Antiplatelet drugs (Antithrobocytic drugs)
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Coagulants
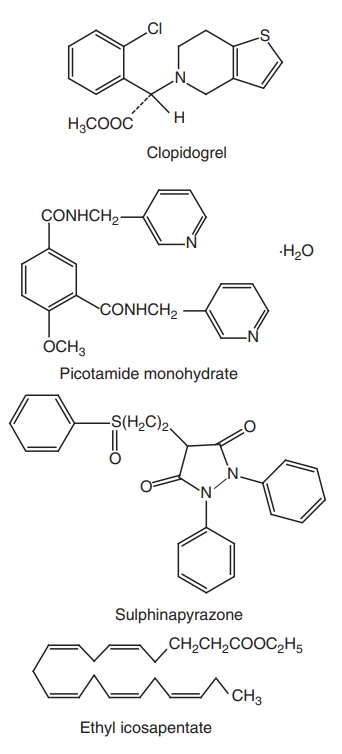
i. Aspirin ii. Dipyridamole (Persantine, Cardiwell) iii. Ticlopidine HCl (Tyklid, Ticlid) iv. Sulphinpyrazone (Anturane) v. Picotamide Monohydrate
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
Antiplatelet drugs (Antithrobocytic drugs)
Platelets
provide the initial haemostatic plug at the sites of vascular injury. Platelet
aggregation is implicated in thrombus formation in arterial systems and
pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Thus, agents that inhibit platelet aggregation
should be able to modify or prevent atherosclerotic disease and thrombosis.
Drugs
interfering with platelet functions are as follows:
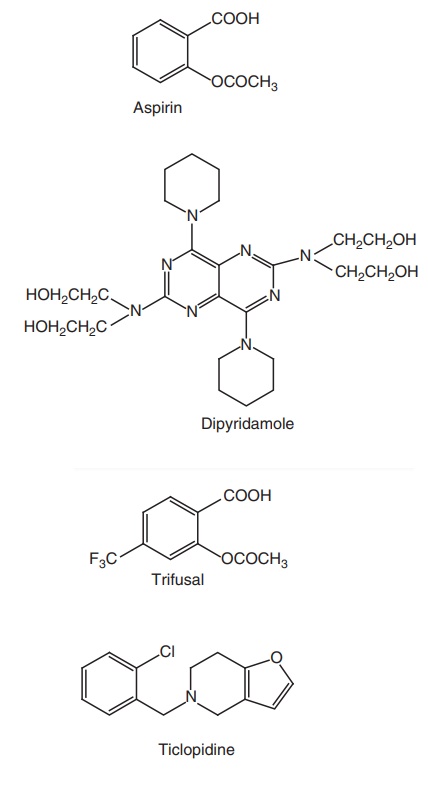
i. Aspirin
Mode of action: Aspirin inhibits the enzyme cycloxygenase and
thromboxane synthetase (TxA2) by binding irreversibly and
interfering with the platelet aggregation.
Synthesis
and drug profile of Aspirin is discussed in under sec I, Chapter NSAIDs.
ii. Dipyridamole (Persantine, Cardiwell)
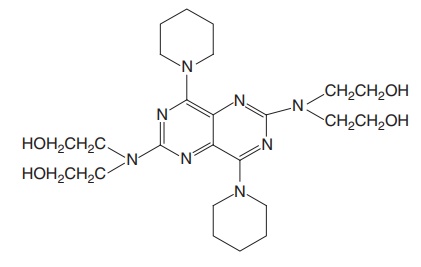
Synthesis

Properties and uses: Dipyridamole is a bright yellow crystalline
powder, practically insoluble in water, soluble in acetone, ethanol, and dilute
solutions of mineral acids. It is an adenosine reuptake inhibitor, inhibitor of
platelet aggregation, and useful in transient ischaemic attacks and secondary
prevention of myocardial infarction.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in methanol and titrate against 0.1 M
perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: 50–75 mg 8 hrly in combination with aspirin.
Dosage forms: Dipyridamole tablets B.P.
iii. Ticlopidine HCl (Tyklid, Ticlid)
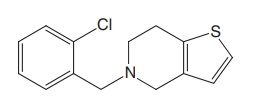
Properties and uses: Ticlopidine hydrochloride is a white crystalline
powder, sparingly soluble in water and ethanol, and very slightly soluble in
ethyl acetate. Ticlopidine is a thieno pyridines used for thrombosis prevention
in patients with atherosclerotic disease. It acts as an inhibitor of adenosine
diphosphate (ADP)mediated platelet aggregation, and hence, used as an
antiplatelet drug.
Synthesis
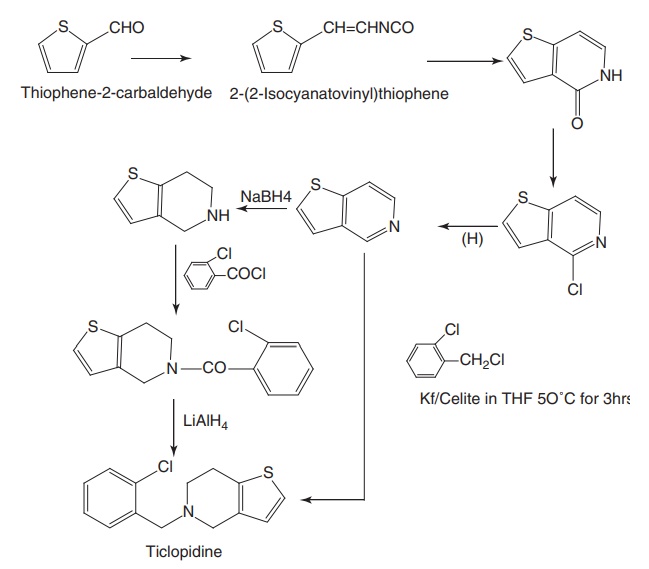
Dosage: The oral dose is 250 mg twice a day.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid and add acetic
anhydride. Titrate against 0.1 M perchloric acid and determine the end point
potentiometrically.
iv. Sulphinpyrazone (Anturane)
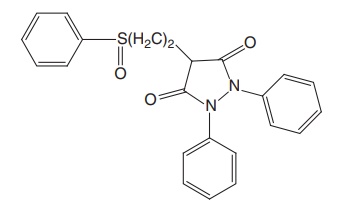
Properties and uses: Sulphinpyrazone is a white powder, very slightly
soluble in water, sparingly soluble in alcohol, but soluble in dilute solutions
of alkali hydroxides. It has antiplatelet and potent uricosuric effects, and
hence, used in the treatment of gout.
Synthesis
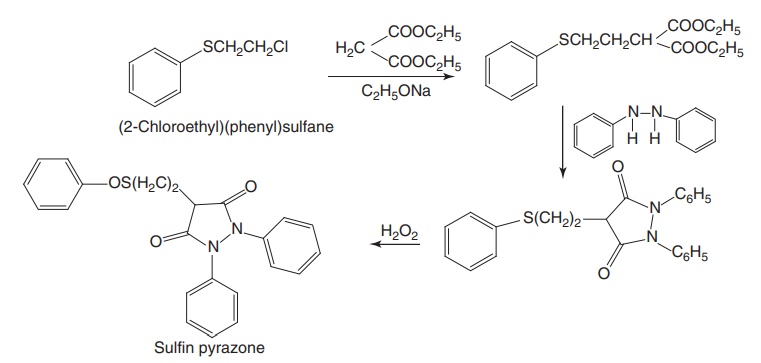
Assay: Dissolve the sample in acetone and titrate against 0.1 M sodium
hydroxide using bromothymol blue as indicator until the colour changes from
yellow to blue.
Dose: The dose is 300 mg four times a day.
Dosage forms: Sulphinpyrazone tablets B.P.
v. Picotamide Monohydrate
Properties and uses: Picotamide monohydrate is a white crystalline
powder, slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, methylene chloride, and dilute
mineral acids. It acts as thromboxane synthetase inhibitor and thromboxane
receptor antagonist; used as antiplatelet agent.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in a mixture of anhydrous acetic acid and
acetic anhydride (1:1) and titrate against 0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the
end point potentiometrically.
Related Topics
