Autonomic Nerve Fibers
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
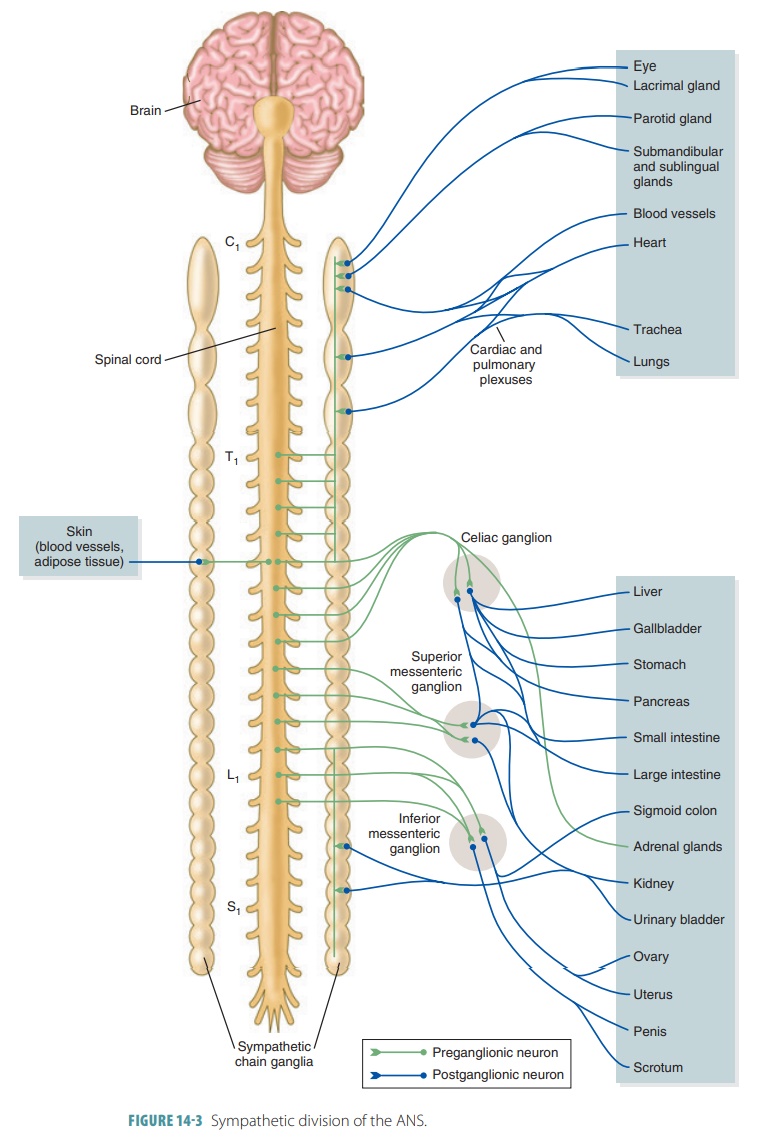
Sympathetic fibers are thoracolumbar, originating in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord.
Autonomic
Nerve Fibers
Sympathetic fibers are
thoracolumbar, originating in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal
cord (FIGURE 14 -3). They have short preganglionic
fibers and long postganglionic fibers. Sympathetic ganglia lie closer to the spinal cord than parasym-pathetic ganglia. The
sympathetic division innervates more organs than the parasympathetic division,
includ-ing the visceral organs of the body cavities and the vis-ceral
structures in the somatic (superficial) areas of the body. Certain glands and smooth muscle structures in the sweat glands
and arrector pili muscles require auto-nomic innervation, served exclusively by
sympathetic fibers. Sympathetic fibers also innervate the smooth muscle walls
of the arteries and veins. Autonomic nerves innervate organs in the central
body cavities. In the autonomic nervous system, there is always a syn-apse
between the CNS and the effector organ.
All preganglionic fibers arise
from cell bodies of preganglionic neurons in the lateral gray horns of spinal cord segments T1 to L2; hence,
the thoracolumbar division is the alternate name for the
sympathetic divi-sion. Many preganglionic sympathetic neurons exist in the
spinal cord’s gray matter, which form its lateral
horns. There are no lateral horns in
the sacral spinal cord regions
because parasympathetic preganglionic neurons are far less abundant there when
compared with the sympathetic neurons in the thoracolumbar regions. The
preganglionic fibers leave the spinal cord via the ventral
root, passing through a white ramus communicans and entering the
sympathetic trunk gan-glion to form part of the sympathetic
trunk. The sym-pathetic
trunks flank each side of the vertebral column and appear like strands of beads
that are glistening and white. Each sympathetic trunk is also known as a sym-pathetic chain, and the sympathetic
trunk ganglia are also called paravertebral or chain ganglia.
Sympathetic fibers arise only
from the thoracic and lumbar spinal cord segments. They leave the spinal cord
at the first thoracic vertebrae. There are usually 23ganglia in each sympathetic trunk (3 cervical, 11
thoracic, 4 lumbar, 4 sacral, and 1 coccygeal). Three different things occur
when a preganglionic axon reaches a trunk ganglion: The pre- and postganglionic neurons can either
synapse at the same level, synapse at a higher or lower level, or synapse in a
distant collateral ganglion. When they synapse in a distant collateral
ganglion, the pregan-glionic fibers play a role in forming several splanchnic nerves. They synapse in collateral ganglia anterior to the vertebral column. Collateral ganglia are not paired or
arranged in segments and only occur in the abdomen and pelvis. However, all
sympathetic ganglia are close to the spinal cord. There are three sympathetic
collateral ganglia located in the abdominal cavity.
Related Topics