Serotonergic (5HT) Receptors
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : 5Hydroxytryptamine, Its Antagonists And Drug Therapy Of Migraine
Gaddum and Picarelli (1957) classified 5HT receptors into musculotropic (D type) and neurotropic (M type) on the basis of pharmacological criteria. The classical 5HT antagonists methysergide and cyproheptadine blocked D type receptors.
SEROTONERGIC (5HT) RECEPTORS
Gaddum and Picarelli
(1957) classified 5HT receptors into musculotropic (D type) and neurotropic (M type)
on the basis of pharmacological criteria. The classical 5HT antagonists methysergide
and cyproheptadine blocked D type receptors. Subsequently 5HT receptors were
differentiated by their high or low affinity for [3H] 5HT in radioligand
binding studies. The present system of classifying 5HT receptors is based on
molecular characterization and cloning of the receptor cDNAs.
Four families of 5HT
receptors (5HT1, 5HT2, 5HT3, 5HT47)
comprising of 14 receptor subtypes have so far been recognized. However, only
some of these have been functionally correlated or their selective agonists/antagonists
defined. Knowledge of subtypes of 5HT receptors has assumed importance because
some newly developed therapeutically useful drugs can only be described as 5HT
receptor subtype selective agonists or antagonists.
All 5HT receptors
(except 5HT3) are G protein coupled receptors which function through
decreasing (5HT1) or increasing (5HT4, 5 HT6,
5HT7) cAMP production or by generating IP3/ DAG (5HT2)
as second messengers. The 5HT3 is ligand gated cation (Na+,K+)
channel which on activation elicits fast depolarization.
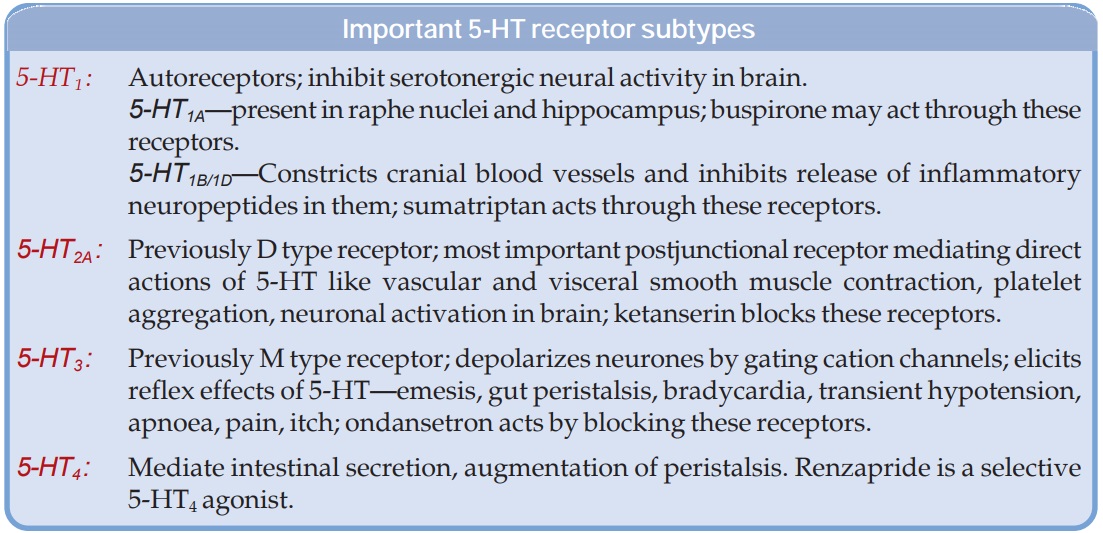
5HT1 Receptors
Five subtypes (5HT1A,
B, D, E, F) have been identified. The 5HT1C
receptor is now designated 5HT2c. All subtypes of 5HT1
receptor inhibit adenylyl cyclase; 5HT1A in addition activates K+
channels (resulting in hyperpolarization) and inhibits Ca2+ channels. These
receptors function primarily as autoreceptors in brain— inhibit firing of 5HT
neurones or release of 5HT from nerve endings.
The most important
location of 5HT1A receptor are raphe nuclei of brainstem and
hippocampus. The antianxiety drug buspirone
acts as a partial agonist of 5HT1A receptor. The 5HT1D receptor
has been shown to regulate dopaminergic tone in substantia nigra–basal ganglia,
and
5HT1B/1D to
cause constriction of cranial blood vessels. The antimigraine drug sumatriptan is a selective 5HT1B/1D
agonist. Other functions subserved by 5HT 1D receptors are
inhibition of NA release from sympathetic nerve endings and that of
inflammatory neuropeptides from nerve endings in cranial blood vessels.
5HT2 Receptors
There are 3 subtypes
of 5HT2 receptor; all are coupled to phospholipase C and
function through generation of IP3/DAG. 5HT2A receptor
also inhibits K+ channels resulting is slow depolarization of
neurones. αmethyl 5HT is a
selective agonist for all 3 subtypes.
5 HT2A is
the most widely expressed postjunctional 5HT receptor (designated earlier as D
type) located on vascular and visceral smooth muscle, platelets and cerebral
neurones especially prefrontal cortex. It mediates most of the direct actions
of 5HT like vasoconstriction, intestinal, uterine and bronchial contraction,
platelet aggregation and activation of cerebral neurones. Ketanserin is a 5HT2 antagonist more selective for 5HT2A.
Contraction of rat gastric
fundus is mediated by 5HT2B receptor.
5HT2C
receptor is located on vascular endothelium— elicits vasodilatation through
EDRF release. Choroid plexus expresses large number of 5HT2C
receptors.
5HT3 Receptor
This is the neuronal 5HT
receptor which rapidly depolarizes
nerve endings by opening the cation channel located within it and corresponds
to the original M type receptor. It mediates the indirect and reflex effects of
5HT at:
·
Somatic and autonomic nerve endings → pain, itch, coronary
chemoreflex (bradycardia, fall in BP due to withdrawal of sympathetic tone,
respiratory stimulation or apnoea elicited by stimulation of receptors in the
coronary bed), other visceral reflexes.
·
Nerve endings in myenteric plexus → augmentation of peristalsis,
emetic reflex.
·
Area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarious
in brainstem → nausea, vomiting.
Ondansetron is a
selective 5HT3 antagonist which inhibits vomiting by blocking these
receptors in brainstem as well as in gut wall. 2Methyl 5HT is a selective 5HT3
agonist.
5HT4–7 Receptors
The 5HT4 receptor has been demonstrated in the mucosa,
plexuses and smooth muscle of the gut → probably involved in augmenting intestinal
secretion and peristalsis. It is also located in brain, especially hippocampus
and the colliculi where it causes slow depolarization by decreasing K+
conductance.
Cisapride and renzapride are selective 5HT4 agonists. The recently cloned 5HT5, 5HT6
and 5HT7 receptors are closely related to the 5HT4
receptor. These are mainly located in specific brain areas, but their
functional role is not known. An interesting finding is that clozapine (atypical neuroleptic) has
high affinity for 5HT6 and 5HT7 receptors in addition to
being a 5HT2A/2C antagonist.
Related Topics
