Duboisia
| Home | | Pharmacognosy |Chapter: Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry : Drugs Containing Alkaloids
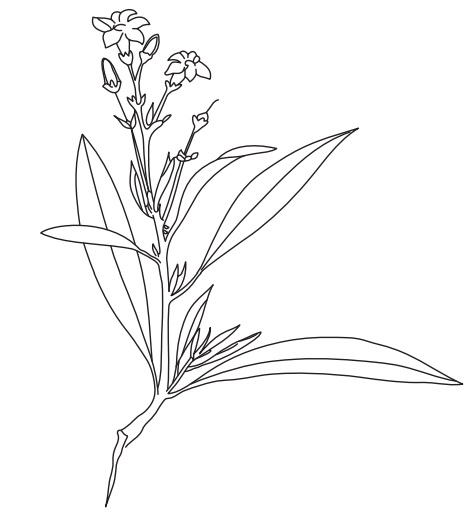
Duboisia consists of the dried leaves of Duboisia myoporoides R., Duboisia hopwoodii, D. leichhardtii, belonging to family Solanaceae.
DUBOISIA
Synonyms
Corkwood, cork tree.
Biological Source
Duboisia consists of the dried leaves of Duboisia myoporoides R., Duboisia hopwoodii, D. leichhardtii,
belonging to family Solanaceae.
Geographical Source
It is mainly found in Australia and Ecuador.
Characteristics
Duboisia hopwoodii: Perennial shrub to 3 m, sometimes as small tree with brown to purplish bark
on the young stems and corky older bark. Leaves are narrow, long and alternate
to 15 cm, with recurved point and straight margins. Open clusters of white
(with purple striped tube) flowers at the end of the branches. Black berry to 6
mm, containing one to two seeds in a dark pulp.
Duboisia myoporoides: Perennial shrub to small tree with corky bark with intensely bitter taste,
Leaves alternate pale green 3–10 cm × 1–1.5 cm, tapered at both ends. Open
clusters of small white flowers at the end of the branches and black juicy
berry, containing a few seeds in a dark pulp.
Duboisia leichardtii: Perennial shrub to small tree with corky bark with intensely bitter taste,
similar to D. myoporo-ides. Leaves
narrowly elliptic pale green 4–10 cm × 1–2 cm, tapered at both ends. Open clusters of small white flowers,
sometimes tinged with mauve, at the end of the branches. Flowers, late winter
to spring. Black juicy berry, containing a few seeds in a dark pulp.
Microscopy (Duboisia myoporoides)
The upper epidermis consists of polygonal tabular cells
covered with thick and striated cuticle. Stomata are very less with very few near
the midrib. The mesophyll has cylindrical palisade cells and just next to it is
a row of sub-rectangular collecting cells and 7 or 8 rows of spongy parenchyma
with scattered idioblasts. Each scattered idioblasts consist of small
micro-sphenoidal crystals of calcium oxalate. In the lower epidermis it has
numerous stomata which are cruciferous in nature. Scattered glandular trichomes
occur on both surfaces which are about 75–95 μ long and 15–25 μ wide at the head. The midrib has well developed ridge and
contains a meristele with xylem and superior supernumerary phloem.
Chemical Constituents
Duboisia myoporoides is considered as the chief
commercial source of scopolamine and
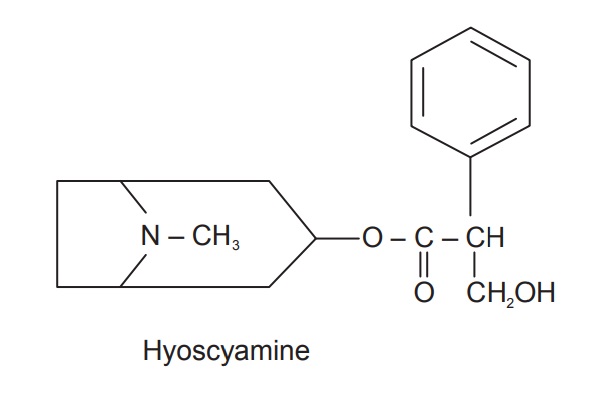
atropine. It contains hyoscyamine which is converted to atropine during
extraction. Along with it, the drug also contains norhyoscyamine, tigloidine,
valtropine, tiglyoxytropine. The synthetic process for scopolamine and atropine
is very costly and hence, much reliance is placed on its natural source.
Atropine (C17H23O3N) occurs as colourless
crystals, with a bitter taste and no odour. It is soluble in chloroform and
alcohol. It is a racemic form of hyoscyamine.
The chief constituent of Duboisia
hopwoodii was found to be nicotine and nonnicotine, with content reportedly
up to 25% of the dried weight of the plant material.
Chemical Tests
1. The addition of gold chloride
solution to atropine in water and hydrochloric acid gives lemon yellow
precipitate.
2. It gives positive Vitali Morin
reaction.
Uses
Duboisia leaves are the main source of atropine and
scopolamine. Atropine is the parasympatholytic drug. It also causes stimulant
action on central, medullary and higher nerve centres. Atropine has many
different therapeutic uses. It is used as an antidote for pilocarpine,
physostigmine and other choline esters. It relieves bronchial spasms in asthma.
As it suppresses the gastric secretions, it is used in peptic ulcer. It has
applications in ophthalmic practice, because of its dilatory effects on pupil
of the eye. It is also used to reduce tremor and rigidity in Parkinsonism.
Scopolamine is used as treatment for air and sea sickness and in the treatment
of stomach ulcers. Sedative, hypnotic and mydriatic (of variable strength),
which augments the activity of the respiratory system. Its alkaloid, Sulphate
of Duboisia, is sometimes used as a substitute for atropine. The homoeopaths
use the tincture and the alkaloid for paralysis and eye infections; a red spot
interfering with vision is an indication for its use. It is antidoted by coffee
and lemon juice.
