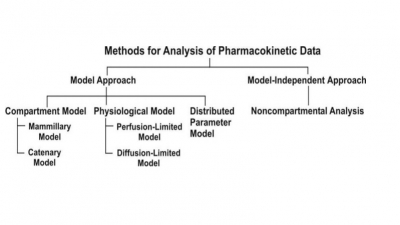
Zero-Order Kinetics (Constant Rate Processes)
| Home | | Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics |Chapter: Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics : Pharmacokinetics Basic Considerations
the zero-order process can be defined as the one whose rate is independent of the concentration of drug undergoing reaction i.e. the rate of reaction cannot be increased further by increasing the concentration of reactants.
Zero-Order Kinetics (Constant Rate Processes)
If n = 0, equation 8.4 becomes:
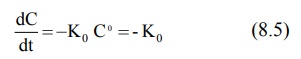
where Ko = zero-order rate constant (in
mg/min)
From equation 8.5, the zero-order process can be
defined as the one whose rate is independent
of the concentration of drug undergoing reaction i.e. the rate of reaction
cannot be increased further by increasing the concentration of reactants.
Rearrangement of equation 8.5 yields:
dC = - K0dt (8.6)
Integration of equation 8.6 gives:
C – C0 = - K0t (8.7)
where Co = concentration of drug at t =
0, and
C = concentration of drug yet to undergo reaction
at time t.
Equation 8.7 is that of a straight line and states
that the concentration of reactant decreases
linearly with time. A plot of C versus t yields such a straight line having
slope - Ko and y-intercept Co (Fig.8.2.).
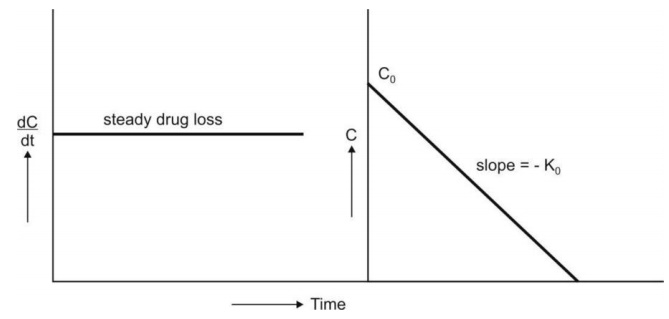
Fig. 8.2. Graphs of zero-order kinetics (equations 8.5 and 8.7)
Related Topics