Hormones and Related Drugs
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Hormones And Related Drugs
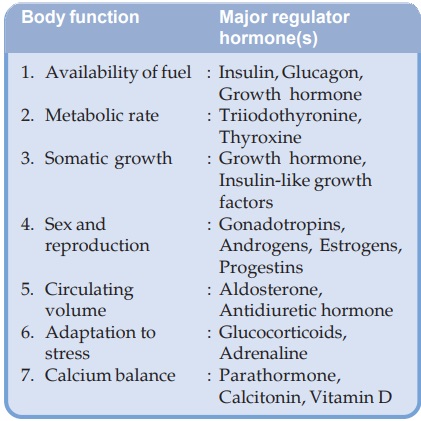
Hormone (Greek hormaein—to stir up) is a substance of intense biological activity that is produced by specific cells in the body and is transported through circulation to act on its target cells.
HORMONES AND RELATED DRUGS
Hormone (Greek hormaein—to stir up) is a substance
of intense biological activity that is produced by specific cells in the body and is transported through circulation to act on its target cells.
Hormones
regulate body functions to bring about a programmed pattern of life events and
maintain homeostasis in the face of markedly variable external/internal
environment.
Hormones
are secreted by the endocrine or ductless glands. These are:
1. Pituitary
a)
Anterior
Growth hormone (GH),
Prolactin (Prl),
Adrenocorticotropic
hormone (ACTH, Corticotropin),
Thyroid stimulating
hormone (TSH, Thyrotropin),
Gonadotropins—Follicle
stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing hormone (LH).
b)
Posterior—Oxytocin,
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, Vasopressin).
2. Thyroid Thyroxine (T4),
Triiodothyronine (T3), Calcitonin.
3. Parathyroid Parathormone (PTH).
4. Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Insulin, Glucagon.
5. Adrenals
a)
Cortex
Glucocorticoids
(hydrocortisone) Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) Sex steroids (dehydroepiandrosterone)
b)
Medulla
Adrenaline,
Noradrenaline
6.
Gonads
Androgens (testosterone)
Estrogens (estradiol) Progestins
(progesterone)
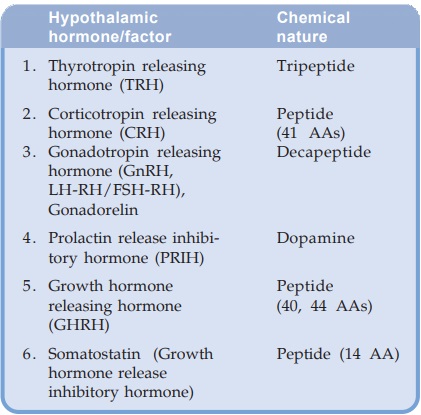
In addition, hypothalamus,
which is a part of the CNS and not a gland, produces many releasing and
inhibitory hormones which control the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones.
Some important ones of these are given below
Placenta also secretes many hormones:
Chorionic gonadotropin
Prolactin
Estrogens
Progesterone
Placental lactogen
Chorionic thyrotropin
The natural hormones
and in many cases their synthetic analogues which may be more suitable
therapeutically, are used as drugs for substitution therapy as well as for
pharmaco-therapy. In addition, hormone antagonists and synthesis/ release inhibitors
are of therapeutic importance.
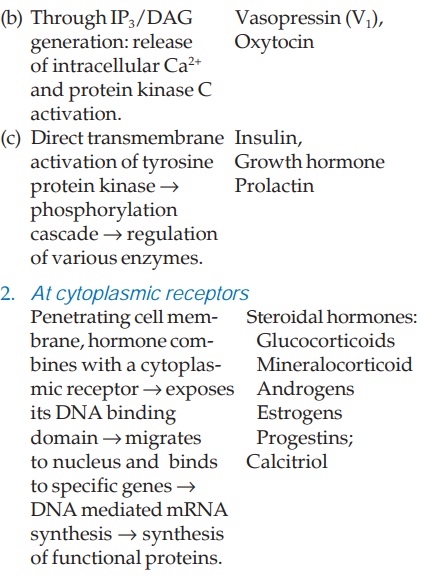
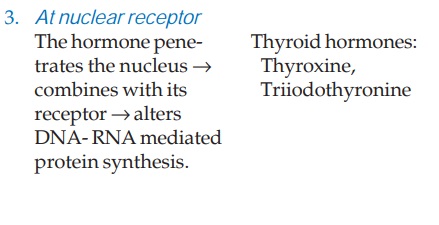
Sites And
Mechanisms Of Hormone Action
The hormones act on
their specific receptors located on or within their target cells. Receptor
activation by the hormones is translated into response in a variety of ways.