Pantothenic Acid
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Vitamins
Pantothenic acid is a component of CoA, which functions in the transfer of acyl groups.
PANTOTHENIC ACID
Pantothenic acid is a
component of CoA, which functions in the transfer of acyl groups (Figure
28.17). CoA contains a thiol group that carries acyl compounds as activated
thiol esters. Examples of such structures are succinyl CoA, fatty acyl CoA, and
acetyl CoA. Pantothenic acid is also a component of the acyl carrier protein
domain of fatty acid synthase. Eggs, liver, and yeast are the most important
sources of pantothenic acid, although the vitamin is widely distributed.
Pantothenic acid deficiency is not well characterized in humans, and no RDA has
been established.
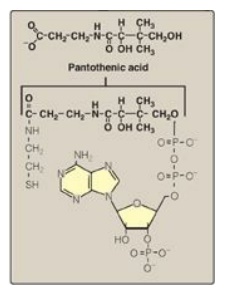
Figure 28.17 Structure of
coenzyme A.
