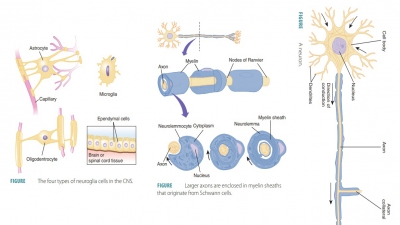
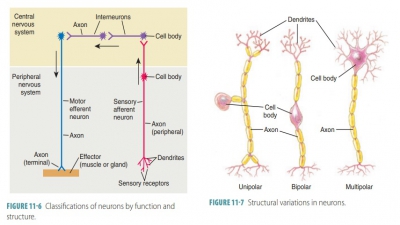
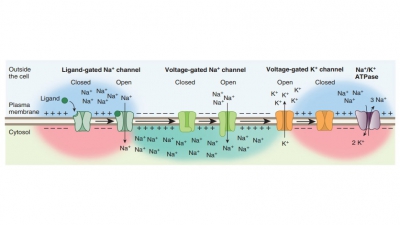
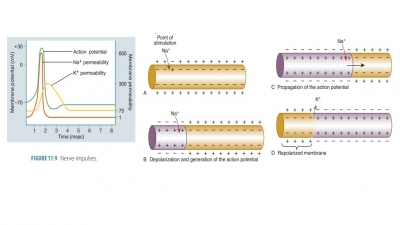
Processing of Impulses
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Control and Coordination: Neural Tissue
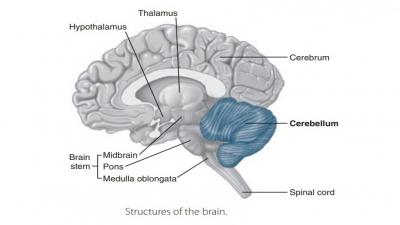
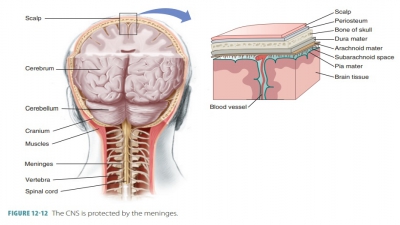
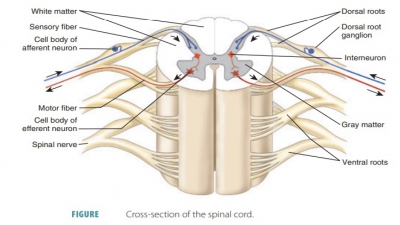
Neurons and axons within the brain and spinal cord affect impulse processing. If the net effect of an input is excitatory, a threshold may be reached, triggering an outgoing impulse.
Processing of
Impulses
Neurons and axons within the
brain and spinal cord affect impulse processing. If the net effect of an input
is excitatory, a threshold may be reached, triggering an outgoing impulse. If
the net effect is subthreshold (but still excitatory), an impulse is not
triggered but the neuron is more excitable to incoming stimulation than
previously. This state is called facilitation.
A neuron is described as facilitated
when its transmembrane poten-tial shifts closer to threshold. Presynaptic facilitation involves
activity at an axoaxonic synapse that increases the amount of neurotransmitter
that is released when an action potential arrives at the synaptic terminal. The
neurotransmitter serotonin is
involved in this type of facilitation. In one form of presynaptic inhibition, when GABA is released, it inhibits opening
of voltage-gated calcium channels in the synaptic terminal. This reduces how
much neurotransmitter is released when an action potential arrives, reducing
the effects of synaptic activity on the postsynaptic membrane.