Selective COX-2 inhibitor
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Analgesics, Antipyretics, and NSAIDs
Selective COX-2 inhibitor : i. Celecoxib (Celact, Cobix, Revibra) ii. Rofecoxib iii. Valdecoxib - Synthesis and Drug Profile
Selective COX-2 inhibitor
The PG that
mediates inflammation, fever, and pain are produced solely via COX-2 (highly
inducible by inflammatory response), and the PGs that are important in GIT,
platelets, uterus, and adrenal function are produced solely via COX-1
(constitutively expressed). Selective COX-2 inhibitors (Celecoxib, Rofecoxib,
and Valdecoxib) are devoid of side effects, such as gastric ulcer. It does not
affect the normal functioning of platelets, uterus, and renal system.
i. Celecoxib (Celact, Cobix, Revibra)
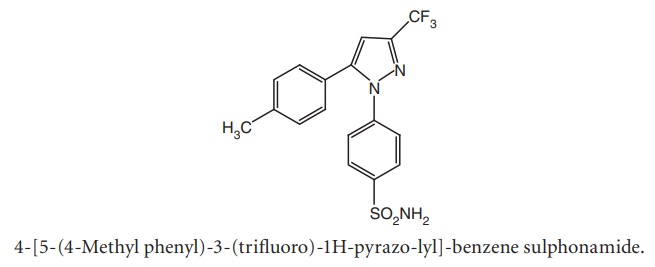
Metabolism: Metabolism of celecoxib occurs in the liver, involves
hydroxylation of 4-methyl group to primary alcohol, which is subsequently
oxidized to its corresponding carboxylic acid.
Properties and uses: It exists as pale yellow crystals, sparingly
soluble in water. Celecoxib is used to treat arthritis, pain, menstrual cramps,
and colonic polyps, and also for the relief of pain, fever, swelling, and
tenderness caused by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing
spondylitis.
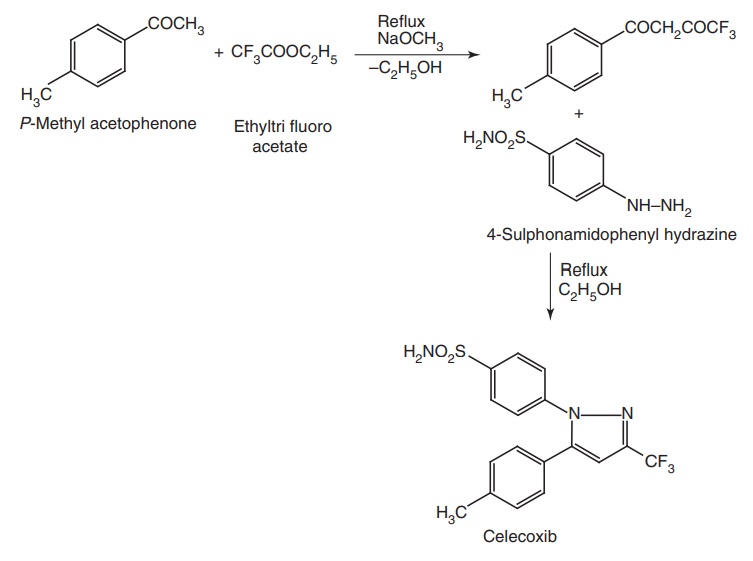
Synthesis
Dose: For osteoarthritis, the adult dose is 200 mg as a single dose or
in two divided doses that may be increased to 200 mg two times a day, if
necessary. For rheumatoid arthritis, the adult dose is 100–200 mg two times a
day. For elderly people the dose is 100 mg two times a day. For dysmenorrhoea,
initially the dose is 400 mg by 200 mg, if necessary, on the 1st day and
maintenance dosage is 200 mg two times a day.
ii. Rofecoxib
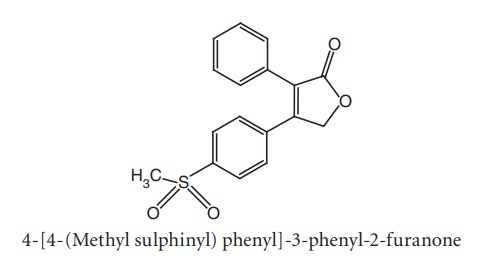
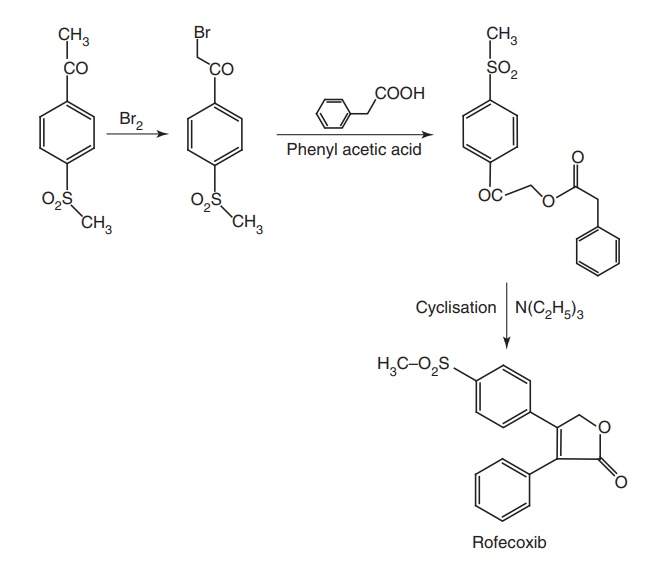
Synthesis
Metabolism: The metabolic route of Rofecoxib appears to follow the reduction
of dihydrofuranone ring system by cystolic enzyme to cis and trans hydroxy
derivatives.
Properties and uses: It exists as white to light yellow powder,
sparingly soluble in acetone, methanol, very slightly soluble in 1-octanol. It
is a COX-2 inhibitor with greater potency and a longer half-life than
celecoxib. Rofecoxib is used to relieve the pain, tenderness, inflammation
(swelling), and stiffness caused by arthritis, and to treat painful menstrual periods
and pain from other causes.
iii. Valdecoxib
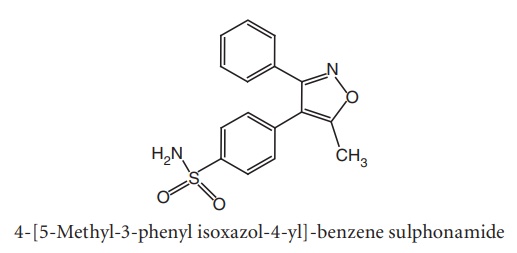
Synthesis
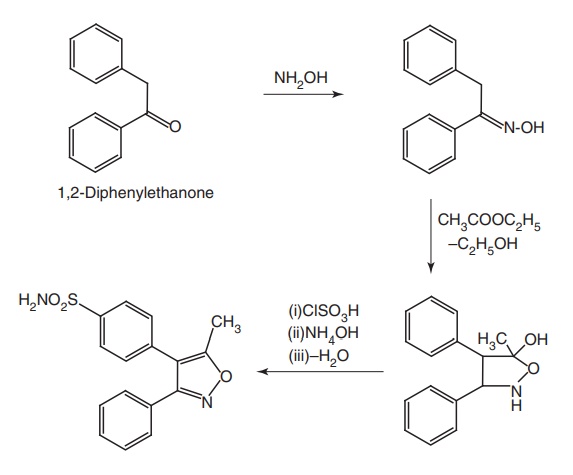
Metabolism: It is metabolized by hydroxylation of 5-methyl group and it is
further metabolized to inactive carboxylate and N-Hydroxylation at the sulphonamide function, leading to the
formation of corresponding sulphinic acid and suphomic metabolites.
Properties and uses: It is soluble in most organic solvents,
insoluble in water. It is a NSAID drug that exhibits anti-inflammatory,
analgesic, and antipyretic activities.
Dose: For dysmenorrhoea the dose is 20 mg twice a day. For
osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis the dose is 10 mg once daily.
Related Topics
