Overall Summary of the Three Series
| Home | | Pharmacovigilance |Chapter: Pharmacovigilance: Fatal Medication Errors and Adverse Drug Reactions - Coroners’ Inquests and Other Sources
Overall, the number of deaths per year has decreased, whereas the number of Coroner’s inquests being undertaken has increased.
OVERALL SUMMARY OF THE THREE
SERIES
Table
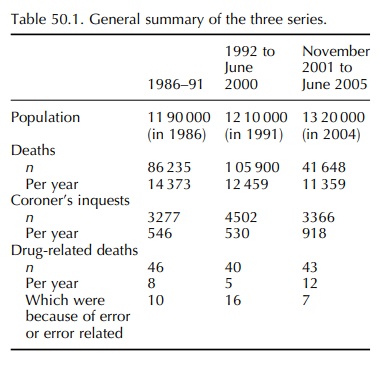
50.1 presents a general summary of the three series. Overall, the number of
deaths per year has decreased, whereas the number of Coroner’s inquests being
undertaken has increased. The number of drug-related deaths per year also
appears to have increased in the third series, but it is difficult to make
compar-isons between the three series due to different methods in identifying
drug-related deaths.
The
drugs associated with fatal adverse drug events over the course of the three
series are presented in Table 50.2. The most startling difference between the
three series of reports is that NSAIDs no longer account for the majority of
the deaths and that there is a significant increase in the number of deaths
that is associated with warfarin. Table 50.3 demonstrates the increase in
warfarin-associated deaths identified in the Coroner’s inquests since 1986.
Over the course of a 10-year period (1986–95), only two cases were found to be
associated with warfarin compared with 17 cases from 1996 to June 2005. A
similar trend over the same period is evident in the number of fatal suspected
ADRs to warfarin spontaneously reported to the United Kingdom Medicines and
Healthcare prod-ucts Regulatory Agency (MHRA) and the Committee on Human
Medicines (CHM) through the Yellow Card scheme.

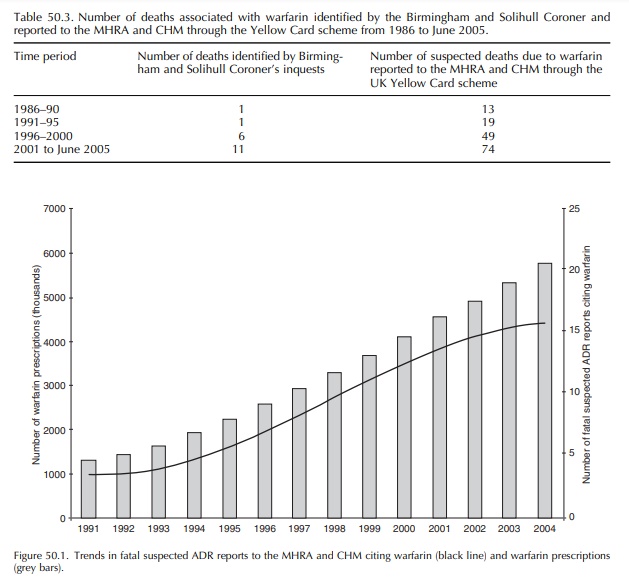
This
increase in the number of fatal suspected ADRs due to warfarin may be explained
by the increased use of warfarin in drug therapy. Data obtained from the
Department of Health indicate an increasing trend in the number of warfarin
prescriptions in the commu-nity in England from 1991 to 2004 (Figure 50.1).
When the data from the Yellow Card scheme are plot-ted alongside the number of
warfarin prescriptions, a strong positive correlation is observed between the
increasing number of reports of deaths suspected to be associated with warfarin
and increasing medica-tion use (Spearman = 0.839, P < 0 0005). This
association is, however, constrained by the inherent limitations of a
spontaneous reporting scheme, as the incidence of deaths due to warfarin
treatment cannot be determined through the Yellow Card scheme.
Related Topics
