Water-soluble polymers
| Home | | Pharmaceutical Drugs and Dosage | | Pharmaceutical Industrial Management |Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drugs and Dosage: Pharmaceutical polymers
Polymers that have sufficient number of electronegative atoms and/or functional groups that can form hydrogen bonds with water tend to dissolve in water and are called water-soluble polymers.
Water-soluble
polymers
Polymers
that have sufficient number of electronegative atoms and/or func-tional groups
that can form hydrogen bonds with water tend to dissolve in water and are called
water-soluble polymers. Water-soluble polymers have an ability to increase the
viscosity of solvents at low concentrations, to swell or change shape in
solution, and to adsorb at surfaces. The rate of dissolution of a water-soluble
polymer depends on its molecular weight. Larger the molecules, stronger the
forces holding the chains together and lower the rate of dissolution. Greater
the degree of crystallinity of the polymer in the solid state, lower the rate
of dissolution. This combination of slow dissolution rate and formation of
viscous surface layer makes high-molecular-weight hydrophilic polymers suitable
for use in controlling the release rate of soluble drugs. For example,
high-molecular-weight HPMC is used as a matrix controlled-release drug delivery
carrier.
Examples
of commonly used water-soluble polymers include the following:
Carboxypolymethylene
(carbomer, carbopol)
Carboxypolymethylene,
also known as carbomer, carbopol, or carboxyvinyl polymer, is a high molecular
weight polymer of acrylic acid, containing a high proportion of carboxyl
groups. This polymer is used as a binding agent in tablets and a suspending
agent in other pharmaceutical preparations. The car-boxylic groups impart it an
acidic character. Thus, its aqueous solutions are acidic. On neutralization
with a base, the carboxylic groups become ionized and form stronger
hydrogen-bond associations with other polymer chains and the solvent, water.
Consequently, carboxypolymethylene solutions become very viscous, with a
maximum viscosity at pH between 6 and 11.
Cellulose
derivatives
Cellulose
itself is insoluble in water. Its partial aqueous solubility is attrib-uted to
substitutions, such as methylation and carboxymethylation. Ethyl
methylcellulose is soluble in hot and cold water and does not form a gel.
Methylcellulose is poorly soluble in water and forms a gel on heating. Sodium
carboxymethylcellulose, being an ionized carboxylic acid salt, is soluble in
water at all temperatures.
Natural gum (acacia)
Acacia
gum, also known as gum arabica, is a complex arabinogalac-tan-type
polysaccharide exuded by acacia trees. Acacia solutions are highly viscous in
water. It is one of the most widely used emulsifiers and thickeners.
Alginates
Alginates,
also called align or alginic acid, is an anionic polysaccharide in the cell
walls of brown algae. It forms a viscous gum on binding with water. Alginate
solutions are less readily gelled than acacia gum and are used as stabilizers
and thickening agents.
Dextran
Dextran
is a complex, branched polymer or polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules.
Hence, it is also called glucan. Partially hydrolyzed dex-tran reduces blood
viscosity and is used as a plasma substitute and a volume expander. It exerts
an osmotic pressure comparable with that of plasma. Thus, it is used to restore
or maintain blood volume in severe trauma.
Polyvinylpyrrolidone
Polyvinylpyrrolidone
(PVP), also known as povidone, is a homopolymer of N-vinyl pyrrolidone (Figure 11.5).
It is commonly used as a suspending and dispersing
agent. It is also used as binding and granulating agent for tablets and as a
vehicle for drugs such as penicillin, cortisone, procaine, and insu-lin to
delay their absorption and prolong their action.
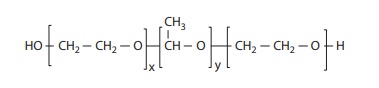
Figure 11.5 Chemical structure of poly(ethylene oxide-co-propylene oxide-co-polyethylene oxide) (PEO-PPO-PEO) (commercially known as Pluronic and poloxamer).
Polyethylene glycol
Polyethylene
glycol (PEG) is a polyether compound with repeating units of ethylene oxide and
a terminal hydroxyl group. The electronegative oxygen confers water solubility
on this polymer. Polyethylene glycols have different physical states, depending
on their molecular weight, with low-molecular-weight PEGs being liquid at room
temperature, while high-molecular-weight PEGs being crystalline solids.
Polyethylene glycols are water-soluble and miscible and can dissolve drugs that
are not soluble in water. Thus, PEGs are commonly used to increase drug solubility.
Polyethylene glycols are also used as plasticizers in coating suspensions to
form an elastic film during tablet coating.
Related Topics
