Excellence in Pharmacovigilance Model
| Home | | Pharmacovigilance |Chapter: Pharmacovigilance: Risk Management - a European Regulatory View
sThe ERMS Working Group adopted an approach to establishing a European Risk Management Strategy based on the model for delivering effective pharma-covigilance known as ‘Excellence in Pharmacovigilance’.
EXCELLENCE IN PHARMACOVIGILANCE
MODEL
sThe ERMS Working Group adopted an approach to establishing a European Risk Management Strategy based on the model for delivering effective pharma-covigilance known as ‘Excellence in Pharmacovigilance’. This was the result of a project set up by the then UK Medicines Control Agency and published in 2003. It is a conceptual framework for achieve-ment of demonstrable effectiveness in terms of public health protection, comprising the following components: (Figure 44.1).
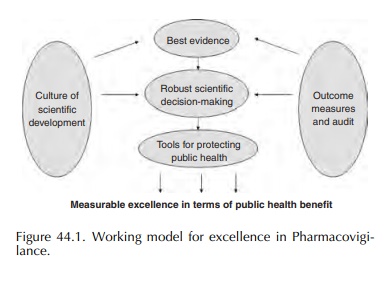
• Best evidence, moving up the ‘evidence
hierarchy’ away from spontaneous ADR reports to more reliable evidence, from
observational studies and clinical trials.
• Robust decision-making, including analysis of
potential impact of signals on risk–benefit balance.
‘Tools’
to protect public health including effective communication mechanisms as well
as action to update the marketing authorisation.
• Routine outcome measures and audit of
regulatory action.
• A culture of scientific development which
keeps pace with new developments and maximises oppor-tunities for improving
pharmacovigilance offered by new scientific and technological advances.
The
so-called ‘Excellence’ model not only defined the prerequisites for an
effective pharmacovigilance system, but argued for a change in mindset, a shift
from searching for evidence of harm to demonstrating safety, and a capability
to demonstrate that serious adverse reactions are rare in the long term. This
in turn requires a consideration at the time of licensing a new medicine of the
level of safety already demonstrated, any possible concerns which need further
investi-gation and appropriate strategies by which further evidence is to be
gathered.
This
proactive approach to demonstrating safety merited wider debate, and the
International Confer-ence on Harmonisation presented an opportunity to gain the
perspective of the United States and Japan. The outcome was the harmonised
tripartite guide-lines E2E on Pharmacovigilance Planning, adopted in November
2004. This guideline sets out the elements of the safety specification and
provides guidance on the structure of the pharmacovigilance plan and
appropriate methodologies to generate information on known risks as well as
what is not known.
Related Topics
