Immune Systems
| Home | | Pharmaceutical Microbiology | | Pharmaceutical Microbiology |Chapter: Pharmaceutical Microbiology : Immune Systems
Immunity may be defined as - ‘the state of being immune to or protected from a disease especially an infectious disease’.
IMMUNE
SYSTEMS
INTRODUCTION
Immunity may be defined as - ‘the state of being immune to or protected
from a disease especially an infectious disease’.
Importantly,
this particular state is invariably induced by having been exposed to the antigenic marker on an microorganism that critically invades the body or by
having been duly immunized with a vaccine
capable of stimulating the production of specific antibodies.
Immunology, the generation of an immune response solely depends upon
the prevailing interaction of three cardinal components of the immune mechanism, such as :
·
immunogen stimulation,
·
humoral immune system, and
·
cellular immune system.
Since
1901 and as to date the epoch making discovery and spectacular evolution of ‘immunobiotechnology’ i.e., conglomeration of immune
system variants, across the world has
revolutionized not only the safer quality of life of human beings but also
provided a broad spectrum of newer avenues in combating the complicated
dreadful not-so-easy diseases of the present day.
Immune Response : In
reality, the immune responses do
refer to such processes whereby animals (including
humans) give rise to certain specifically
reactive proteins (known as ‘antibodies’)
and adequate cells in response to a great number of foreign organic molecule and macromolecule variants. Based on the
scientifically demonstrated proofs and evidences the generalized immune response essentially possesses four major primary characteristic features, such as :
(a) discrimination,
(b) specificity,
(c) anamnesis,
and
(d) transferability
by living cells.
1. Discrimination
It
usually designates the ‘ability of the
immune system’ to have a clear-cut discrimination
between ‘self’ and ‘nonself’ ; and, therefore, it
invariably responds exclusively to such materials that happen to be foreign to the host.
2. Specificity
It refers
to such a response that is extremely specific either solely for the inducing material or antigen to which the immune cells or antibodies would interact in a much prominent and
greater strength.
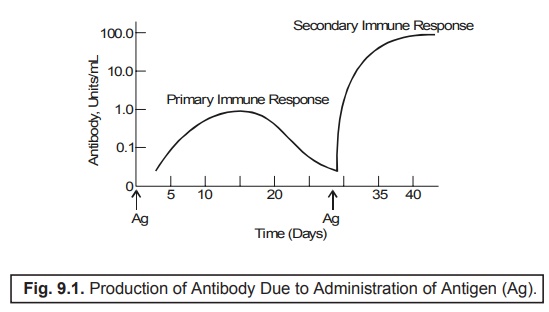
3. Anamnesis
It most
commonly refers to the critical ability to elicit a larger specific response
much more rapidly on being induced
by a ‘second exposure’ to the same
very foreign antigen. It is also
termed as the anamnestic response or
the immunologic memory, as
illustrated in Fig. 9.1.
4. Transferability by Living Cells
Interestingly, the active immunity is observed to be
exclusively transferable from one particular inbred animal specimen to another
by the respective ‘immune cells’ or ‘lymphocytes’, and definitely not by immune serum*.
Adjuvants
: It has been duly observed that there
exist quite a few nonspecific
substances, namely : alum, mineral
oil, that essentially do possess the abiliy to prolong as well as intensify
the ensuing immune response to a
particular antigen on being injected simultaneously with the antigen. In fact, such materials are
termed as adjuvants by virtue of the
fact that they profusely aid the immune
response.
Immune
Serum : It is
capable of transferring temporarily the
passive immunity, whereas the active
immu-nity certainly needs the long-term regenerative ability of the living cells.
Innate
Resistance : Besides, the aforesaid nonspecific
defenses, one may usually encounter certain degree of innate resistance (i.e.,
inherent resistance) to some specific human diseases.
Examples : Various
examples are as given below :
(i)
Canine distemper,
(ii)
Hog and Chicken cholera, and
(iii)
Measles.
Nevertheless, the effect of measles is
observed to be comparatively quite mild specifically for the individuals
belonging to the European ancestry, whereas for the individuals belonging to
the Pacific Island it proved to be quite severe.
Special
Points : There are fwo special points, such as :
(a) The innate resistance of an
individual to measles exclusively depends on such other cardinal factors as :
age, general health, nutritional status, and genetic factors, and
(b) Natural selection
from several generations being duly exposed to ‘measles virus' probably led to
the more frequent inheritance of genes which eventually offered certain extent
of resistance to the virus.
Related Topics
