truxillo
coca, Java coca, Bolivian coca.
Biological Source
Coca consists of the dried leaves of various species of Eryth-mxylon, that is, Erythroxylon coca Lam (Huanco or
Bolivian coca) or Erythroxylon coca var. Spruceanum (Peruvian, Truxillo or Java
coca) also known as Erythroxylon
truxillense Rusby., belonging to family Erythroxylaceae.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in Bolivia, Peru, Indonesia, Ceylon, Java
and India.
Cultivation
Coca shrubs grow well in the situations similar to tea
plantations. It requires rich, light and well-drained soil at an altitude of
1,500–6,000 m. Cultivation is carried out by sowing seeds. Fertilizers have
their effects over these plants. In the second year the leaves will be matured
enough to collect in dry weather. The collected leaves are dried in shade and
packed.
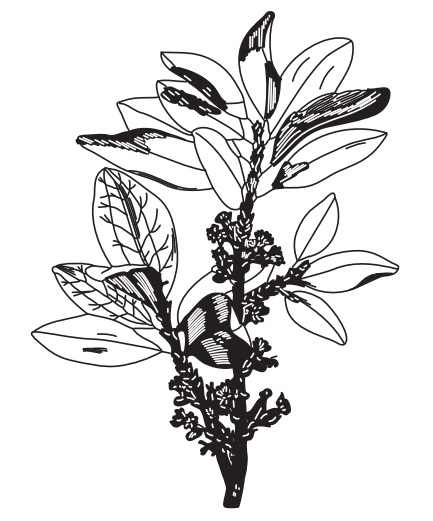
Characteristics
Erythroxylon coca: leaves are brownish-green in colour,
oval, entire and glabrous, with a
bitter taste, 3–8 cm long and 1.5–4 cm wide.
Erythroxylon truxillense: the leaves are much smaller and pale green in colour, elliptical,
entire, glaborous, not glossy, with bitter taste.

Microscopy
The epidermis has straight anticlinal walls and stomata
present are of the rubiaceous type only on the lower surface. The mesophyll
reveals the presence of single layer of palisade parenchyma cells only below
the upper epidermis. Prism of calcium oxalate crystals are seen in the spongy
parenchyma. The midrib has vascular bundle composed of xylem and phloem with a
band of pericyclic fibres below and few sclerenchyma above. Leaf has an
outstanding ridge, filled with collenchyma, presence of lignified idioblasts,
and development of sclerenchyma above and below the side veins are its unique
characters.
Chemical Constituents
Coca leaves contain the alkaloids Cocaine, Annamyl Cocaine,
and Truxilline or Cocamine. Truxillo or Peruvian leaves contain more alkaloid
than the Bolivian, though the latter are preferred for medicinal purposes. Java
Coca contains tropacocaine and four yellow crystalline glucosides in addition
to the other constituents.
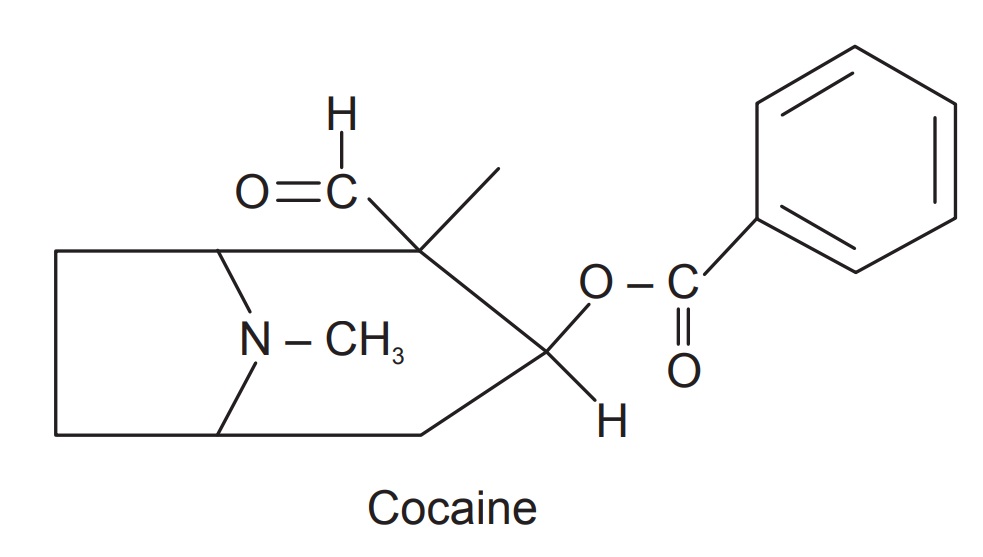
Uses
The actions of Coca depend principally on the alkaloid
Cocaine. Cocaine has stimulant action on CNS. The leaves are extensively chewed
to relieve hunger and fatigue. Coca alkaloids cause also hallucination. Coca
leaves are used as a cerebral and muscle stimulant, especially during
convalescence, to relieve nausea, vomiting and pains of the stomach without
upsetting the digestion. Cocaine also has local anesthetic action on skin and
mucous membrane; and is used as dental anaesthesia and minor local surgery of
ophthalmic, ear, nose and throat. Chemical structure of cocaine has lead to
several synthetic annaesthetics like anaesthesia, novocain, stovain, etc.
Adulterant
Jaborandi leaves are used as an adulterant of Coca leaves.
