Quinoline and isoquinolines
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Anthelmintics
Quinoline and isoquinolines: Praziquantel (PZQ, Biltricide), Oxamniquine (Vansil)
Anthelmintics - Synthesis and Drug Profile
Quinoline and isoquinolines
Praziquantel (PZQ, Biltricide)
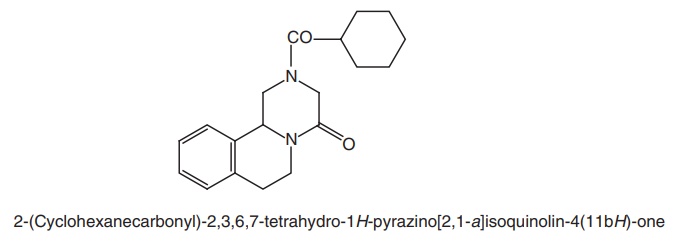
Metabolism: In serum, the major metabolites are 4-hydroxycyclohexyl
carboxylate, but in the urine, 50%–60% of the initial PZQ exist as
dihydroxylated products. Hydroxylation reactions are catalyzed by CYP2B6 and
CYP3A4.
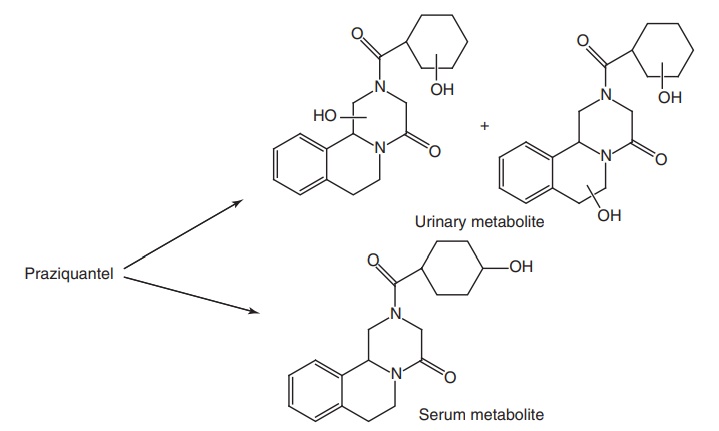
Synthesis
Properties and uses: PZQ is a white crystalline powder, very slightly
soluble in water, soluble in alcohol, and in methylene chloride. It is used for
the treatment of schistosomiasis and liver fluke infections. It causes
legumental damage to the worms, which activates the host defence mechanisms and
results in the destruction of the worms.
Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography technique.
Dose: The oral dose is 600 mg tablet two to three times a day.
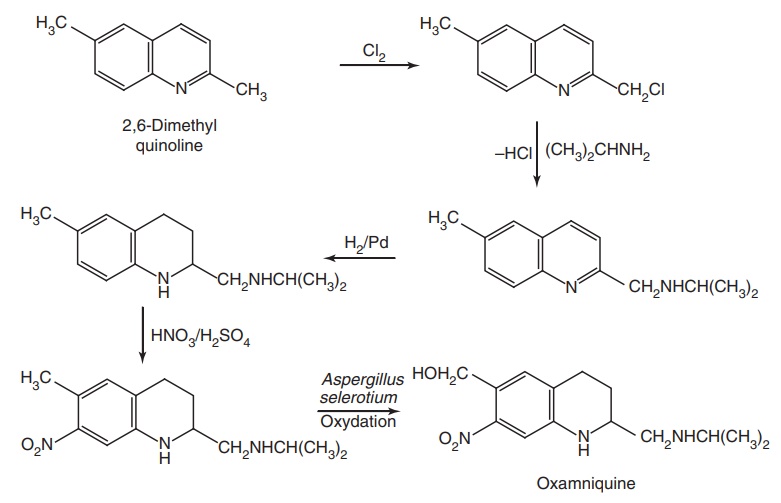
Oxamniquine (Vansil)
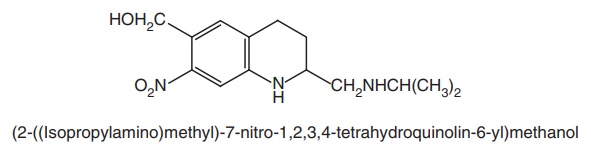
Synthesis
Mode of action: Schistosoma mansoni is highly susceptible to oxamniquine.
Adenosine-5’-triphosphate (ATP)-dependent enzymatic activation of the drug in
susceptible schistosomes forms unstable phosphate esters, which disassociate to
yield a chemically reactive carbocation this intermediate alkylates the DNA.
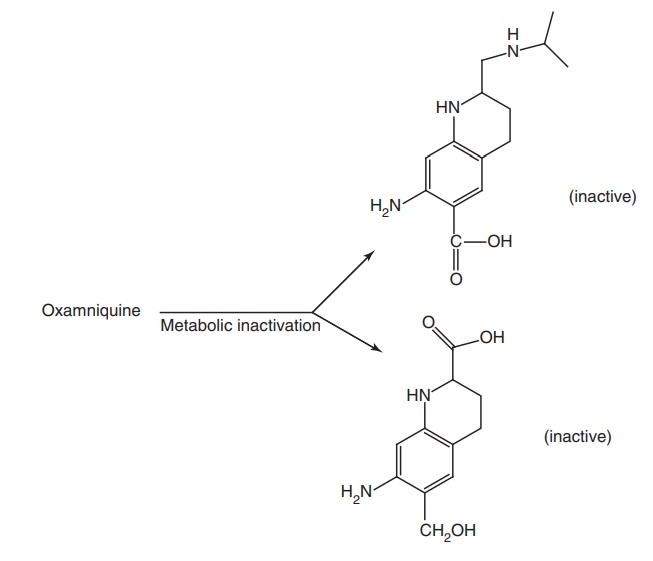
Metabolism: It is metabolized by oxidative reaction and it gives inactive metabolites
of acid and alcohol derivatives.
Dose: The dose for oral route after meals depends upon geographical areas. In the western hemisphere, the dose is 15 mg/kg as a single dose, in Africa 15–60 mg/kg over 1–3 days.
