Energy Produced by the Cycle
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex
Two carbon atoms enter the cycle as acetyl CoA and leave as CO2. The cycle does not involve net consumption or production of OAA or of any other intermediate.
ENERGY PRODUCED BY THE CYCLE
Two carbon atoms enter
the cycle as acetyl CoA and leave as CO2. The cycle does not involve
net consumption or production of OAA or of any other intermediate. Four pairs
of electrons are transferred during one turn of the cycle: three pairs of
electrons reducing three NAD+ to NADH and one pair reducing FAD to
FADH2. Oxidation of one NADH by the electron transport chain leads
to formation of approximately three ATP, whereas oxidation of FADH2
yields approximately two ATP. The total yield of ATP from the oxidation of one
acetyl CoA is shown in Figure 9.7. Figure 9.8 summarizes the reactions of the
TCA cycle.
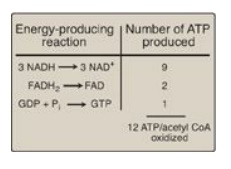
Figure 9.7 Number of ATP
molecules produced from the oxidation of one molecule of acetyl coenzyme A
(CoA) using both substrate-level and oxidative phosphorylation.
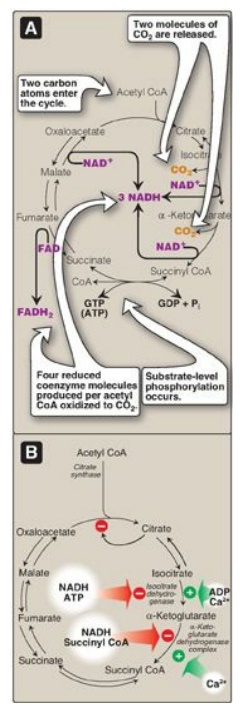
Figure 9.8 A. [Note: GTP and
ATP are interconverted by nucleoside diphosphate kinase.] Production of reduced
coenzymes, ATP, and CO2 in the citric acid cycle. B. Inhibitors and
activators of the cycle.
Related Topics
