Psychomotor Stimulants
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : CNS Stimulants
CNS Stimulants - Psychomotor Stimulants - Synthesis and Drug Profile - a. Amphetamine b. Fenfluramine (Pondialon) c. Phentermine d. Methylphenidate HCl (Ritalin) e. Pemoline - Structure, Properties, uses, Synthesis, Assay, Storage, Dosage forms, Dose |
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Psychomotor Stimulants
a. Amphetamine
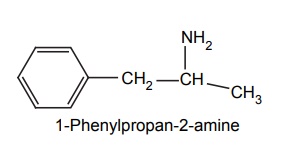
Synthesis
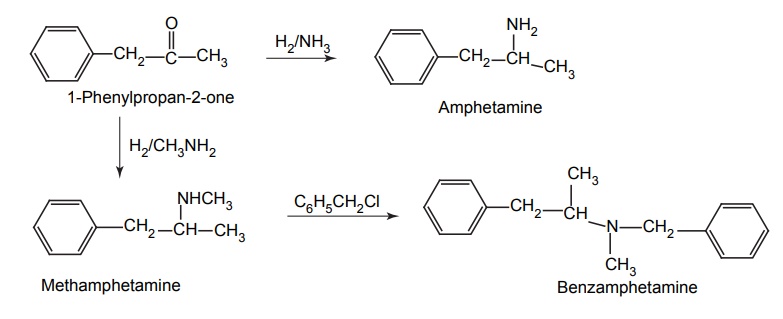
Mode of action: Amphetamine increases synaptic dopamine and noradrenaline primarily by stimulating presynaptic release rather than by blockade of the reuptake as in the case of cocaine.
Uses: It is an anorectic and has been used in the weight control of obese individuals. It has potential for abuse and cardiovascular effects.
Dose: For narcolepsy, 10 mg/day, for obesity, 5–10 mg/day, 30–60 min before meals.
b. Fenfluramine (Pondialon)
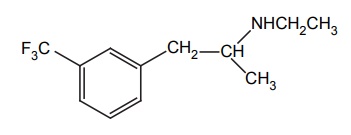
Properties and uses: It is a white amophous powder, sparingly soluble in water, used as respiratory stimulant.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in chloroform and acetone. Add mercuric acetate solution and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid.
Synthesis
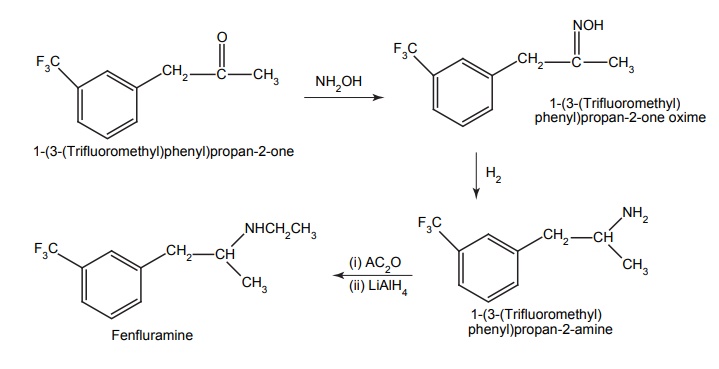
Dose: By oral route for adults: 20 mg thrice a day, 30 min to 1 h before each meal.
c. Phentermine
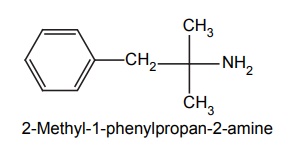
Synthesis
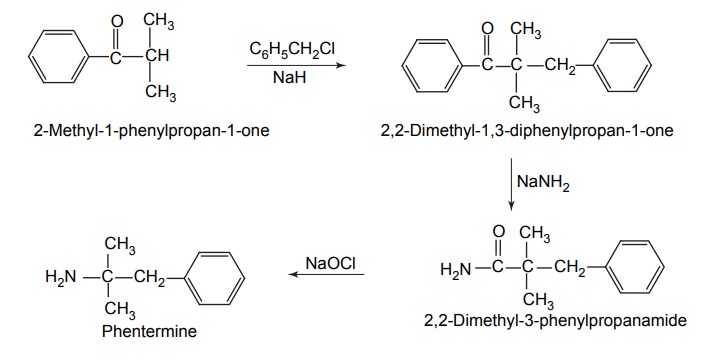
Use: It is used as an appetite suppressant.
Dose: The usual dose is 15–30 mg at breakfast.
d. Methylphenidate HCl (Ritalin)
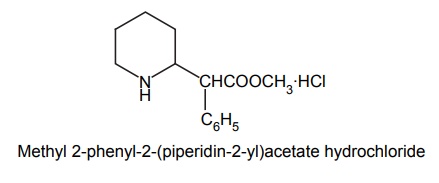
Synthesis
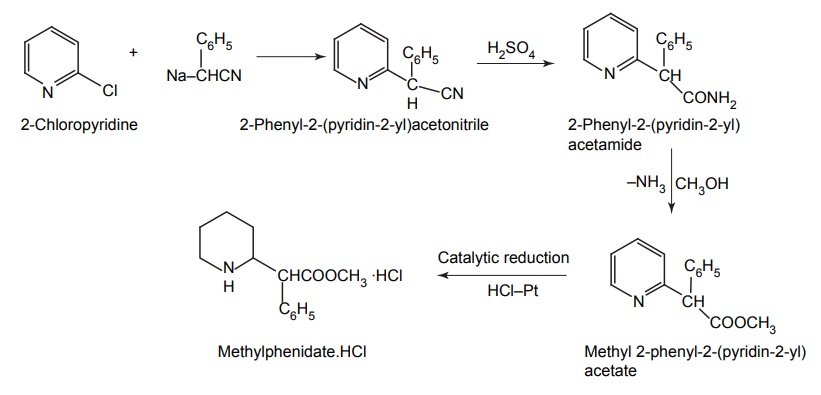
Mode of action: It is similar to amphetamine, but superior in its pharmacological action. It increases the release of dopamine and noradrenaline, and it is useful in hyperkinetic children.
Properties and uses: It is a white fine crystalline powder, soluble in water, and sparingly soluble in chloroform and acetone. It is used as a potent CNS stimulant.
Dose: The usual dose by oral or parenteral is 10–60 mg/day.
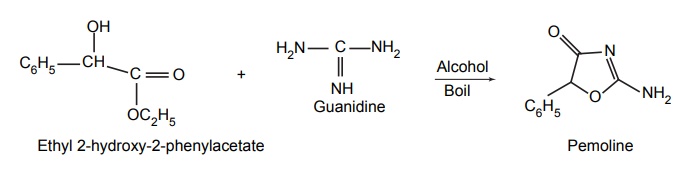
e. Pemoline
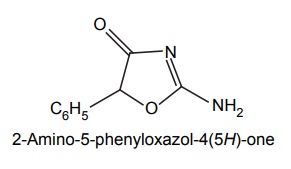
Synthesis
Properties and uses: It is a white crystalline powder, slightly soluble in alcohol. It is used in the treatment of narcolepsy fatigue, mental depression, chronic schizophrenia, and as a mild stimulant in geriatric patients.
Related Topics
