Coverings of Connective Tissue
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Support and Movement: Muscle Tissue
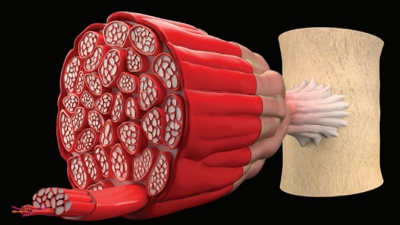
Fascia surrounds every muscle and may form cord-like tendons beyond each muscle’s end.
Coverings of
Connective Tissue
Fascia surrounds every muscle and
may form cord-like tendons beyond each muscle’s end. Tendon fibers may intertwine
with bone fibers to attach muscles to bones. Broad sheets of fibers that may
attach to bones or to the coverings of other muscles are known as aponeuroses.
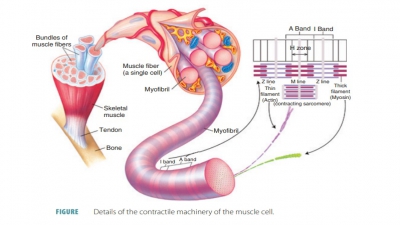
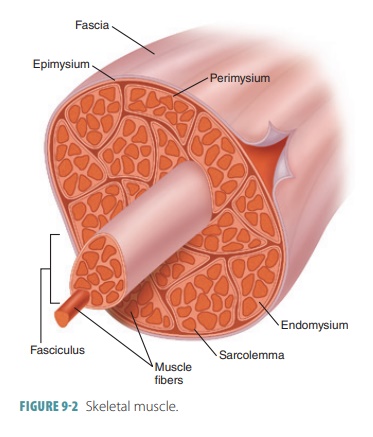
Skeletal muscles are closely
surrounded by a layer of connective tissue known as an epimysium. The
muscle is separated into small compartments or sheaths by another layer known as the perimysium. Inside these compartments
are fascicles, which are bundles of skeletal muscle fibers. Inside the fas-cicles,
muscle fibers are contained within connec-tive tissue layers. These layers form
a thin covering (endomysium). The many layers of connective tis-sue that enclose and separate
skeletal muscles allow a great deal of independent movement. In the endo-mysium
are capillary networks supplying blood to the muscle fibers, myosatellite cells (stem cells that help
repair damaged muscles), and nerve fibers controlling the muscles. FIGURE 9-2 depicts
the components of the skeletal muscle.
Related Topics