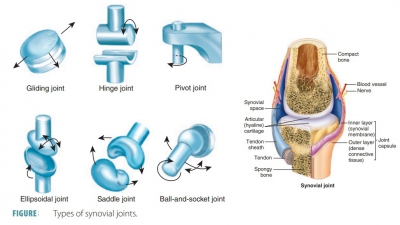
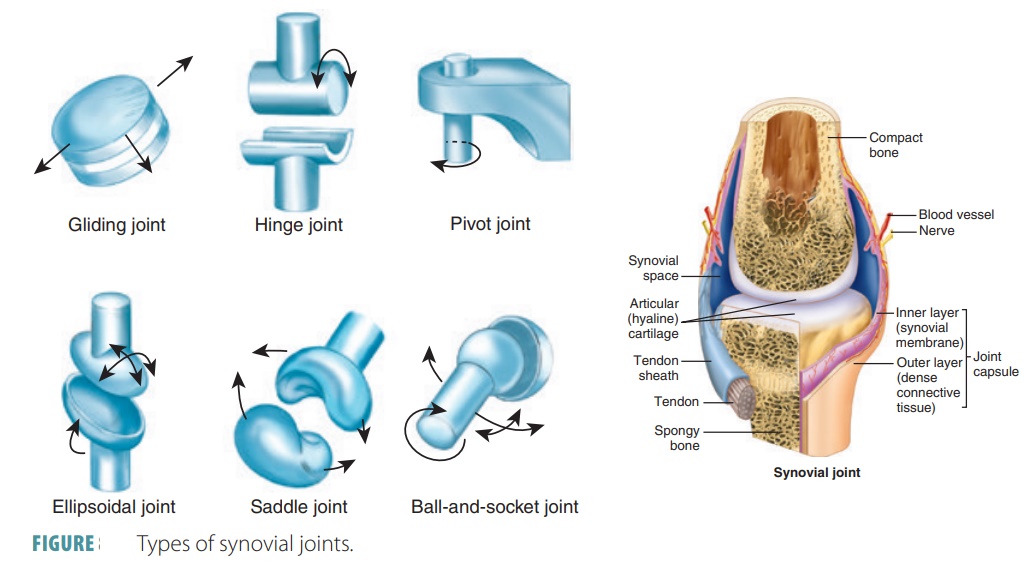
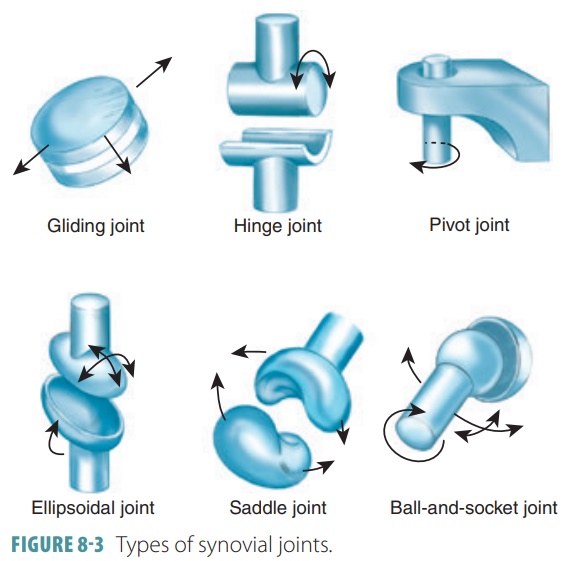
Types of Synovial Joints
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Support and Movement: Articulations
List different types of synovial joints.
Types of
Synovial Joints
Synovial joints are not all identical. There are six further subdivisions of synovial joints: gliding, hinge, pivot, ellipsoidal, saddle, and ball-and-socket joints.
Gliding Joints
Gliding
joints have nonaxial movement
that involves linear gliding and flat, articular surfaces. For exam-ple,
the intercarpal joints, intertarsal joints, sacroil-iac joints, and the joints
between vertebral articular surfaces.
Hinge Joints
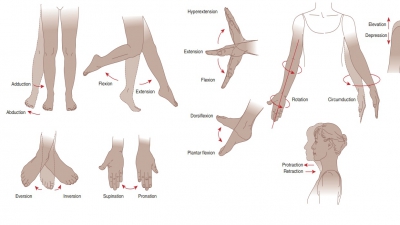
Hinge joints have uniaxial movement that involves flexion and extension along a medial/lateral axis.
They also have cylinders and troughs.
For example, the elbow joints and interphalangeal joints.
Pivot Joints
Pivot joints have uniaxial movement that involves rotation around a vertical axis. They have bone and ligament sleeves as
well as rounded bones (axles). For example, the proximal radioulnar joints and
the atlan-toaxial joint.
Ellipsoidal Joints
Ellipsoidal
joints have biaxial movement
that involves adduction and abduction around an anterior/
posterior axis as well as flexion and
extension around a medial/lateral axis. Their articular surfaces are
oval-shaped. For example, the metacarpophalangeal (knuckle) joints, radiocarpal
joints, and wrist joints.
Saddle Joints
Saddle joints
have biaxial movement that involves flexion and extension
as well as adduction and abduc-tion. These joints function around the same type
of axis configurations as condylar joints. Articular sur-faces are both concave
and convex. For example, the carpometacarpal joints of the thumbs.
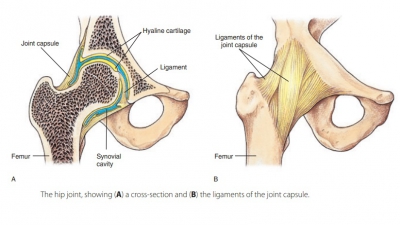
Ball-and-Socket Joints
Ball-and-socket
joints have multiaxial
movement that involves rotation, adduction, abduction, flexion, and
extension. These joints use vertical, anterior/ posterior, and medial/lateral
types of axis structures, with spherical heads in cup-like sockets. For
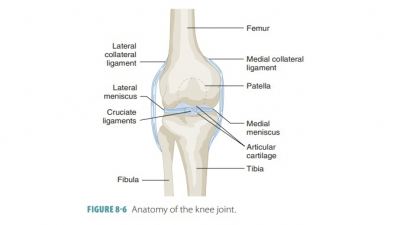
example, the shoulder and hip joints. Types of synovial joints are shown in FIGURE 8-3.
1. List
different types of synovial joints.