Biguanides and Diaminopyrimidines
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antimalarials
a. Biguanides : Proguanil HCl (Paludrine), b. Diaminopyrimidines : Pyrimethamine (Daraprim), Trimethoprim (Proloprim)
Antimalarials - Synthesis and Drug Profile
a. Biguanides
Mode of action: Biguanides inhibit dihydrofolate reductase
enzyme and interfere in the folic acid metabolism. This leads to inhibition of
the nuclear division in malarial parasites.
Proguanil HCl (Paludrine)
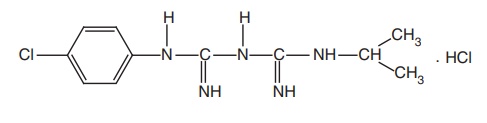
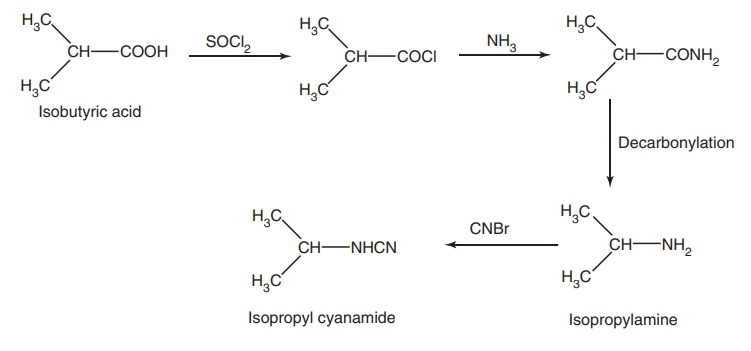
Synthesis
Step I. Synthesis of p-chloro
phenyl guanidine

Step II. Synthesis of isopropyl cyanamide
Step III. Condensation of the products of Steps I and II
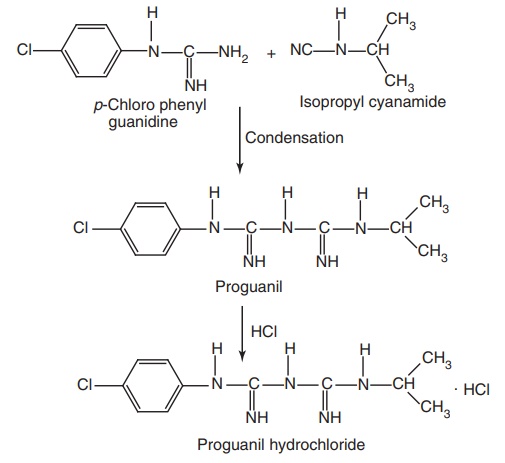
Metabolism: Proguanil is a prodrug, which is metabolized in the liver to
diaminotriazine (cycloguanil) that acts as a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor
of Plasmodium species and inhibits
DNA synthesis.
Properties and uses: Proguanil hydrochloride is a white crystalline
powder, slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol, and
practically insoluble in methylene chloride. It is used mainly for prophylactic
treatment of malaria.
Assay: Suspend the sample in anhydrous acetic acid, shake and heat at
50°C for 5 min. Cool to room temperature, add acetic anhydride, and titrate
with 0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: The recommended dose as a prophylactic and a suppressant is 100
to 200 mg per day in nonimmune subjects; 300 mg/week or 200 mg twice/week in semi-immune
subjects. In the case of acute vivax malaria,
initial loading dose is 300 g–600 mg followed by 300 mg per day for 5–10 days.
For the treatment of falciparum malaria,
the dose is 300 mg two times daily for 5 days.
b. Diaminopyrimidines
Mode of Action: It inhibits the reduction of folic acid and
dihydrofolic acid to the active tetrahydrofolate coenzyme form.
Pyrimethamine (Daraprim)
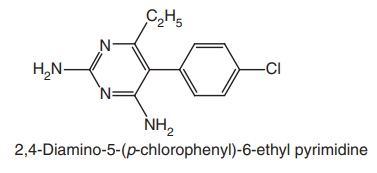
Synthesis
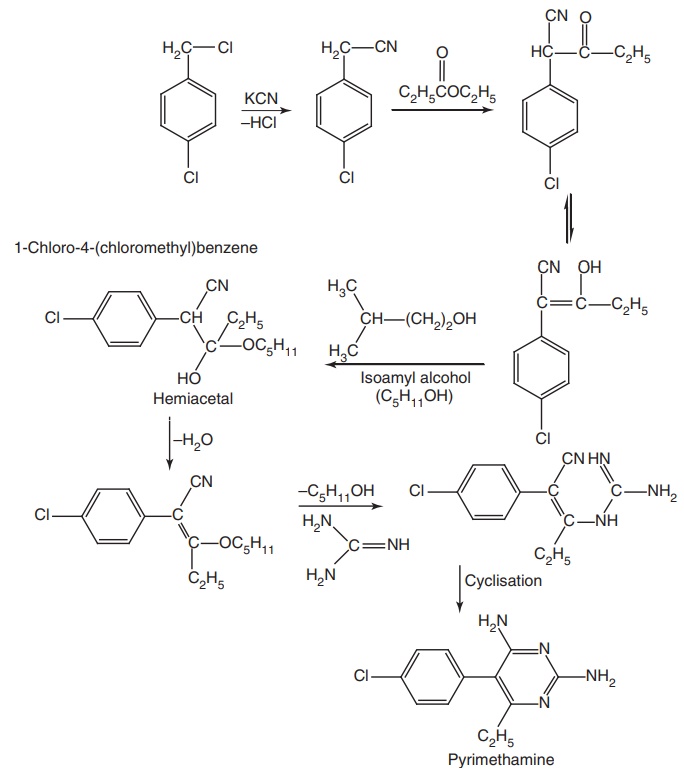
Properties and uses: Pyrimethamine exists as a white crystalline
powder or colourless crystals, practically insoluble in water, and slightly
soluble in alcohol. Pyrimethamine inhibits the reduction of folic acid and
dihydrofolic acid to the active tetrahydrofolate coenzyme form. It finds its
extensive use as a suppressive prophylactic for the prevention of severe
attacks due to P. falciparum and P. vivax. It is also used in the
treatment of taxoplasmosis and as an immuno suppressive agent.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid by heating gently.
Cool and titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point
potentiometrically.
Dose: The administered dose as a suppressive is 25 mg once a week, as
a therapeutic 50–75 mg once a day for two days when used alone, otherwise 25
mg.
Dosage forms: Pyrimethamine tablets I.P., B.P.
Trimethoprim (Proloprim)
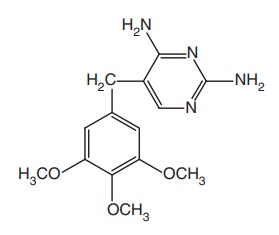
Synthesis
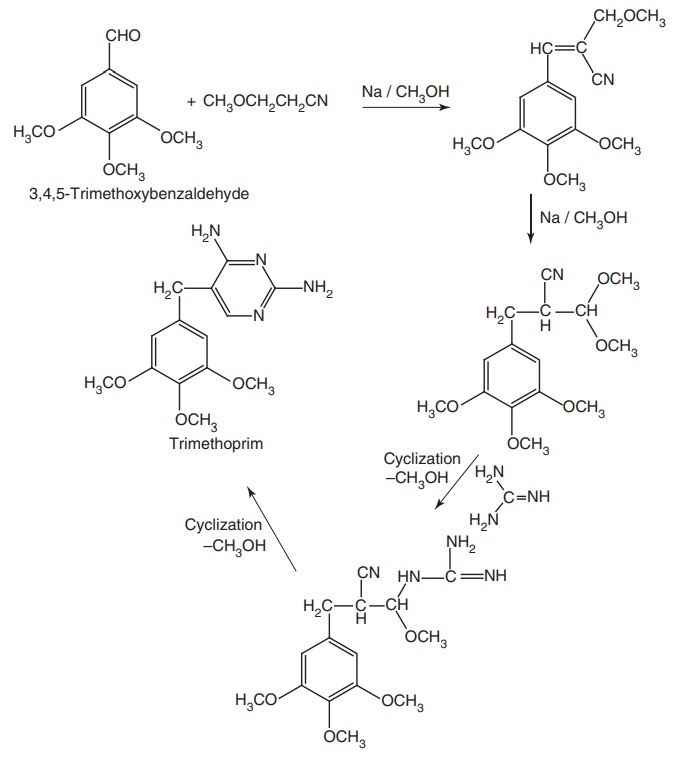
Properties and uses: Trimethoprim exists as a white or
yellowish-white powder, very slightly soluble in water, and slightly soluble in
ethanol. It is a potent inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase. It has been
employed in conjugation with sulphamethopyrazine in the treatment of
chloroquine-resistant malaria. It has also been used in conjugation with
sulphonamides in the treatment of bacterial infections. Trimethoprim is an
antibacterial, effective against malarial parasite.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid and titrate with
0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: The administered dose is 1.5 g with 1 g of sulphametopyrazine
per day for 3 days.
Dosage forms: Co-trimoxazole intravenous infusion B.P., Co-trimoxazole oral
suspension B.P., Paediatric co-trimoxazole oral suspension B.P., Co-trimoxazole
tablets dispersible B.P., Co-trimoxazole tablets paediatric B.P., Co-trimoxazole
tablets B.P., Trimethoprim oral suspension B.P., Trimethoprim tablets B.P.
Related Topics
