Muscle Tissue
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Support and Movement: Muscle Tissue
Muscles are needed for many body activities, including breathing, talking, walking, and even sneezing.
Muscle Tissue
After
studying this chapter, readers should be able to
1. Compare
the contraction mechanisms of cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle.
2. Differentiate
between muscle tissue excitability, contractility, extensibility, and
elasticity.
3. Explain
the four major functions of muscle.
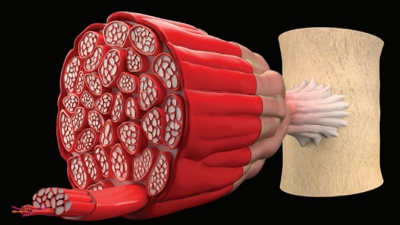
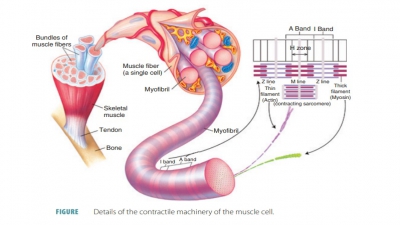
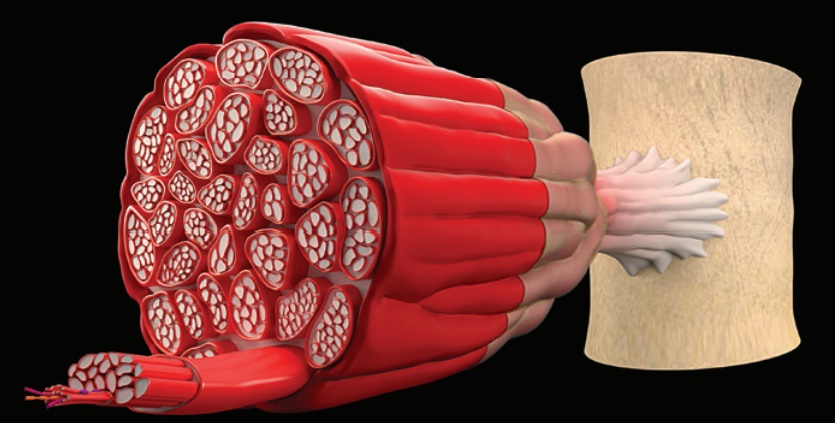
4. Describe
the structure of a skeletal muscle.
5. Identify
the functions of transverse tubules, myofibrils, and the sarcoplasmic
reticulum.
6. Describe
a motor end plate and the function of a neurotransmitter.
7. Discuss
the sliding filament model.
8. Explain
the relationship between cellular respiration and heat production.
9. Differentiate
between isotonic and isometric muscle contractions.
10. Describe
two major types of smooth muscle.
Overview
Muscles are needed for many body
activities, including breathing, talking, walking, and even sneezing.
Important body functions performed by muscles include movement, joint
stabilization, support of soft tissues, encircling digestive and urinary tract
openings, posture maintenance, nutrient storage, and the generation of heat.
Muscles contract by using chemical energy from nutrients. They are made up of
highly specialized cells. Other actions of muscles include generating the
heartbeat, distribution of heat, moving body fluids and food through the body,
and providing muscle tone, which does
not produce active movements. Instead, it keeps muscles healthy, firm, and
ready to respond to stimulation. The three types of muscle are skeletal,
smooth, and cardiac. This chapter focuses primarily on skeletal muscle.
Skeletal muscle tone additionally helps to maintain posture and stabilize
joints.
Related Topics