Tissues
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Levels of Organization : Tissues
There are trillions of cells in the human body, each with specialized functions.
Tissues
After
studying this chapter, readers should be able to
1. Describe
the four major types of tissues.
2. Discuss
the types and functions of epithelial tissue.
3. Identify
endocrine and exocrine glands.
4. Explain
the characteristics of mast cells, macrophages, and adipocytes.
5. Describe
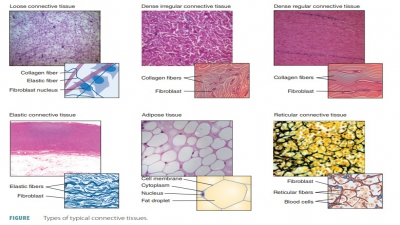
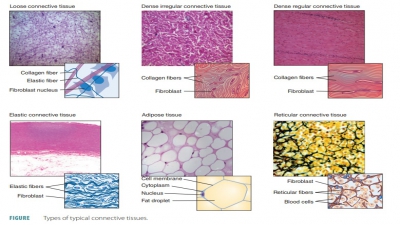
three types of connective tissue fibers.
6. Explain fluid connective tissues.
7. Describe
the various types of cartilage.
8. Describe
how bone tissue establishes the framework of the body.
9. Describe
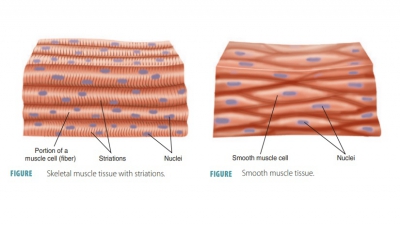
the three types of muscle tissue and their characteristics.
10. Discuss
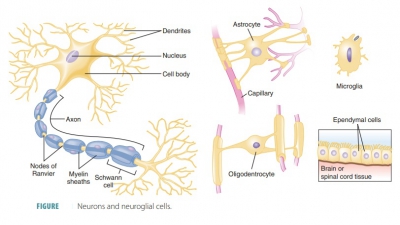
the basic structure and role of neural tissue.
Overview
There are trillions of cells in
the human body, each with specialized functions. Cells are the body’s basic
units of structure and function, and their specialization enables the body to
function in highly efficient ways. For this ability, several different types of
cells must coordinate their efforts. The combination of different cell types,
with similar structures and func-tions, creates tissues. The four basic tissue types are epithelial, connective, nervous, and
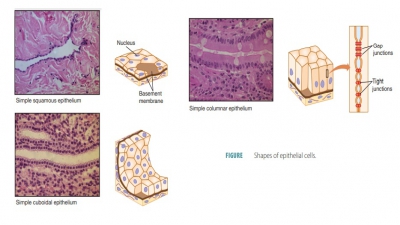
muscle tissues. In general, epithelial tissues have covering functions,
connective tissues have supporting functions, ner-vous tissues have controlling
functions, and muscle tissues produce movement. However, most organs contain all
four tissue types. The study of tissues is called histology.