Insulin
| Home | | Pharmacology |Chapter: Essential pharmacology : Insulin, Oral Hypoglycaemic Drugs and Glucagon
Insulin was discovered in 1921 by Banting and Best who demonstrated the hypoglycaemic action of an extract of pancreas prepared after degeneration of the exocrine part due to ligation of pancreatic duct.
INSULIN
Insulin was discovered
in 1921 by Banting and Best who demonstrated the hypoglycaemic action of an
extract of pancreas prepared after degeneration of the exocrine part due to
ligation of pancreatic duct. It was first obtained in pure crystalline form in
1926 and the chemical structure was fully worked out in 1956 by Sanger. Insulin
is a two chain polypeptide having 51 amino acids and MW about 6000. The Achain
has 21 while Bchain has 30 amino acids. There are minor differences between
human, pork and beef insulins:
Thus, pork insulin is
more homologous to human insulin than is beef insulin. The A and B chains are
held together by two disulfide bonds.
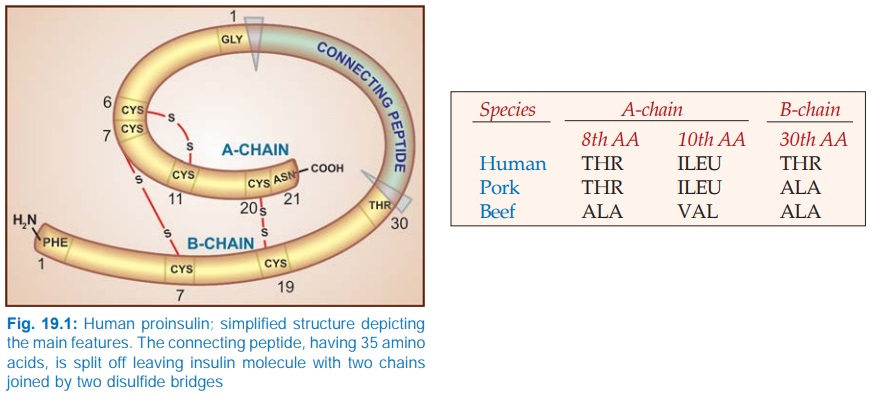
Insulin is synthesized
in the β cells of pancreatic
islets as a single chain peptide Preproinsulin
(110 AA) from which 24 AAs are first
removed to produce Proinsulin (Fig.
19.1). The connecting or ‘C’ peptide (35 AA) is split off by proteolysis in
Golgi apparatus; both insulin and C peptide are stored in granules within the
cell. The C peptide is secreted in the blood along with insulin.
Assay
Insulin is bioassayed
by measuring blood sugar depression
in rabbits (1 U reduces blood glucose of a fasting rabbit to 45 mg/dl) or by
its potency to induce hypoglycaemic convulsions in mice. 1 mg of the
International Standard of insulin = 28 units. With the availability of pure
preparations, it can now be assayed chemically also. Plasma insulin can be
measured by radioimmunoassay or enzyme immunoassay.
