Ureido penicillins
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antibiotics
Ureido penicillins: i. Aziocillin (Azlin) ii. Piperacillin (Pipracil, Pracil)
Penicillin - Synthesis and Drug Profile
Ureido penicillins
i. Aziocillin (Azlin)
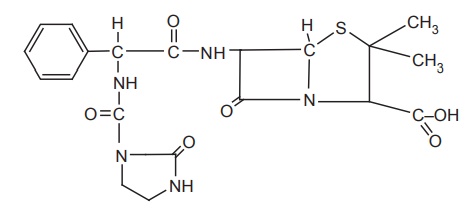
Synthesis
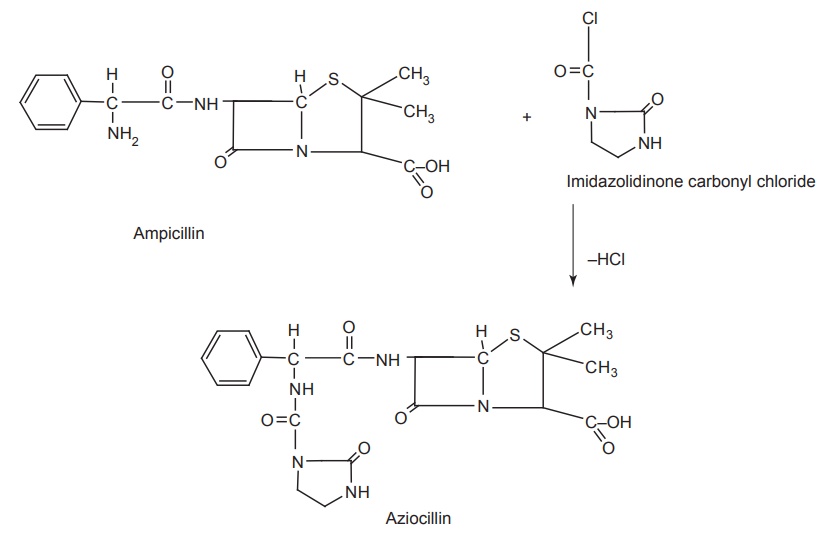
Properties and uses: It is the newest of ureidopenicillins, and is
about 10 times more active than carbenicillin against Pseudomonas and Streptococci.
Dose: The dose is 8–18 g per day in 4–6 divided doses.
ii. Piperacillin (Pipracil, Pracil)
Synthesis
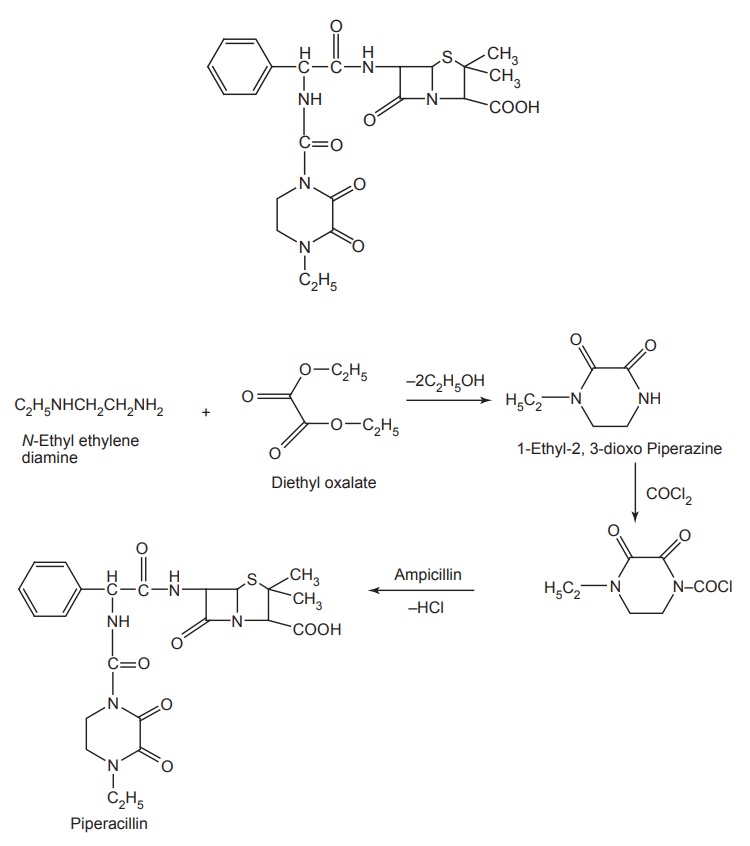
Properties and uses: Piperacillin sodium is a white hygroscopic
powder, soluble in water and methanol, practically insoluble in ethyl acetate.
It is available as a powder for solubilization and injection. It is best given
in combination with an aminoglycoside antibiotic.
Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography technique.
Dose: For serious and complicated infections: The adult dose as sodium
is 200–300 mg/kg daily in divided doses or 3–4 g per day in divided doses of
every 4 or 6 h. For life threatening conditions: especially those caused by Pseudomonas or Klebsiella spp, the dose
is at least 16 g per day; usual maximum dose is 24 g per day. For children: 1
month–12 years, as sodium 100–300 mg/kg daily in 3–4 divided doses. For
neonates: The dose for less than 7 days or lesser than 2 kg, that is, 150 mg/kg
daily in 3 divided doses; for more than 7 days and more than 2 kg, that is, 300
mg/kg in 3–4 divided doses, IV route is preferred for infants and children.
Single dose more than 500 mg should not be given via IM injection.
Parenteral:
For mild or uncomplicated infections: The adult dose as sodium is 100–125 mg/kg
daily, the usual dose, if given via IV injection/infusion is 2 g every 6 or 8 h
or 4 g every 12 h, if given via IM injection the dose is 2 g every 8 or 12 h.
Prophylaxis of infection during surgery, for adults: as sodium the dose is 2 g
just before the procedure or when the umbilical cord is clamped in caesarean
section, followed by at least two doses of 2 g at intervals of 4 or 6 h within
24 h of procedure.
Related Topics
