Other antibiotics
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antibiotics
Examples of other antibiotics are chloramphenicol, rifampicin and mupirocin.
Other antibiotics
Examples of
other antibiotics are chloramphenicol, rifampicin and mupirocin.
i. Chloramphenicol or chloromycetin
Chloramphenicol
has a spectrum of activity resembling that of the tetracyclines except that it
exhibits a bit less activity against some gram-positive bacteria. It is
isolated from Salmonella venezuelae by
Ehrlich et al in 1947. It contains chlorine and is obtained from an
actinomycete, and thus, named as chloromycetin. It is specifically recommended
for the treatment of serious infections caused by H. influnzae, S. typhi (typhoid), S.
pneumoniae, and N. meningitides. Its ability to penetrate into the CNS presents an alternative
therapy for meningitis and exhibits antirickettsial activity.
Structure
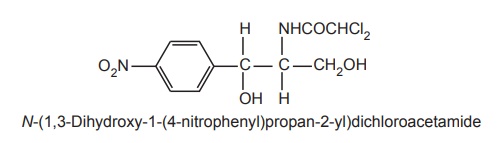
Properties and uses: Chlorampenicol is a white or greyish-white or
yellowish-white crystalline powder or fine crystals, slightly soluble in water,
soluble in alcohol and propylene glycol. It was the first, and still is the only
therapeutically important antibiotic to be produced in competition with
microbiological processes. It contains a nitrobenzene moiety and is a
derivative of dichloroacetic acid. Since it has two chiral centres, four
isomers are possible. The D-(-) threo is the biologically active form. It is
used in the treatment of typhoid fever caused by S. typhi. The most serious adverse effect of chloramphenicol is
bone marrow depression and fatal blood dyscrasias.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in water, dilute with the same solvent, and
measure the absorbance at the maximum of 278 nm using ultraviolet
spectrophotometer.
Dose: Usual adult dose is 500 mg every 6 h.
Dosage forms: Chloramphenicol capsules I.P., B.P., Chloramphenicol ear drops
I.P., B.P., Chloramphenicol eye ointment I.P., B.P., Chloramphenicol eye drops
B.P.
Synthesis
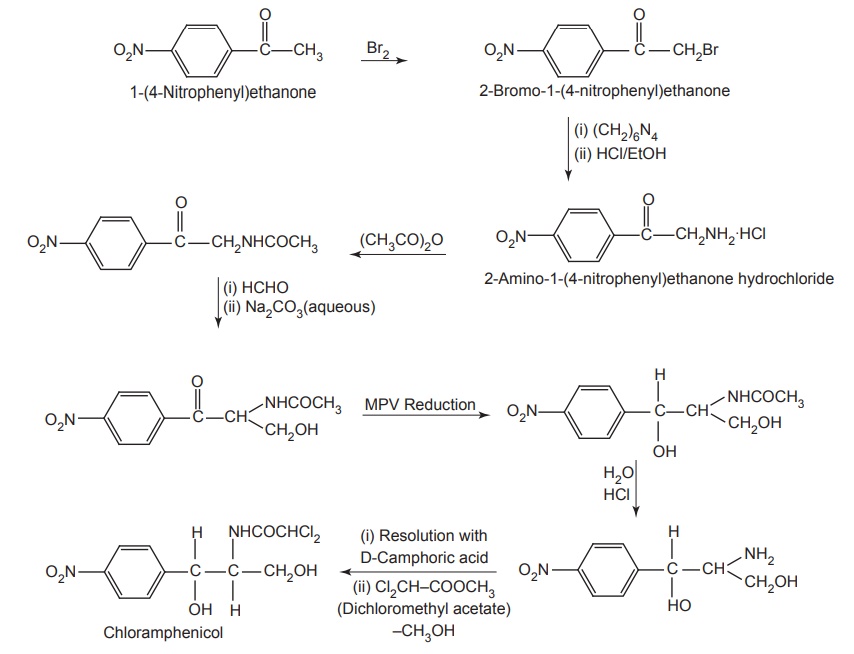
SAR of Chloramphenicol
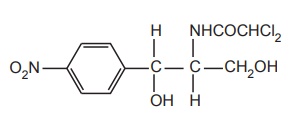
a.
Modification
of p-nitrophenyl group.
b.
Modification
of dichloroacetamide side chain.
c.
Modification
of 1, 3-prepanediol.
Modification of p-nitrophenyl group: The p-nitrophenyl
group may be modified through the following ways:
a.
Replacement
of the nitro group by other substituents leads to a reduction in activity.
b.
Shifting of
the nitro group from the para position also reduces the antibacterial activity.
c.
Replacement
of phenyl group by the alicyclic moieties results in less potent compounds.
Modification of dichloroacetamido side chain: Other dihalo derivatives of the side chain are
less potent although major activities are retained.
Modification of 1,3-propanediol: If the primary alcoholic group on C-1 atom is
modified, it results in a decrease in activity; hence, the alcoholic group seems
to be essential for activity.
ii. Rifampicin
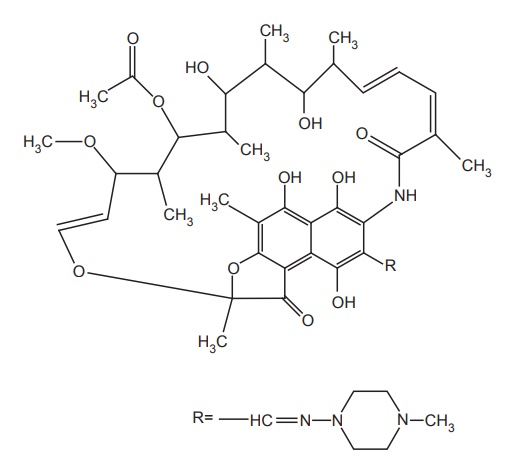
Properties and uses: Rifampicin is a reddish-brown or brownish-red
crystalline powder, slightly soluble in water, acetone, and alcohol and soluble
in methanol. It is a broad-spectrum bactericidal antibiotic, structurally
similar to complex macrocyclic antibiotic obtained from S. mediterrani. They belong to a new class of antibiotics called as
ansamycins. Five types, that is, rifampicin A, B, C, D, and E are present. It
penetrates well into cerebrospinal fluid and is, therefore, used in the
treatment of tuberculous meningitis.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in methanol and dilute it with the same
solvent. Dilute the solution with phosphate buffer solution pH 7.4 and measure
the absorbance at the maximum at 475 nm, using phosphate buffer solution pH 7.4
as blank.
Related Topics
