Biguanides
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Oral Hypogylcaemic Drugs
Oral Hypogylcaemic Drugs : Biguanides - i. Phenformin ii. Metformin (Diamet, Diaphage Glyciphage, Glycomet) - Synthesis and Drug Profile
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Biguanides
Mode of action: Biguanides do not have direct action on
increasing or decreasing the glucose level. This reduces glucose levels
primarily by decreasing hepatic gluconeogenisis by increasing the insulin
action on muscles and fat. It also reduces the absorption of glucose from
intestine.
i. Phenformin
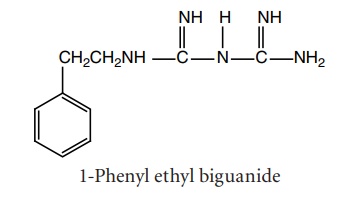
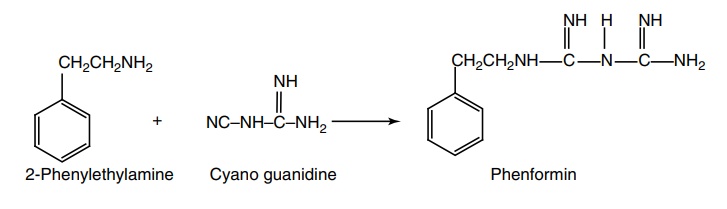
Synthesis
Route-I. From: 2-Phenylethylamine
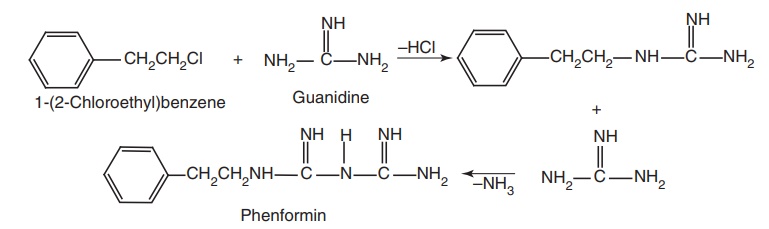
Route-II. From: 1-(2-Chloroethyl) benzene
Properties and uses: Used only in stable type II diabetics, it may be
used alone or in conjunction with another oral hypoglycaemic agents, such as sulphonylureas
or with insulin.
Dose: The normal dose is 25 mg tablets 1–4 times a day, usually 50–150
mg daily with breakfast.
ii. Metformin (Diamet, Diaphage Glyciphage, Glycomet)
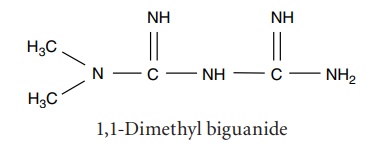
Synthesis
Route I. From: Dimethylamine
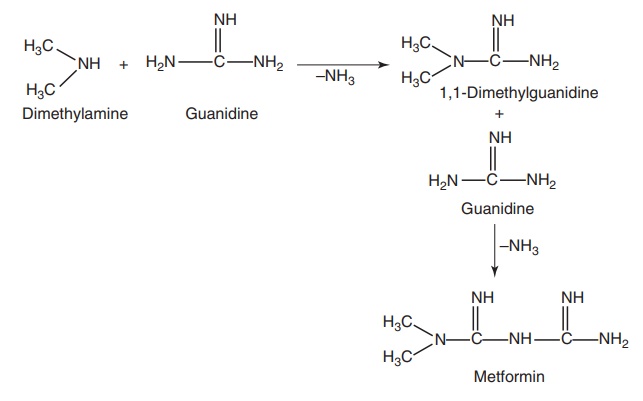
Route II. From: Dimethylamine
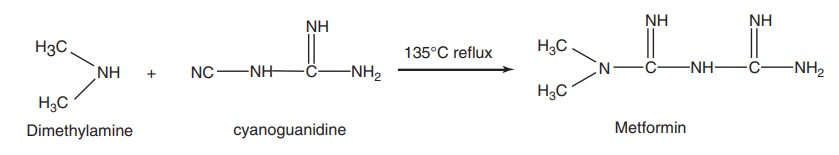
Properties and uses: Metformin hydrochloride exists as white
crystals, freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol, practically
insoluble in acetone and methylene chloride. It is usually given along with
sulphonylureas.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous formic acid, add acetonitrile,
and titrate against 0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point
potentiometrically.
Dose: Initial dose is 500 mg thrice daily or 850 mg twice daily with
meals.
Dosage forms: Metformin tablets B.P.
Related Topics
