Spinal Neuronal Pathways
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Central Nervous System
1. Describe first-order, second-order, and third-order sensory neurons. 2. Differentiate the functions of the ascending and descending spinal pathways.
Spinal
Neuronal Pathways
The primary spinal tracts or fasciculi make up multi-neuron pathways and connect the brain to the rest of the body. They contain spinal cord
neurons, parts of peripheral neurons, and brain neurons. Spinal neu-ronal
pathways are signified by decussation,
relay, somatotopy, and symmetry. Most pathways cross from one side of the CNS to the other, which
is described as decussation. Most also consist of a chain of several neurons contributing
to successive pathway tracts in the relay of information. Most pathways have a
precise spatial relationship among tract fibers (somatotopy), which resemble the body’s ordered mapping. Ascend-ing
sensory tracts, for example, fibers that transmit inputs from sensory receptors
in superior regions of the body, lie lateral to others that convey sensory
infor-mation from inferior body regions. There is symmetry to all pathways and tracts. One member of each pair is
present on either side of the brain or spinal cord.
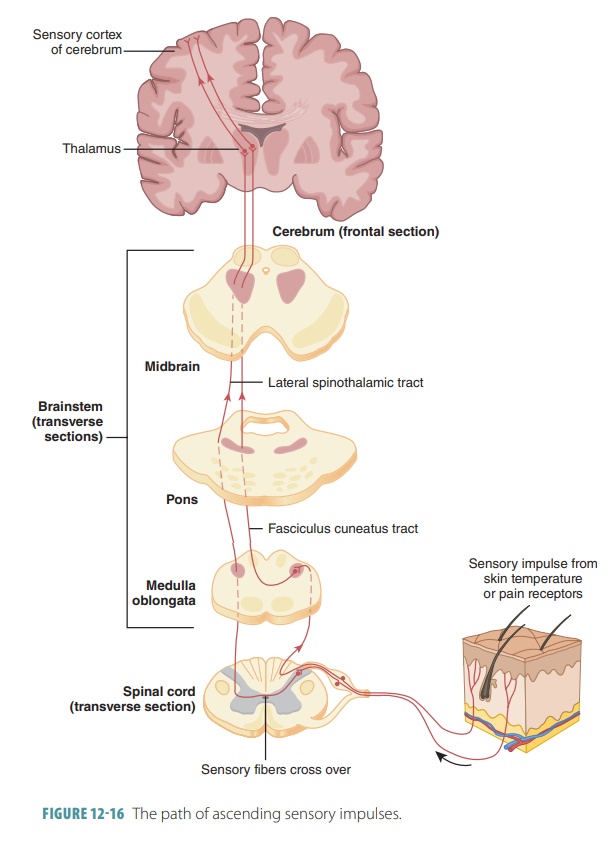
Ascending Pathways to the Brain
Ascending pathways conduct
sensory impulses toward the brain and consist of three types of neurons:
■■ First-order neurons: These
have cell bodies in a ganglion
(either dorsal root or cranial root) and conduct impulses from the skin’s
cutaneous recep-tors and from proprioceptors to the brain stem or spinal cord.
A first-order neuron synapses with a second-order neuron.
■■ Second-order neurons: These
have cell bodies in the spinal cord’s
dorsal horn or in the medullary nuclei that transmit impulses to the thalamus
or cerebellum.
■■ Third-order neurons: These
have cell bodies in the thalamus and
send impulses to the cerebrum. There are no third-order neurons in the
cerebellum.
There are three primary types of
ascending pathways on each side of the spinal cord: the dor-sal column-medial lemniscal pathways, spinothalamic pathways,
and spinocerebellar pathways. The
dorsal column-medial lemniscal
pathways mediate precise transmission of inputs of certain sensory receptors
such as for discriminative touch and vibrations. The spinothalamic pathways
receive signals from many sensory receptor types, making multiple synapses in
the brain stem. The spinothalamic pathways transmit temperature, touch, pain,
and pressure impulses. The spinocerebellar pathways transmit information about
tendon or muscle stretching to the cerebellum so it can coordinate the
activities of the skeletal muscles.
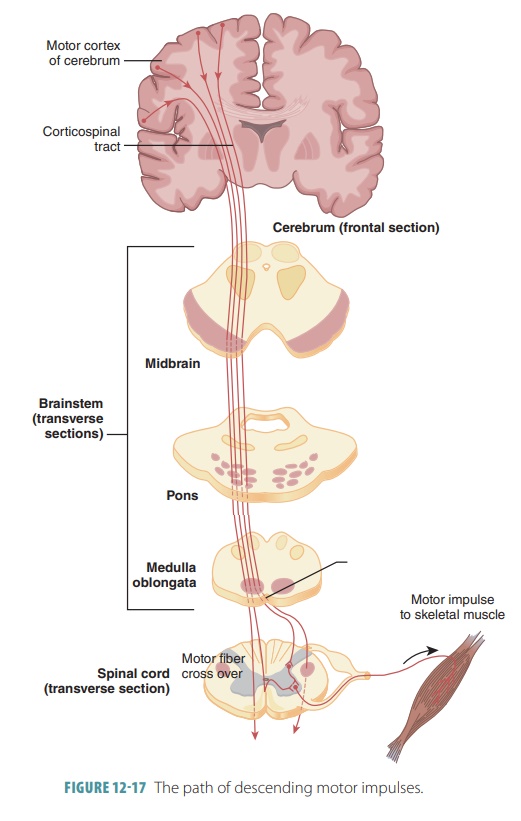
Descending Pathways and Tracts
The descending pathways transmit
impulses from the brain to the spinal cord, via direct and indirect pathways.
■■ Upper motor neurons: These
are pyramidal cells of the motor cortex as well as neurons of the subcortical
motor nuclei.
■■ Lower motor neurons: These
are from the ventral horn and directly innervate skeletal muscles. Direct (pyramidal) pathways originate
primarily with the pyramidal neurons in the precentral gyri and send impulses
through the brain stem via large pyramidal
(corticospinal) tracts.
The indirect pathways include all
other motor pathways except the pyramidal pathways and brain stem motor nuclei.
Formerly, indirect pathways were referred to as the extrapyramidal system; however, they are now referred to as
indirect (multineuronal) pathways or
may be individually named. Indirect pathways are most involved in maintaining
balance and posture (via the axial muscles), coarse limb move-ments, and the
following of objects in the visual field with the head, neck, and eyes. The vestibulospinal tract and reticulospinal tract use varying postural muscle tone to maintain balance. Flexor muscles are controlled
by the rubospinal tracts, whereas the superior
colliculi and tectospinal tracts control head movements
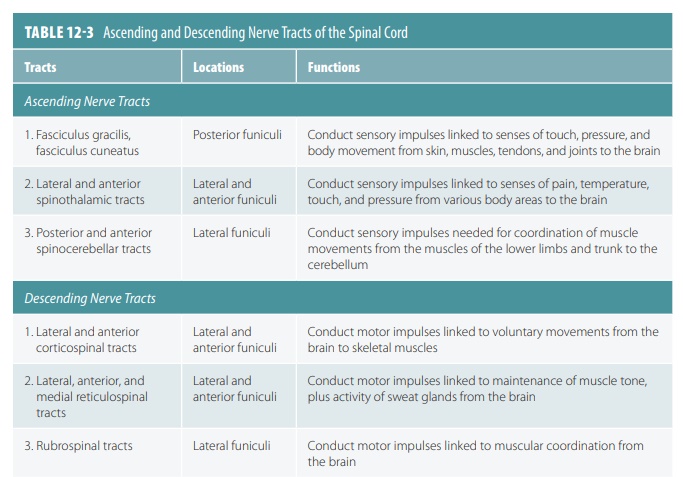
in relation to visual stimuli. TABLE 12-3 describes the ascending and descending nerve tracts of the
spinal cord. FIGURES 12-16 and 12- 17 show how these nerve tracts function between the brain,
spinal cord, and sensory and motor fibers.
1. Describe
first-order, second-order, and third-order sensory neurons.
2. Differentiate
the functions of the ascending and descending spinal pathways.