Summary
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: The Heart
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and blood vessels.
Summary
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and blood
vessels. It provides oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing wastes. The
heart is located within the mediastinum, resting on the diaphragm. It is
enclosed in the pericardium, a double-walled sac. The pulmonary circuit
consists of vessels that carry blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and
back to the left atrium. The systemic circuit consists of vessels that lead
from the left ventricle to the body cells and back to the heart, includ-ing the
aorta and its branches. The aorta is the largest artery in the body, with
respect to diameter.
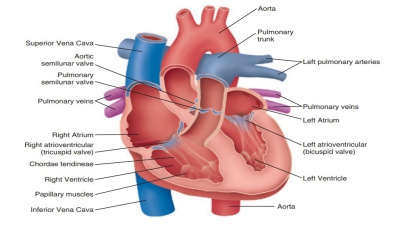
The wall of the heart has three layers: epicardium,
myocardium, and endocardium. The heart is divided into two atria and two
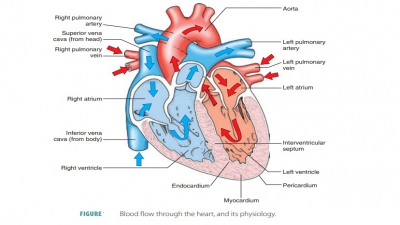
ventricles. Blood low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide enters the right
side of the heart and is pumped into the pulmonary circulation. After
oxygenation in the lungs and some removal of carbon dioxide, it returns to the
left side of the heart. The left ventricle pumps blood out of the heart to the
rest of the body.
The cardiac cycle consists of the atria contracting while
the ventricles relax, and vice versa. Electrical activity of the cardiac cycle
can be recorded via an ECG. The cardiac cycle consists of the P wave, QRS
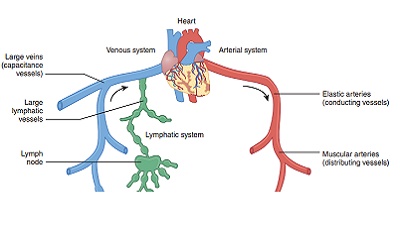
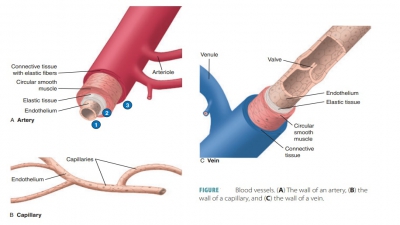
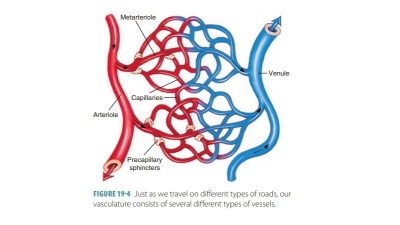
complex, and T wave. Blood vessels form a closed cir-cuit of tubes that carry
blood from the heart to the body cells and back again. Blood pressure is the
force that blood exerts against the insides of blood vessels. Though the
cardiovascular system is usually normal during gestation and childhood, there
is the possibil-ity of abnormalities and disorders to develop. Com-mon problems
with aging include atherosclerosis, valve thickening, stenosis, and fibrosis.
The cardiovas-cular system is seriously damaged by smoking, stress, inactivity,
and poor diet.