SAR of Sulphonamides
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antibacterial Sulphonamides
The major features of SAR of sulphonamides include the following:
SAR of Sulphonamides
The major
features of SAR of sulphonamides include the following:
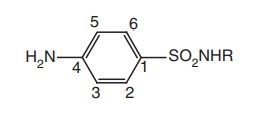
·Sulphanilamide skeleton is the minimum
structural requirement for antibacterial activity.
·The aminoand sulphonyl-groups on the benzene
ring are essential and should be in 1 and 4 position.
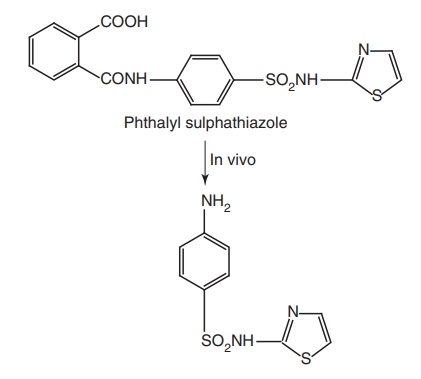
·The N-4 amino group could be modified to be
prodrugs, which are converted to free amino function in vivo.
·Sulphur atom should be directly linked to the
benzene ring.
·Replacement of benzene ring by other ring
systems or the introduction of additional substituents on it decreases or
abolishes its activity.
·Exchange of the –SO2NH group by –CONH
reduces the activity.
·On N-1-substituted sulphonamides, activity
varies with the nature of the substituent at the amino group. With substituents
imparting electron-rich characters to SO2 group, bacteriostatic
activity increases.
·Heterocyclic substituents lead to highly potent
derivatives, while sulphonamides, which contain a single benzene ring at N-1
position, are considerably more toxic than heterocyclic ring analogues.
·The free aromatic amino groups should reside para to the sulphonamide group. Its
replacement at ortho or meta position results in compounds
devoid of antibacterial activity.
·The active form of sulphonamide is the ionized,
maximum activity that is observed between the pKa values 6.6–7.4.
·Substitutions in the benzene ring of
sulphonamides produced inactive compounds.
·Substitution of free sulphonic acid (–SO3H)
group for sulphonamido function destroys the activity, but replacement by a sulphinic
acid group (–SO2H) and acetylation of N-4 position retains back the activity.
·m. Sulphonamides bind to the basic centres of
arginine, histidine, and lysine sites of proteins. The binding groups are
alkyl, alkoxy, and halides. The binding affects the activity of sulphonamides;
protein binding appears to modulate the availability of the drug and its
half-life.
·The lipid solubility influences the
pharmacokinetic and antibacterial activity, and so increases the half-life and
antibacterial activity in vitro.
Related Topics
