Nux Vomica
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Alkaloids
Nux vomica consists of the dried ripe seeds of Strychnos nux vomica Linn, belonging to family Loganiaceae; containing not less than 1.2% strychnine.
NUX VOMICA
Synonyms
Semen strychni, Nux vomica Seed, Poison Nut, Semen
strychnos, Quaker Buttons, Bachelor’s buttons, Dog buttons, Vomit nut, Crow
fig.
Biological Source
Nux vomica consists of the dried ripe seeds of Strychnos nux vomica Linn, belonging to family Loganiaceae; containing not less than 1.2% strychnine.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in South India, Malabar Coast, Kerala,
Bengal, Eastern Ghats, North Australia and Ceylon.
Cultivation and Collection
The plant is a small tree around 12 m in height. Ripe and
mature fruits are collected in the month of November to February. The fruits
are 3–5 cm in diameter and are sub-spherical yellowish brown orange like
berries. The epicarp is leathery and the pulp is bitter whitish and
mucilaginous in which two to five seeds are embedded. The epicarp is separated
and the seeds are removed and washed to remove pulp. They are dried on mats in
the sun and graded according to size and exported.
Characteristics
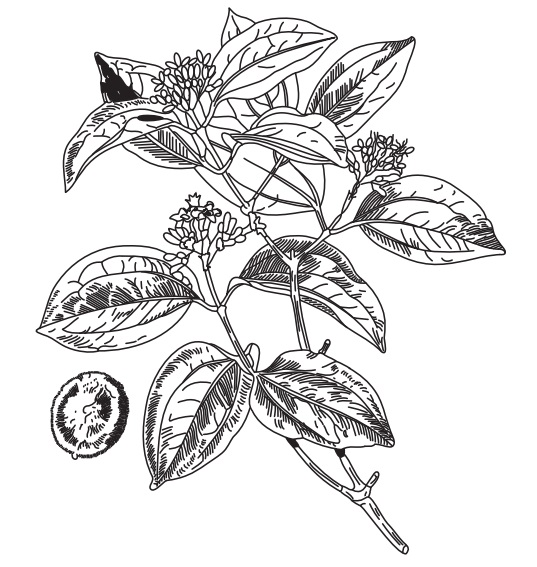
A medium-sized tree with a short, crooked, thick trunk, the
wood is white hard; close grained, durable and the root very bitter. Branches
irregular, covered with a smooth ash-coloured bark; young shoots deep green,
shiny. Leaves opposite, short stalked, oval, shiny, smooth on both sides, about
4 inches long and 3 inches broad. Flowers small, greenish-white, funnel shape,
in small terminal cymes, blooming in the cold season and having a disagreeable
smell. Fruit, about the size of a large apple with a smooth hard rind or shell
which when ripe is a lovely orange colour, rilled with a soft white jelly-like
pulp containing five seeds covered with a soft woolly like substance, white and
horny internally. Seeds have the shape of flattened disks densely covered with
closely appressed satiny hairs, size is 10–30 mm in diameter 3–5 mm thick,
radiating from the centre of the flattened sides and giving to the seeds a characteristic
sheen; they are very hard, with a dark grey horny endosperm in which the small
embryo is embedded; no odour but a very bitter taste.

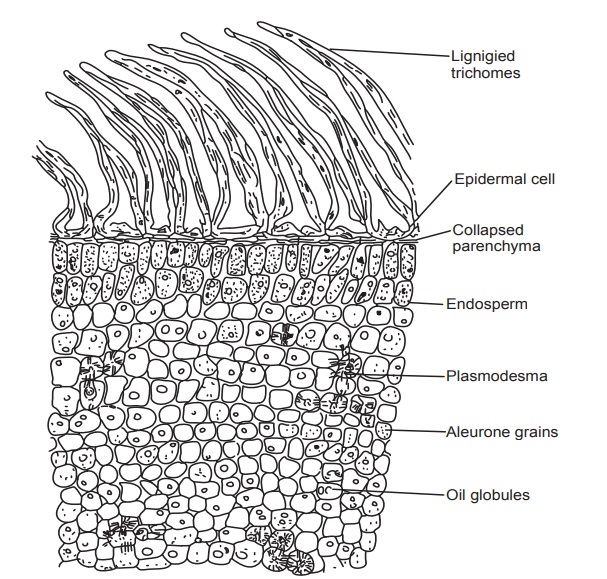
Microscopy
Epidermis consists of thick-waved, bent and twisted
lignified covering trichomes. The base of the trichome is large thick walled
with slit like pits. The upper part of the trichome is nearly at right angle to
the base and has wavy walls. Endosperm consists of thick walled isodiametric
cells consisting of hemicellulose which swells with water and contains
plasmodesma. Aleurone grains and fixed oil are present in endosperm and embryo.
Chemical Constituents
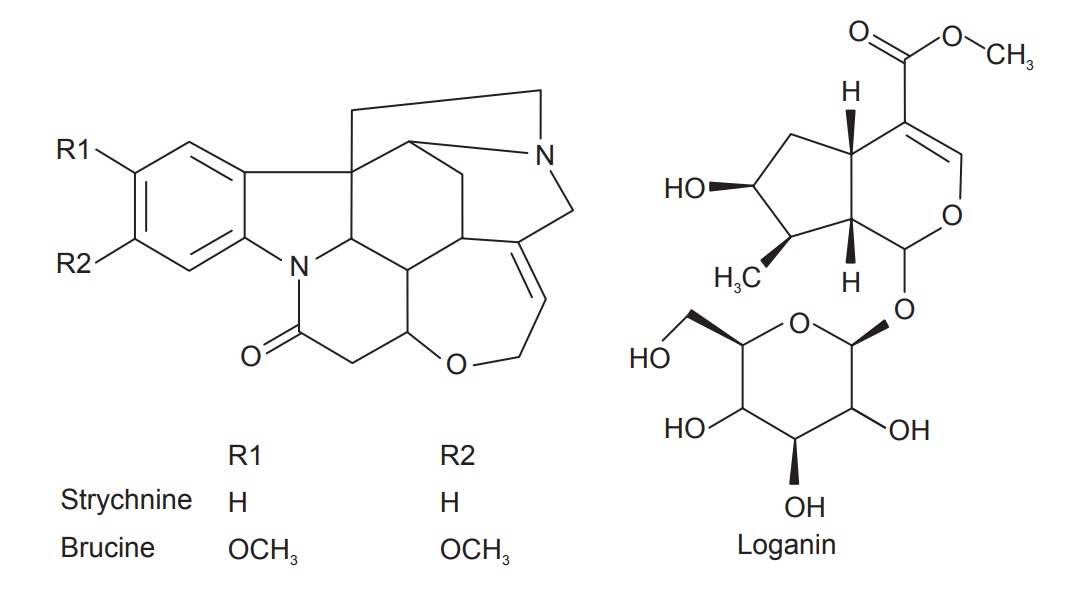
Nux vomica contains the alkaloids, Strychnine (1.25%) and
Brucine (1.5%), also traces of strychnicine, and a glucoside Loganin, about 3%
fatty matter, caffeotannic acid and a trace of copper. It contains about
2.5–3.5% bitter indole alkaloids. Strychnine is therapeutically active and toxic
alkaloid and is located in central portion of endosperm. Brucine is chemically
dimethoxystrychnine and is less toxic and has very little physiological action.
It is intensely bitter and is used as a standard for determining the bitter
value, of many bitter drugs. Brucine is more in the outer part. Vomicine and
pseudostrychnine are minor alkaloids.
The seeds also contain chlorogenic acid or caffeotannic
acid. Alkaloids are combined with chlorogenic acid or caffeotannic acid.
Loganin, a glucoside is also present. Cell walls of endosperm of nux vomica are
thick walled and contain reserve material hemicellulose consisting of mannan
and galactan which on hydrolysis yield mannose and galactose. Fatty matter is
3% aleurone grains and a trace of copper is present in the endosperm of the
seed. The pulp of the fruit contains about 5% of loganin together with the
alkaloid strychnicine.
Chemical Tests
1. Strychnine
Test: To a section
of endosperm add ammonium vanadate and sulphuric acid. Strychnine in the
middle portion of endosperm is stained purple.
2. Potassium
dichromate test: Strychnine
gives violet colour with potassium
dichromate and conc. sulphuric acid.
3. Brucine
Test: To a thick
section add concentrated nitric acid.
Outer part of endosperm is stained yellow to orange because of brucine.
4. Hemicellulose
Test: To a thick
section add iodine and sulphuric
acid. The cell walls are stained blue.
Uses
The properties of nux vomica are substantially those of the
alkaloid Strychnine. In the mouth it acts as a bitter, increasing appetite; it
stimulates peristalsis, in chronic constipation due to atony of the bowel it is
often combined with cascara and other laxatives with good effects. Strychnine,
the chief alkaloid constituent of the seeds, also acts as a bitter, increasing
the flow of gastric juice; it is rapidly absorbed as it reaches the intestines,
after which it exerts its characteristic effects upon the CNS, the movements of
respiration are deepened and quickened and the heart slowed through excitation
of the vagal centre. Strychnine has a stimulant action on spinal cord and
reflex movements are better. It is considered as nervine and sex tonic. The
senses of smell, touch, hearing and vision are rendered more acute, it
improves the pulse and raises blood pressure and is of great value as a tonic
to the circulatory system in cardiac failure. In toxic doses strychnine causes
violent tetanus like convulsions and death takes place due to asphyxia and respiratory
failure.
Brucine closely resembles strychnine in its action, but is
slightly less poisonous; it paralyses the peripheral motor nerves. It is said
that the convulsive action characteristic of strychnine is absent in brucine
almost entirely. It is used in pruritis and as a local anodyne in inflammations
of the external ear. Nux vomica is also known as vomiting nut but it has no
vomiting properties. However Strychnos
potatorum has emetic action.
Marketed Products
It is one of the ingredients of the preparation known as Neo
Tablets (Charak Pharma Pvt. Ltd.).
