H2-receptor antagonists
| Home | | Medicinal Chemistry |Chapter: Medicinal Chemistry : Antiulcer Agents
Antiulcer Agents - H2-receptor antagonists : i. Cimetidine (Tagamet) ii. Famotidine (Famocid, Famtac) iii. Ranitidine (Zantac) iv. Etintidine v. Oxmetidine vi. Nizatidine vii. Roxatidine (Rotane, Zorpex) - Synthesis and Drug Profile
SYNTHESIS AND DRUG PROFILE
H2-receptor antagonists
Mode of action: These drugs inhibit the acid production by reversibly competing with histamine for the binding with H2-receptor on the basolateral membrane of parietal cells. The most predominant effect of H2-receptor antagonist is on basal acid secretion. Histamine on H2-receptors produces cAMP-dependent protein kinase to elicit the response in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). The H2-antagonists reversibly bind the H2-receptors and reduce the cAMP formation, which is responsible for the activation of proton pump and subsequently reduces the gastric acid formation in the GIT.
i. Cimetidine (Tagamet)
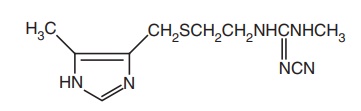
Synthesis
Route I. From:
Ethyl-5-methyl-imidazole-4-carboxylate
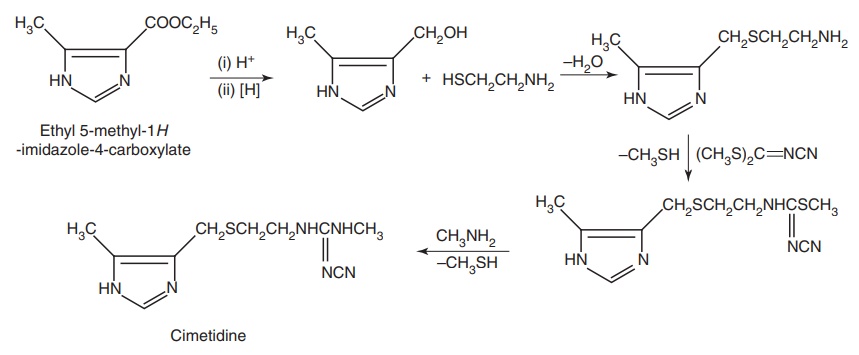
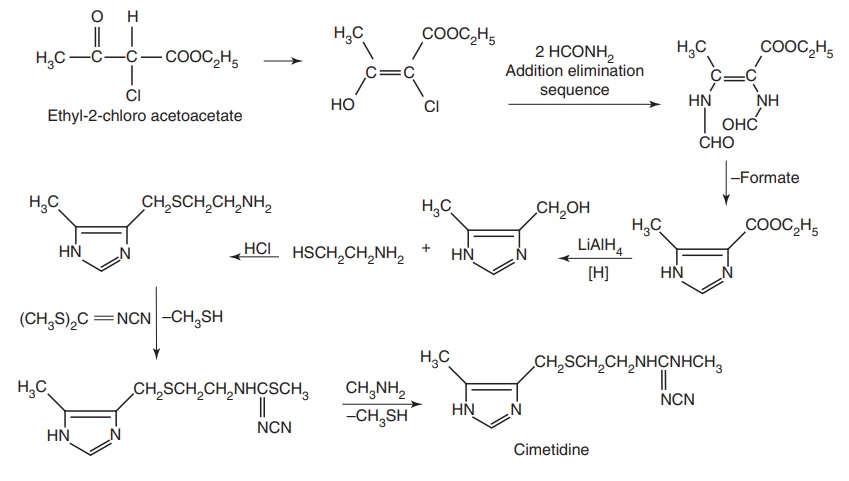
Route II: From: Ethyl-2-chloro acetoacetate
Properties and uses: Cimetidine hydrochloride is a white crystalline
powder, soluble in water, and sparingly soluble in ethanol. It is a H2-receptor
antagonist that not only inhibits gastric acid secretion, but also prevents other actions of histamine
mediated by H2-receptors. It is used in the treatment of peptic ulceration.
Cimetidine has a weak antiandrogenic effect. Gynaecomastia may occur in
patients treated for a month or more.
Assay: Dissolve the substance in a mixture of 0.01 M HCl and alcohol
(1:10) and titrate against 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Determine the end point
potentiometrically.
Dose: Oral dose is 200 mg thrice a day with meals and 400 mg at night.
ii. Famotidine (Famocid, Famtac)
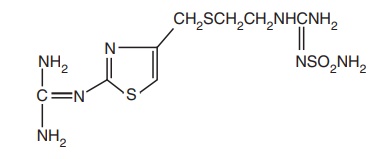
Synthesis
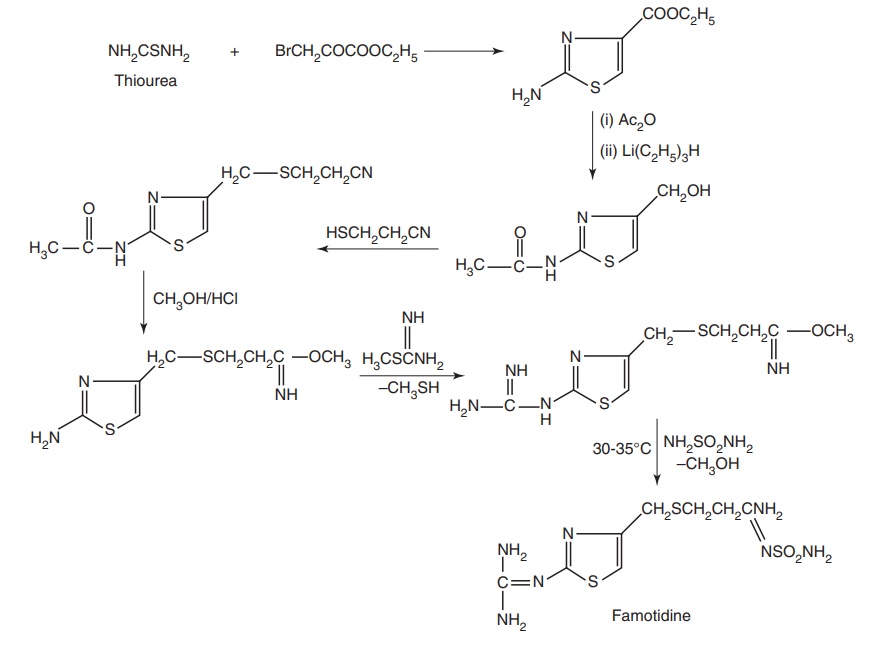
Properties and uses: Famotidine is a white or yellowish-white
crystalline powder or crystals, very slightly soluble in water, soluble in
anhydrous ethanol and glacial acetic acid, but practically insoluble in ethyl
acetate. It acts as a competitive, reversible H2-antagonist with a
slow onset of equilibrium. This type of blockade is called nonequilibrium
antagonism. It is used in the treatment of duodenal and gastric ulcers,
Zollinger–Ellison syndrome, and heart burn.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid and titrate against
0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end-point potentiometrically.
Dose: The dose for gastric or duodenal ulcer is 40 mg at night for 4–8
weeks. The dose for prophylaxis or relapse is 20 mg at night. Not recommended
for usage in children.
Dosage forms: Famotidine tablets B.P.
iii. Ranitidine (Zantac)
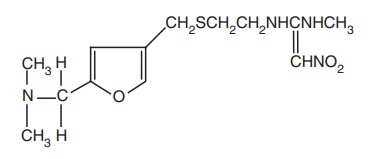
Synthesis
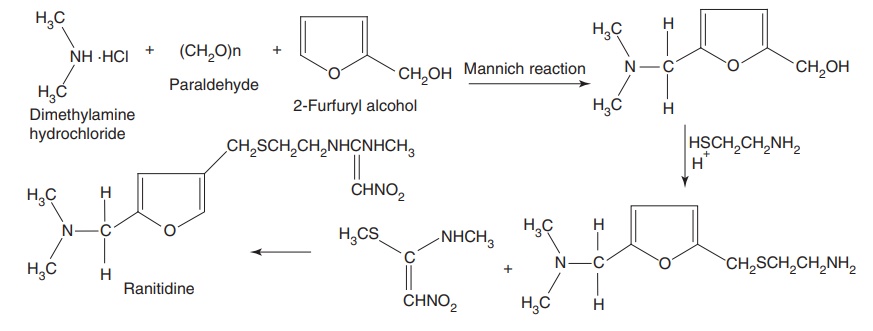
Metabolism of cimetidine, ranitidine, and
fomotidine: Hydroxylation of
the imidazole C-4 methyl group of cimitidine occurs. Ranitidine is excreted
largely unchanged, but minor metabolic pathways include Ndemethylation as well as Nand
S-oxidation. The metabolites are
thought not as contributing to the therapeutic properties of parent drugs, with
the exception of nizanidine, from which the N-demethyl
metabolites retains H2-antihistamine activity.
Properties and uses: Ranitidine hydrochloride is a white or pale
yellow crystalline powder, soluble in water, slightly soluble in anhydrous
ethanol and methylene chloride. In Ranitidine, the imidazole ring of cimitidine
was replaced by furan in conjugation with some rearrangement of the terminal
functionality; the substituted guanidine group has been isosterically modified
by utilizing a nitromethenyl moiety to basicity. It is used in the treatment of
duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, and pathological hypersecretory conditions.
Assay: Dissolve the sample in water and titrate against 0.1 M sodium
hydroxide. Determine the end point potentiometrically.
Dose: The dose is 150 mg (as the hydrochloride) two times a day.
Dosage forms: Ranitidine HCl injection I.P., Ranitidine HCl tablets I.P.,
Ranitidine injection B.P., Ranitidine oral solution B.P., Ranitidine tablets
B.P.
iv. Etintidine
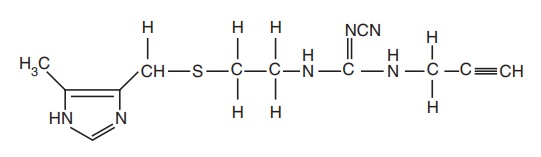
Synthesis
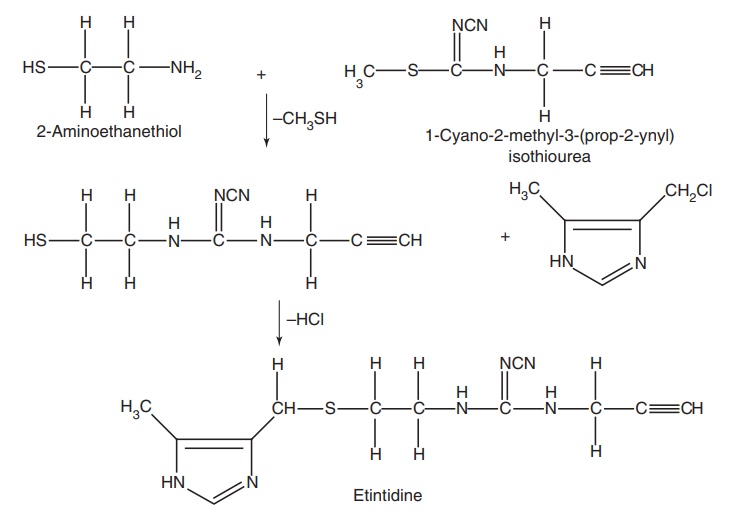
Uses: Used as antiulcer and it is twice as active as cimetidine.
v. Oxmetidine
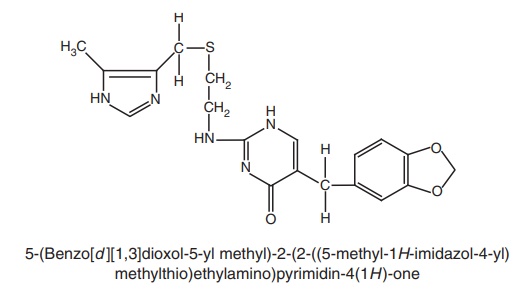
Synthesis
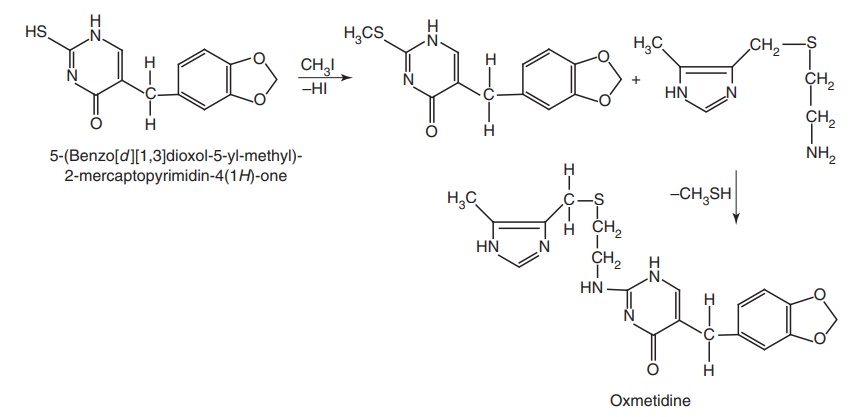
Properties and uses: It shows a time dependent and slow onset of
action, which differentiates it from ranitidine. It is reported to have
histamine H2-receptor blocking activity.
vi. Nizatidine
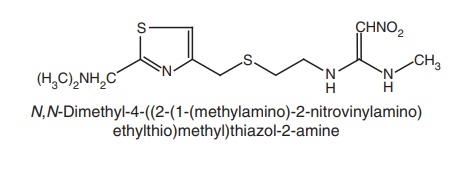
Synthesis
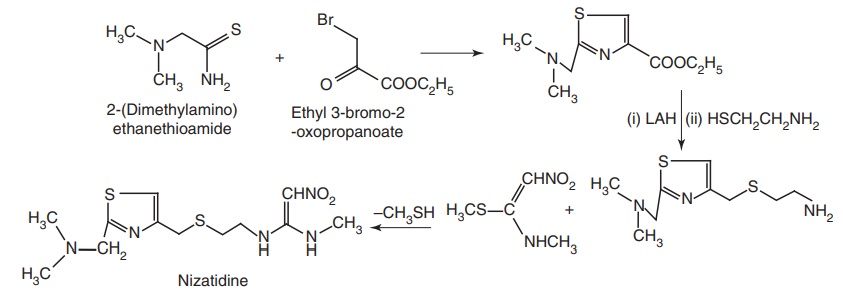
Properties and uses: Nizatidine is a white or slightly brownish
crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water, and soluble in methanol. It is
used as histamine H2-receptor antagonist in the treatment of peptic ulcer.
Assay: It is assayed by adopting liquid chromatography techniques.
Dosage forms: Nizatidine intravenous infusion B.P.
vii. Roxatidine (Rotane, Zorpex)
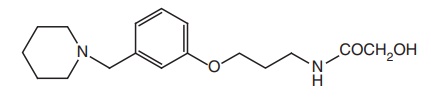
Synthesis
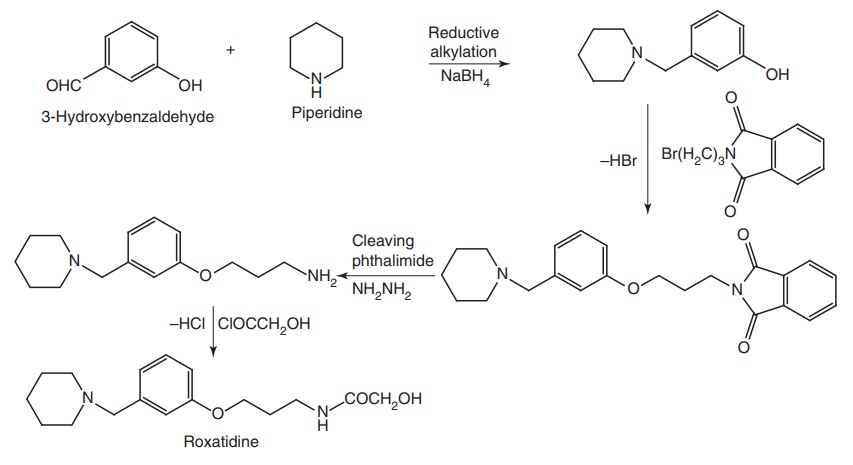
Dose and uses: Oral dose for peptic ulcer for adults is 150 mg
at bedtime or 75 mg twice a day for 4–6 weeks; maintenance dose is 75 mg at
bedtime. Dose for gastroesophageal reflux disease/oesophagitis, including
erosions and ulcerations for adults is 75 mg twice a day or 150 mg at bedtime
for 6–8 weeks. The dose for gastritis for adults is 75 mg once daily in the
evening. For Zollinger–Ellison syndrome, the dose for adult is 75 mg twice a
day. In anaesthetic premedication for adults, the dose is 75 mg in the evening
on the day before surgery and repeated every 2 h before induction of
anaesthesia, alternatively, 150 mg once on the night before surgery.
Related Topics
