Nervous or Neural Tissues
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Levels of Organization : Tissues
Nervous tissues are specialized for the conduction of electrical impulses from one region of the body to another. They are also called neural tissues or nerve tissues.
Types of
Tissues
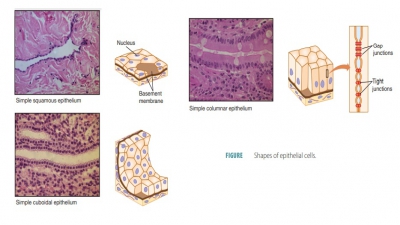
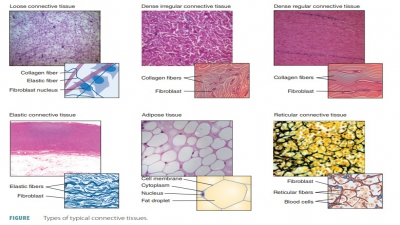
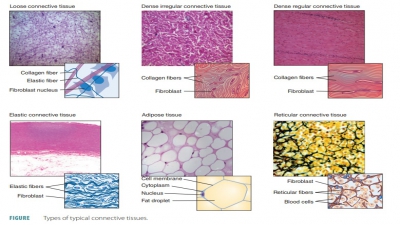
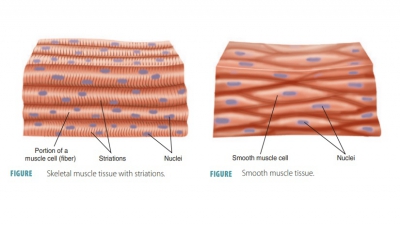
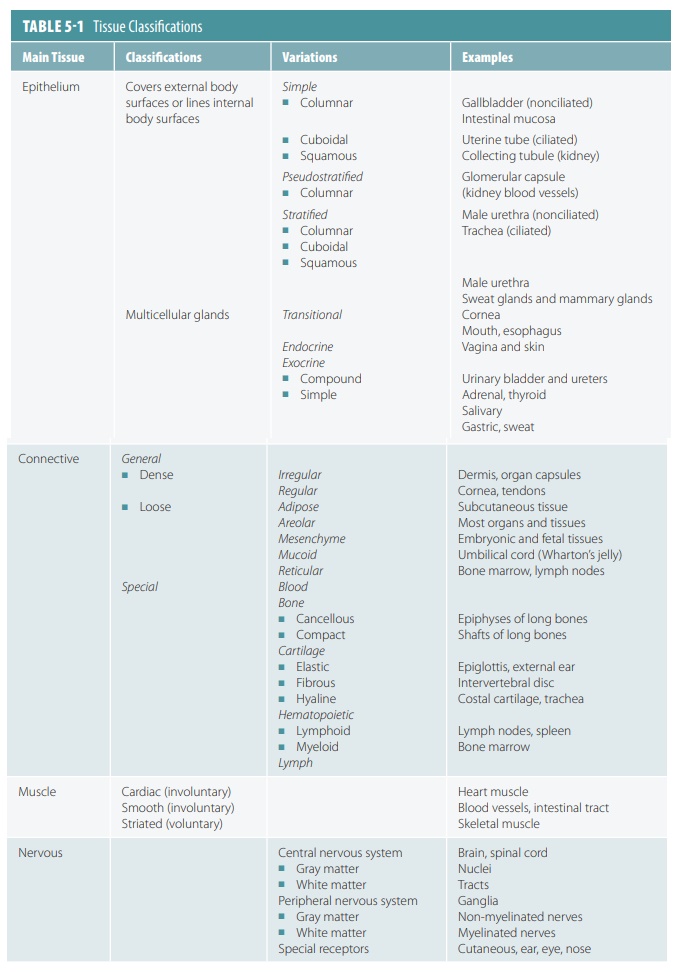
The human body is primarily made up of four major types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Epithelial tissues cover body surfaces, cover and line internal organs, and make up the glands. Connective tissues are widely distributed throughout the body, filling internal spaces, and func-tion to bind, support, and protect body structures. Muscle tissues are specialized for contraction and include the skeletal muscles of the body, the heart, and the muscular walls of hollow organs. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are used for movement of the body. Nervous tissues carry information from one part of the body to another via electrical impulses. They are found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves (TABLE 5-1).
The human body is primarily made up of four major types of tissues:
1. epithelial,
2. connective
3. muscle, and
4. nervous.
Nervous
Tissues
Nervous tissues are specialized
for the conduction of electrical impulses from one region of the body to
another. They are also called neural
tissues or nerve tissues. Nervous tissues contain two
basic types of cells: neurons and
several kinds of supporting cells, collectively called neuroglia or glial
cells. Approxi-mately, 98% of nervous tissues are found in the brain,
peripheral nerves, and spinal cord. Thought process occurs because of the
brain’s neurons, as electrical impulses occur in the form of changes in
transmem-brane potential. Impulse frequency and patterns con-vey information.
Neurons are the longest cells in the body, with some of them measuring about 39
inches in length. Neurons can mostly not divide under nor-mal conditions.
Therefore, they do not have a great ability to repair themselves after being
injured. A typ-ical neuron has a large cell
body, with a large nucleus and nucleolus.
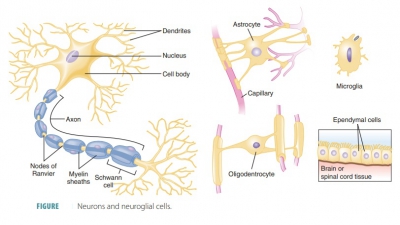
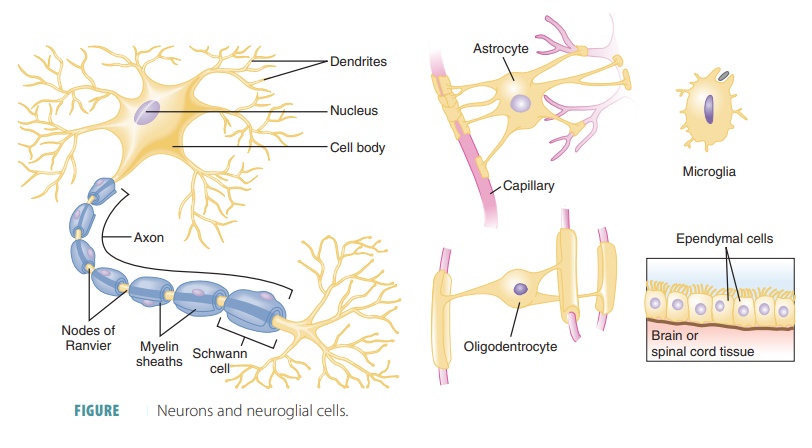
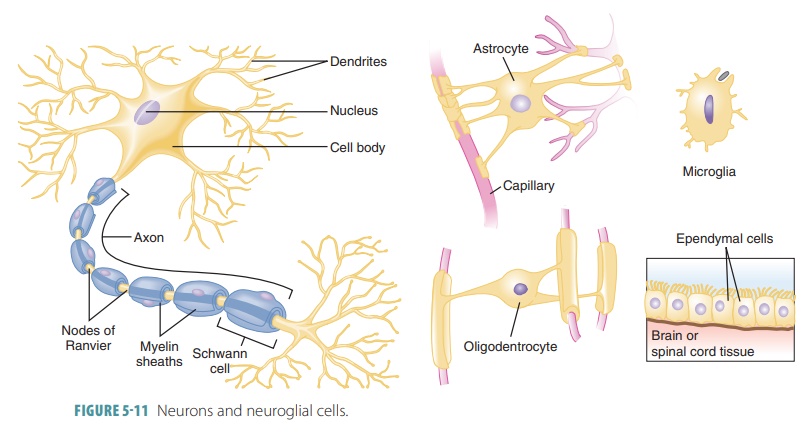
The basic cells of nervous
tissues are the neu-rons (nerve cells; FIGURE
5-11). Neurons are the structures of
neural tissue that respond to envi-ronmental changes by transmitting impulses
along axons (cellular processes) to other neurons, muscles, or glands. Since
axons are usually long and slender, they as also known as nerve fibers. Axons respond to stimuli via processes called dendrites . Neurons coordinate, integrate, and regulate a wide variety of
functions in the body. Neuroglial
cells are crucial to
neuronal functioning. These cells divide and sup-port nervous tissue
components. Neuroglial cells also phagocytize other cells, supply nutrients to
neurons and help in communications
between cells. The four types of neuroglia are astrocytes, oligodendroglia,
microglia, and ependymal cells.
1. What
are the functions of the neurons?
2. What
are the major functions of the neuroglia?
3. Compare neuroglial cells with neurons.