Penicillinase resistant penicillins
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antibiotics
Penicillinase resistant penicillins : i. Methicillin ii. Oxacillins (Isoxazolyl penicillins)
penicillin - Synthesis and Drug Profile
Penicillinase resistant penicillins
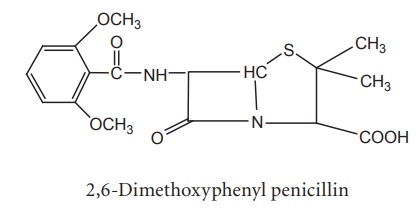
i. Methicillin
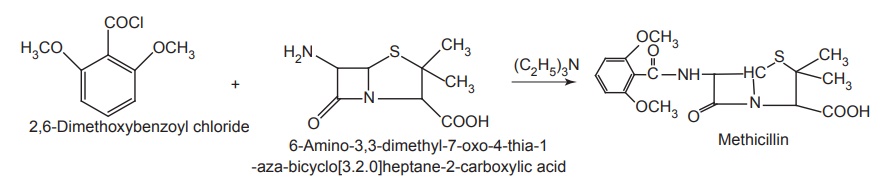
Synthesis
Properties and uses: Methicillin sodium is a white crystalline solid,
odourless, soluble in water, slightly soluble in chloroform, but insoluble in
ether. It is particularly resistant to inactivation by the penicillinase found
in Staphylococci and somewhat more
resistant than penicillin G to penicillinase from Bacillus cereus. Methicillin sodium has been introduced for use in
the treatment of Staphylococci infections
caused by the strains resistant to other penicillins. It is given by IM or by
slow IV infusion every 4–6 h.
ii. Oxacillins (Isoxazolyl penicillins)
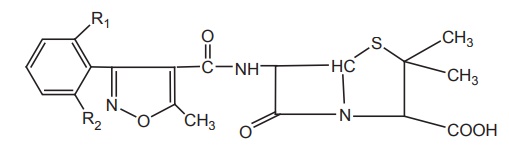
Properties and uses: Oxacillin sodium monohydrate is a white powder,
soluble in water and methanol, insoluble in methylene chloride. The use of
oxacillin and other isoxazolyl penicillins should be restricted to the
treatment of infections caused by Staphylococci
that are resistant to penicillin G, although their spectrum of activity is
similar to that of penicillin G.
Synthesis
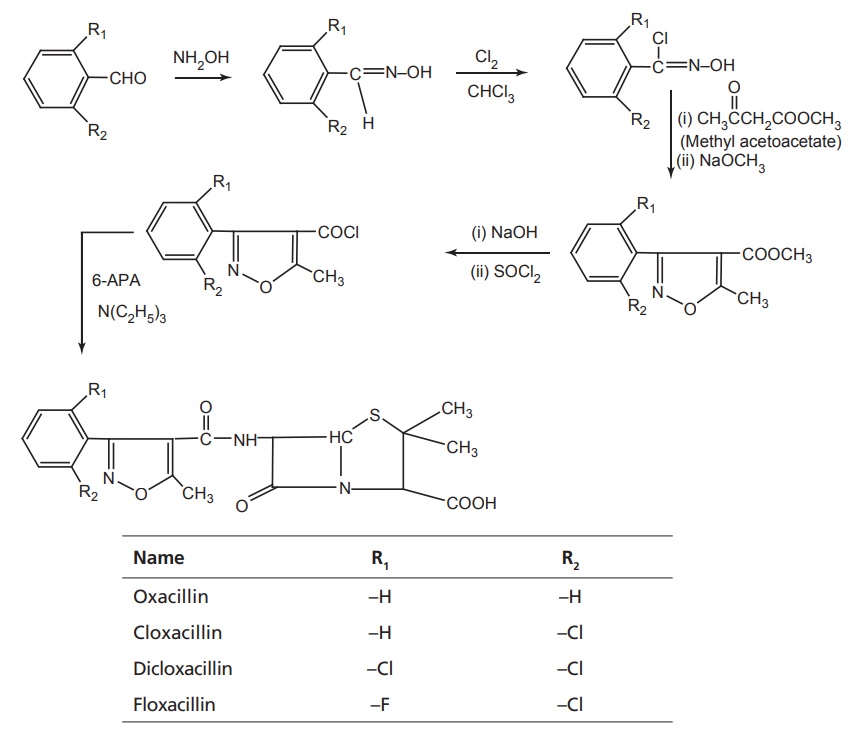
Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography technique.
Related Topics
