Summary
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Control and Coordination: Neural Tissue
Nervous tissue includes neurons and neuroglial cells.
Summary
Nervous tissue includes neurons
and neuroglial cells. The nervous system is divided into the CNS and PNS. Sensory
functions receive stimulation from receptors concerning internal and external
changes. Sensory information is used to carry out motor functions, which in
turn stimulate effectors to respond. Neurog-lial cells include microglial
cells, astrocytes, oligoden-drocytes, and ependymal cells. Astrocytes are the
most abundant glial cells and are very important for main-taining the integrity
of the CNS. Oligodendrocytes provide insulation around CNS axons. In the PNS,
Schwann cells form myelin sheaths. A neuron con-sists of a cell body,
dendrites, and an axon. Dendrites and cell bodies provide receptive surfaces. A
single axon arises from the cell body and may be enclosed in a neurolemma and
myelin sheath. Axons may have occasional branches known as axon collaterals,
which usually extend in right angles. An axon with a myelin sheath is called
myelinated.
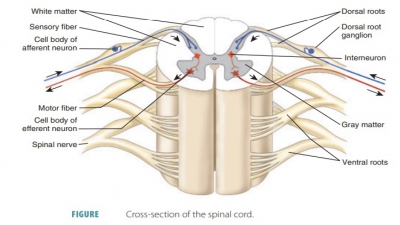
In the CNS, dense groups of
myelinated axons form the white matter. Those that are unmyelinated along with
neuron cell bodies form the gray matter. Nerve fibers are classified by their
diameter, degree of myelination, and speed of conduction and are divided into
group A, group B, and group C fibers. Functional classifications of neurons
include sensory (afferent) neurons, interneurons, and motor (effer-ent neurons).
Structural classifications of neurons include multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar
neurons. The surface of a cell membrane is usually electrically charged
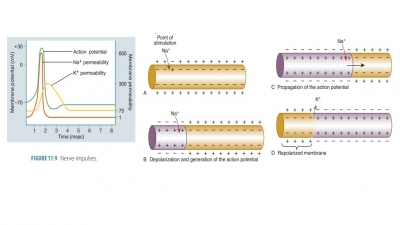
(polarized) compared with its inner contents. An action potential is a change
in neuron membrane polarization and a return to its resting state. It is an
all-or- none phenomenon, occurring completely or not at all. The absolute
refractory period is the time between sodium channels opening until they begin
to reset to their resting state.
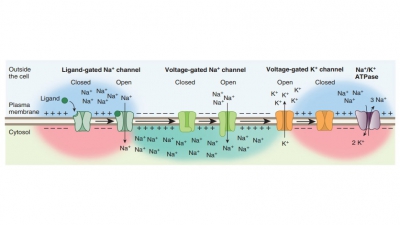
Distribution of ions is
determined in part by selective channels located in cell membranes. The
difference in charges between the outside of the cell membrane and the inside
of it in a resting cell is known as a resting potential. The cytosol of cells
contains less sodium ions but more potassium ions compared with the
extracellular fluid. Potassium ions diffuse out of cells very easily in
comparison with how easily sodium ions can enter. Nerve cells respond with
excit-ability to changes in surroundings. Depolarization opens sodium channels
and then inactivates them. In repolarization, sodium channels are inactivating,
with potassium channels open. In hyperpolarization, some potassium ion channels
remain open, and sodium ion channels are reset.
In a nerve cell membrane, an action
potential causes a local bioelectric current to reach other por-tions of the
membrane. A wave of action potentials is a nerve impulse. Impulses are
conducted over the entire surface of unmyelinated axons, but there is reduced
impulse conduction in myelinated axons because of the insulation provided by
the myelin. A synapse is a junction between two neurons. Presynaptic neurons
carry impulses into synapses and postsynaptic neu-rons respond. Chemical
synapses are more prevalent than electrical synapses, and are mostly comprised
of axon terminals and neurotransmitter receptor regions. Less common electrical
synapses consist of gap junctions. Synaptic fatigue occurs when demands for ACh
cannot keep pace with the availability of this neurotransmitter.
Axons have synaptic knobs, which
secrete neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters reaching the postsynaptic neuron
membrane are either excitatory or inhibitory. ACh is released at neuromuscular
junctions and is eventually degraded to acetic acid and choline via the enzyme
AchE. The way the nervous system processes and responds to nerve impulses is
based on the organization of neurons in the brain and spinal cord. The aging
process affects the entire nervous system in many different ways and usually
reduces function as a result of slower impulse processing abilities.