Solved Problems on Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation By Free-Radical Reactions
| Home | | Organic Chemistry |Chapter: Organic Chemistry : Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation By Free-Radical Reactions
Questions and Answers, Solved Problems on Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation By Free-Radical Reactions - Organic Chemistry
PROBLEMS
9.1. Give balanced
chemical equations for each mechanistic step for the fol-lowing
transformations:
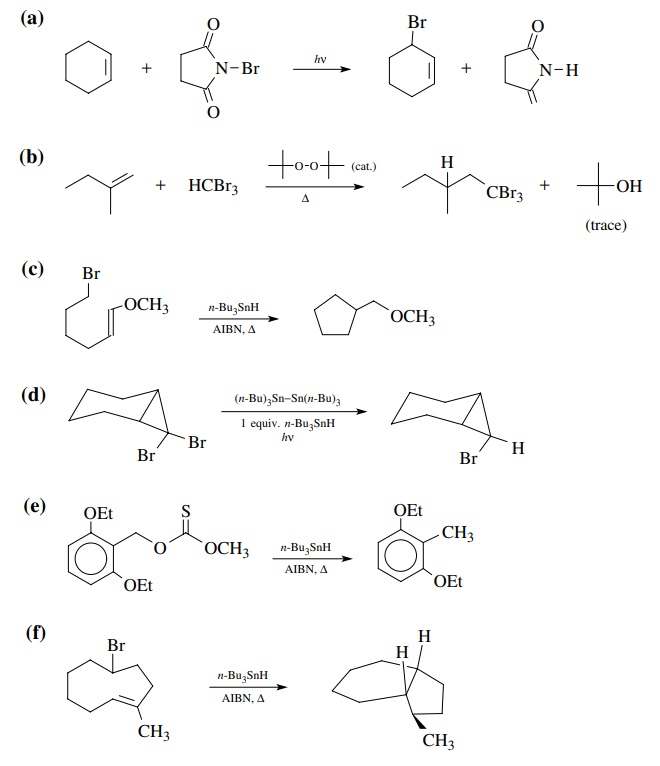
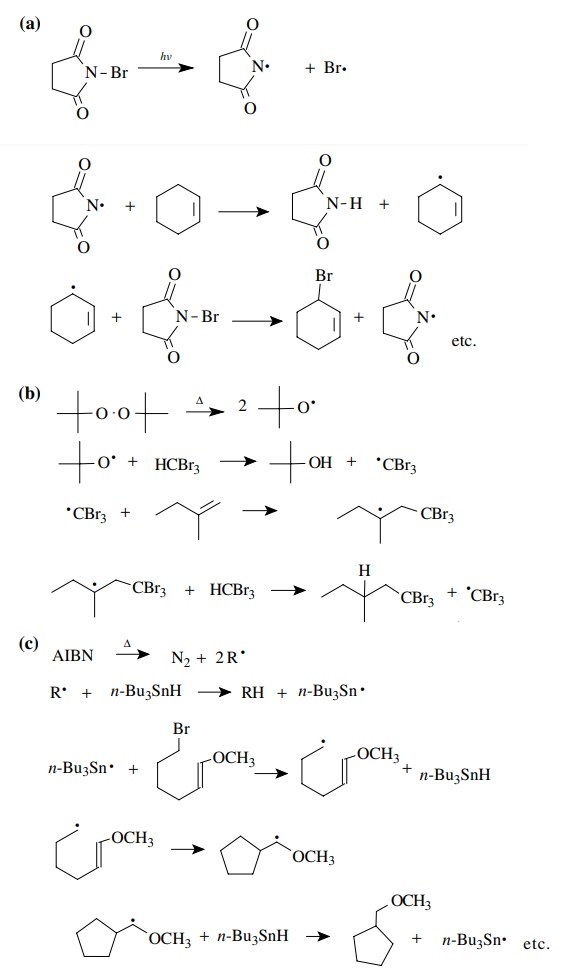
Answer:
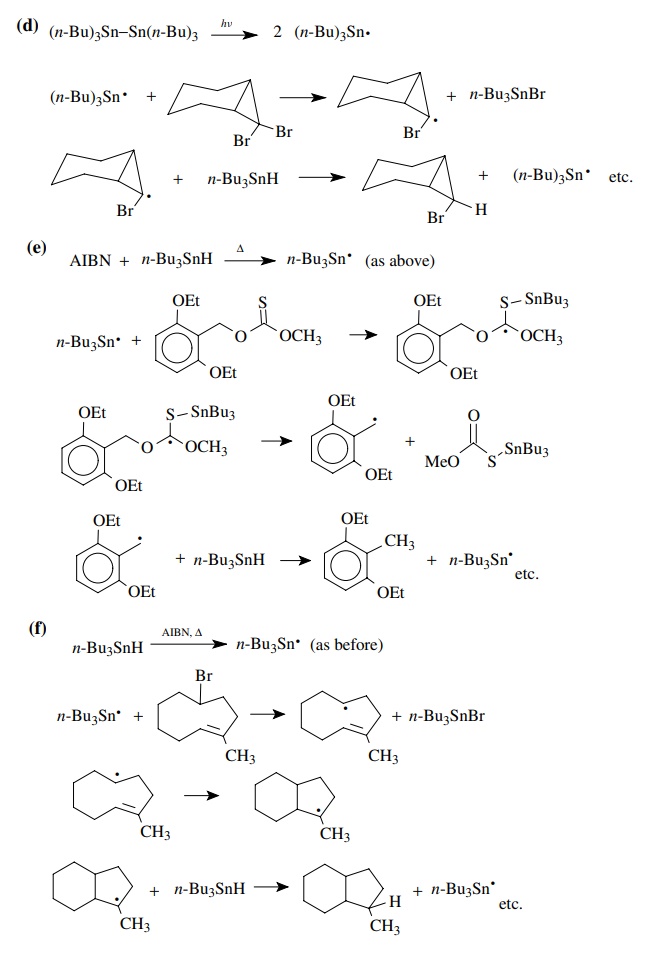
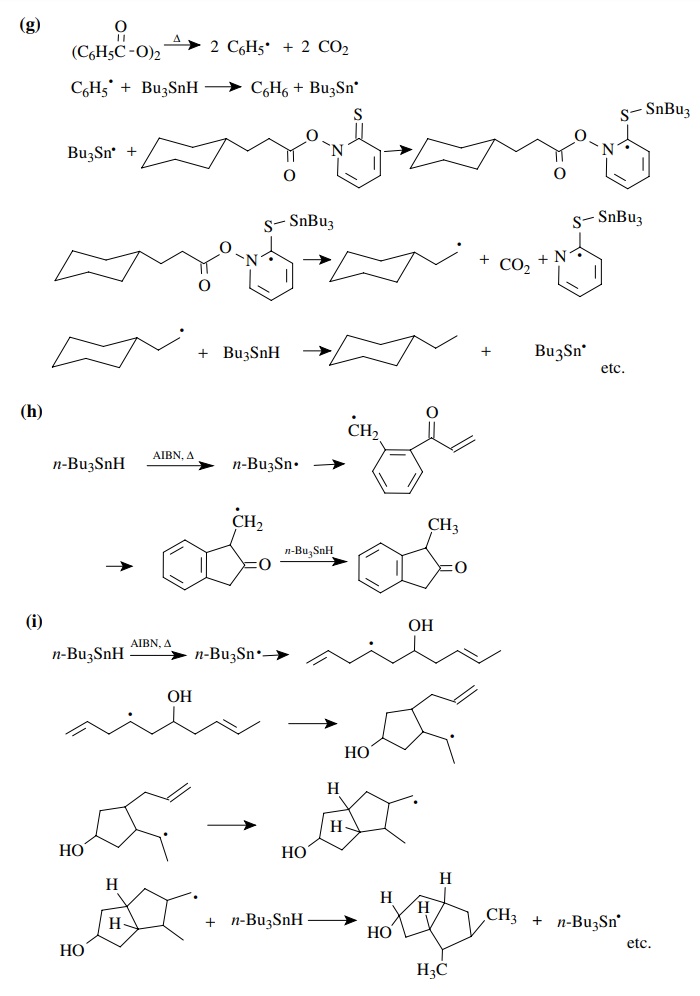
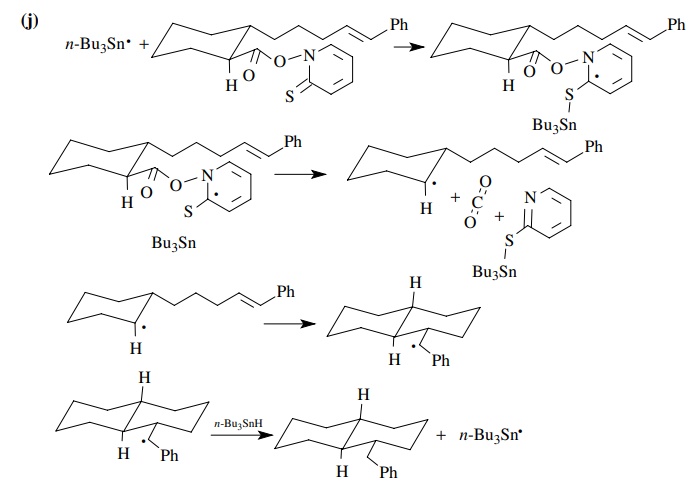
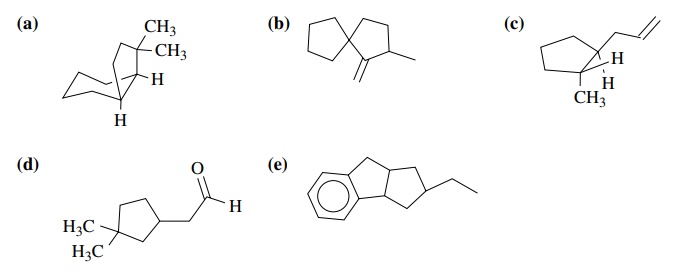
9.2. For each of the
following reactions, the structures of possible isomeric products are shown.
Predict which product will be favored and give the reasons for your prediction.
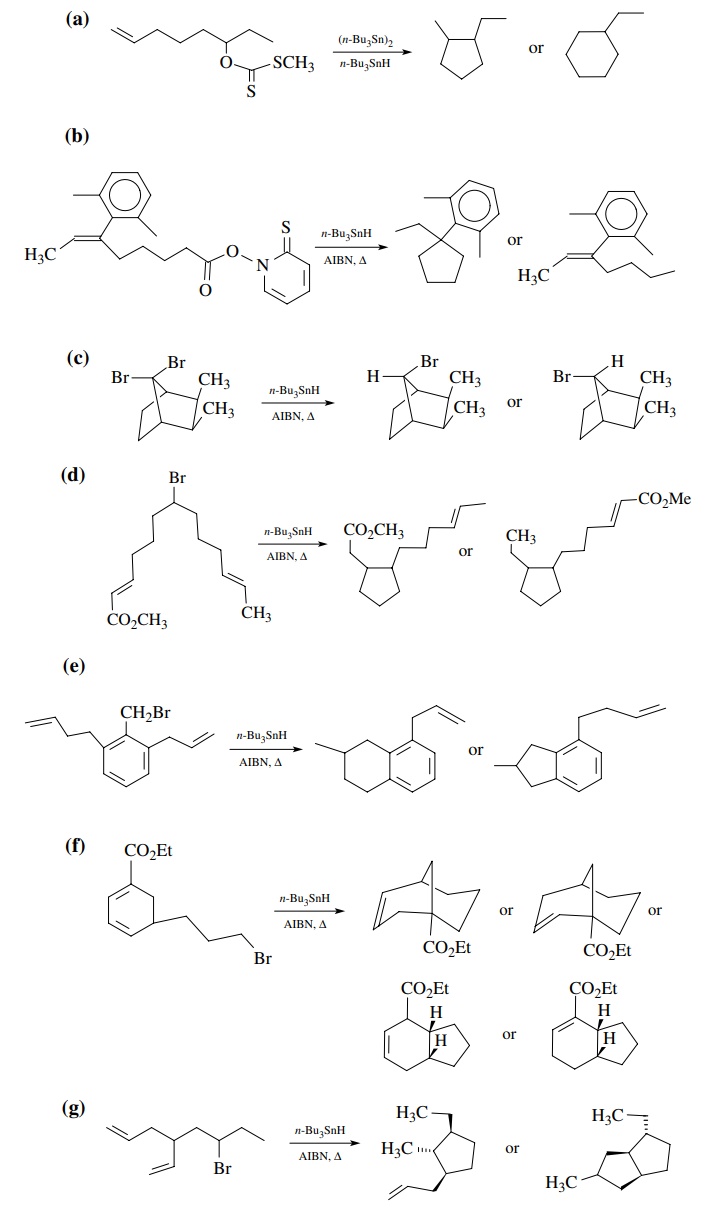
Answers:
(a)
exo-5-membered cyclization favored over endo-6.
(b)
Tough call, but hindered nature of the internal olefin position where
cyclization must occur should retard cyclization. Reduction prevails.
(c)
Approach to molecule by the tin radical and hydrogen donor takes place from the
least hindered side away from the methyl groups.
(d)
Cyclization occurs preferentially to the unsaturated ester because the product
radical is resonance stabilized.
(e)
Exo-5 cyclization is favored because it is faster than exo-6 cyclization
because the olefin is closer to the radical center.
(f)
Five-membered ring formation is faster than six and six-membered ring
for-mation will also be more sterically hindered due to the carboethoxy group.
The product radical is resonance delocalized so a mixture is probably formed.
However, the conjugated product would probably be favored slightly.
(g)
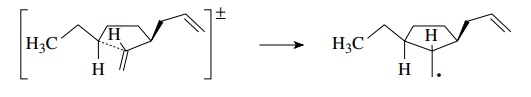
This transition state for ring closure minimizes steric interactions and is
favored. It leads to the trans, trans stereochemistry in the product radical.
The trans stere-ochemistry between the radical and the double bond prevents
further cyclization and reduction takes place to give the monocyclic product.
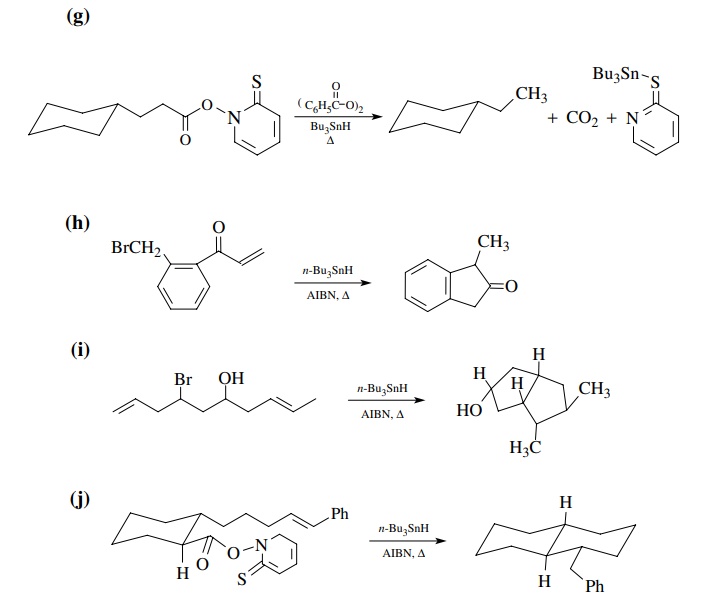
9.3. Give the products of the following reactions. Where more than one product is likely to be formed in significant yield, indicate which will be the major product.
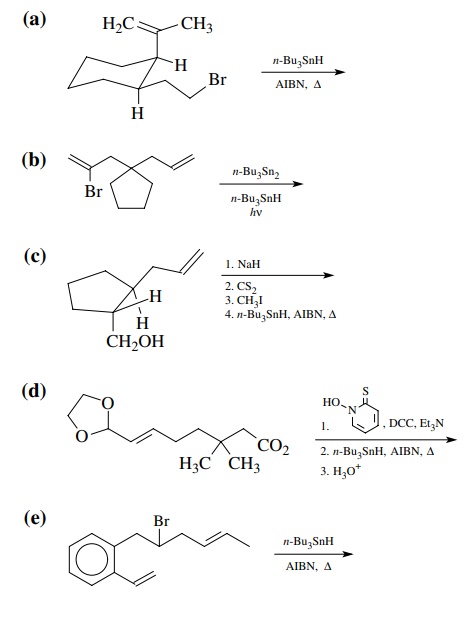
Answer: