Summary
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Levels of Organization : Cells
The cell is the basic unit that performs all the vital physiologic functions in the body.
Summary
The cell is the basic unit that
performs all the vital physiologic functions in the body. The three parts of
the cell are the semipermeable cell membrane, the cytoplasm, and the nucleus.
The cell membrane is mostly made up of lipids and proteins, usually in a double
layer of phospholipid molecules. The mem-brane lipids are mostly phospholipids,
but also con-tain glycolipids, cholesterol, and lipid rafts. There are two
distinct types of membrane proteins: integral and peripheral. The peripheral
proteins may be anchoring proteins, recognition
proteins, enzymes, receptor proteins,
carrier proteins, or channels. There are alsomembrane carbohydrates, which
have anchoring, locomotion, binding specificity, lubrication, protec-tion, and
recognition functions.
The cytoplasm is a gel-like
material suspending the cell’s organelles. The organelles in the cytoplasm each
have specific actions that help to carry out the cell’s activities. They are
vital to the life of the cell, tis-sue, and organism. Microtubules are hollow
tubes that are the largest components of the cytoskeleton. They form and
dissemble various components and allow for movement of organelles.
Microfilaments of actin and myosin provide cell movement and contraction. The
cell nucleus is the control center for cellular operations. Inside the
nucleus, a fluid called nucleoplasm sus-pends the nucleolus, nucleosome, and
chromatin. The nucleus also contains chromosomes. The DNA con-trols protein
synthesis in the nucleus. Gene activation in protein synthesis involves
temporary removal of histones and utilizes messenger RNA to carry the
information required to synthesize proteins. Transla-tion is the forming of a
linear amino acid chain, which allows functional polypeptides to be assembled
in the cytoplasm. A cell’s nucleus has either direct or indirect control of its
cell structure and functionThe cell membrane uses passive and active
mech-anisms to allow various substances to enter or leave the cell. Cell
membranes may be freely permeable, selectively permeable, or impermeable.
Passive cell mechanisms include diffusion, osmosis, and filtration. Primary
active transport, via hydrolysis of ATP, allows molecules to move across cell
membranes. Active cell mechanisms require energy and specific carrier
mol-ecules, and include active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis. Phagocytosis
(cell eating) and pinocyto-sis (cell drinking) are forms of endocytosis.
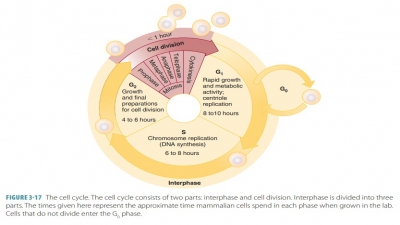
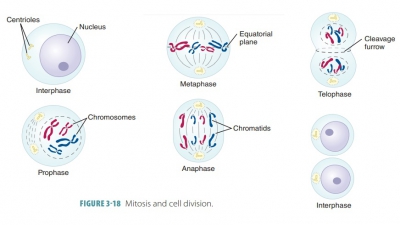
Mitosis occurs in somatic cells, with cell numbers increasing as cell nuclei
divide. The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and
telophase. Game-togenesis is the process in which germ cells form and later
mature into sperm (via spermatogenesis) or ova (via oogenesis). In meiosis,
cell division reduces the amount of chromosomes by half, as genetic material
from both parents mixes.
A neoplasm is a mass of tissue
produced by abnormal cell growth and division. The two types of tumors are
benign or malignant. Tumors that are malignant spread into surrounding tissues
in a process known as metastasis.
Related Topics