Plasma Expanders
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Plasma Expanders
A haemorrhagic shock may result from the loss of blood during burns, wounds, or surgery. Mild shock results when there is a loss of 15% to 20% in the total blood volume.
DRUGS ACTING ON BLOOD AND BLOOD FORMING ORGANS
Plasma Expanders
INTRODUCTION
A
haemorrhagic shock may result from the loss of blood during burns, wounds, or
surgery. Mild shock results when there is a loss of 15% to 20% in the total
blood volume. Further loss of blood, up to 40% of total blood volume may lead
to severe shock during which the cardiovascular functioning is severely
affected. To restore this functioning, saline should be administered as an
initial emergency measure. Plasma expanders can also be used to overcome the
initial losses.
There are of
two types of plasma expanders: (i) Natural products and (ii) Synthetic products
Natural products: These include transfusion of whole blood or
the preparations of plasma proteins. Blood products containing plasma proteins
are human albumin (albumisol) and plasma protein fraction (PPF). Both of these
preparations are usually given by intravenous infusion.
Synthetic products: Dextran, hetastarch, perfluorochemicals,
polyvinylpyrrolidone, and gelatin are some of the synthetic plasma expanders,
out of which dextran has been used extensively.
i. Dextran
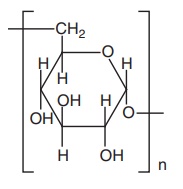
Dextran
could be considered as being almost close to ideal plasma expanders. Dextrans
are colloidal glucose polymers that are obtained from sucrose by the action of
bacteria, Leuconostoc mesenteroides.
The dextran molecule consists mainly of 1:6 glucoside linkages with relatively
few 1:4 linkages and has an average molecular weight of 40 millions. This form
is not clinically suitable. Hence, it is partially hydrolyzed in vitro to give
dextran with average molecular weight of 40,000, 70,000, 11,000, and 15,000
daltons. They are known as dextran-40, dextran-70, dextran-110, and
dextran-150, respectively. Of these, dextran-40 and dextran-70 are of clinical
importance. Solutions of dextran in isotonic sodium chloride is used to
increase the circulating blood volume and to maintain the venous pressure,
right arterial pressure, stroke volume, and cardiac output. Only dextran
solutions are used in the treatment of hypoproteinaemia, nephrosis, and
toxaemia of late pregnancy. Dextran does not posses oxygen-carrying capacity.
The dextran
solution is pharmacologically inactive and has been reported as having no
significant deleterious effect on renal, hepatic, or any other vital functions.
Occasionally, sensitization reaction may occur in some patients. The bleeding
time, fibrin polymerization on platelet function may be impaired in vivo.
Dextrans are contraindicated in patients with anaemia, severe thrombocytopenia,
and low plasma fibrinogen level.
ii. Human albumin
It is
obtained from pooled human plasma; 100 ml of 20% human albumin solution is the
osmotic equivalent of about 400 ml of fresh frozen plasma or 800 ml of whole
blood. It can be used without regard to the patient’s blood group and does not
interfere with coagulation. Unlike whole blood or plasma, it is free of risk of
transmitting serum hepatitis because the preparation is heat-treated. There is
also no risk of sensitization with repeated infusions. It has been used in
acute hypoproteinaemia, acute liver failure, and dialysis.
iii. Degraded gelatin polymer (polygeline)
It is a
polypeptide with an average MW 30,000, which exerts osmotic pressure similar to
albumin, and is not antigenic and hypersensitivity reactions are rare. It does
not interfere with the grouping and cross matching of blood and remains stable
for 3 years. It can be used for the priming of heart–lung dialysis machines.
iv. Hydroxyethyl starch (HES, hetastarch)
It is a
complex mixture of ethoxylated amylopectin of various molecular sizes, average
MW 4.5 lakh (range 10,000–1 million). The colloidal properties of 6% HES
approximate those of human albumin. Plasma volume expands slightly in excess of
the volume infused. It has been used to improve harvesting of granulocytes
because it accelerates erythrocyte sedimentation. Adverse effects are vomiting,
mild fever, itching, chills, flu-like symptoms, swelling of salivary glands,
urticaria, perorbital oedema, and bronchospasm are the anaphylactoid reactions.
v. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)
It is a
synthetic polymer (average MW 40,000) used as a 3.5% solution. It interferes
with the blood grouping and cross matching. It has been found to bind
penicillin and insulin in circulation, so that the same is not available for
action. It is not frequently used as a plasma expander.
Related Topics
