Chapter Summary, Questions Answers - Biotechnology and Human Disease
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Biotechnology and Human Disease
Restriction endonucleases are bacterial enzymes that cleave double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) into smaller fragments.
CHAPTER SUMMARY
Restriction
endonucleases are bacterial enzymes that cleave double-stranded DNA (dsDNA)
into smaller fragments. Each enzyme cleaves at a specific four to eight–base
pair sequence (a restriction site), producing DNA segments called restriction
fragments. The sequences that are recognized are palindromic. Restriction
enzymes form either staggered cuts (sticky ends) or blunt-end cuts on the DNA.
Bacterial DNA ligases can join two DNA fragments from different sources if they
have been cut by the same restriction endonuclease. This hybrid combination of
two fragments is called a recombinant DNA molecule. Introduction of a foreign
DNA molecule into a replicating cell permits the amplification (production of
many copies) of the DNA, a process called cloning. A vector is a molecule of
DNA to which the fragment of DNA to be cloned is joined. Vectors must be
capable of autonomous replication within the host cell, must contain at least
one specific nucleotide sequence recognized by a restriction endonuclease, and
must carry at least one gene that confers the ability to select for the vector
such as an antibiotic resistance gene. Prokaryotic organisms normally contain
small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids that can serve
as vectors. They can be readily isolated from the bacterium (or artificially
constructed); joined with the DNA of interest; and reintroduced into the
bacterium, which will replicate, thus making multiple copies of the hybrid
plasmid. A DNA library is a collection of cloned restriction fragments of the
DNA of an organism. A genomic library is a collection of fragments of dsDNA
obtained by digestion of the total DNA of the organism with a restriction
endonuclease and subsequent ligation to an appropriate vector. It ideally
contains a copy of every DNA nucleotide sequence in the genome. In contrast,
complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries contain only those DNA sequences that are
complementary to messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules present in a cell and differ
from one cell type to another. Because cDNA has no intervening sequences, it
can be cloned into an expression vector for the synthesis of human proteins by
bacteria or eukaryotes. Cloned, then purified, fragments of DNA can be
sequenced, for example, using the Sanger dideoxy method. A probe is a small
piece of RNA or single-stranded DNA (usually labeled with a radioisotope, such
as 32P, or another recognizable compound, such as biotin or a fluorescent dye)
that has a nucleotide sequence complementary to the DNA molecule of interest
(target DNA). Probes can be used to identify which clone of a library or which
band on a gel contains the target DNA. Southern blotting is a technique that
can be used to detect specific sequences present in DNA. The DNA is cleaved
using a restriction endonuclease, and the pieces are separated by gel
electrophoresis and are denatured and transferred (blotted) to a nitrocellulose
membrane for analysis. The fragment of interest is detected using a probe. The
human genome contains many thousands of polymorphisms (DNA sequence variations
at a given locus). Polymorphisms can arise from single-base changes and from
tandem repeats. A polymorphism can serve as a genetic marker that can be
followed through families. A restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is
a genetic variant that can be observed by cleaving the DNA into restriction
fragments using a restriction enzyme. A base substitution in one or more
nucleotides at a restriction site can render the site unrecognizable by a
particular restriction endonuclease. A new restriction site also can be created
by the same mechanism. In either case, cleavage with the endonuclease results
in fragments of lengths differing from the normal that can be detected by DNA
hybridization. This technique can be used to diagnose genetic diseases early in
the gestation of a fetus. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), another method
for amplifying a selected DNA sequence, does not rely on the biologic cloning
method. PCR permits the synthesis of millions of copies of a specific
nucleotide sequence in a few hours. It can amplify the sequence, even when the
targeted sequence makes up less than one part in a million of the total initial
sample. The method can be used to amplify DNA sequences from any source.
Applications of the PCR technique include: 1) efficient comparison of a normal
gene with a mutant form of the gene, 2) detection of low-abundance nucleic acid
sequences, 3) forensic analysis of DNA samples, and 4) prenatal diagnosis and
carrier detection (for example, of cystic fibrosis). The products of gene
expression (mRNA and proteins) can be measured by techniques such as the
following: Northern blots are very similar to Southern blots except that the
original sample contains a mixture of mRNA molecules that are separated by
electrophoresis, then hybridized to a radiolabeled probe; microarrays are used
to determine the differing patterns of gene expression in two different types
of cells (for example, normal and cancer cells); enzyme-linked immunosorbent
assays a n d Western blots (immunoblots) are used to detect specific proteins.
Proteomics is the study of all the proteins expressed by a genome. The goal of
gene therapy is the insertion of a normal cloned gene to replace a defective
gene in a somatic cell. Insertion of a foreign gene into the germline of an
animal creates a transgenic animal that can produce therapeutic proteins or
serve as a model for human diseases.
Study Questions
Choose the ONE best answer.
33.1 HindIII is a restriction endonuclease. Which
of the following is most likely to be the recognition sequence for this enzyme?
A. AAGAAG
B. AAGAGA
C. AAGCTT
D. AAGGAA
E. AAGTTC
Correct answer = C. The vast majority of restriction
endonucleases recognize palindromes in double-stranded DNA, and AAGCTT is the
only palindrome among the choices. Because the sequence of only one DNA strand
is given, the base sequence of the complementary strand must be determined. To
be a palindrome, both strands must have the same sequence when read in the 5I
→3I direction. Thus, the complement of 5I -AAGCTT-3 I is also 5I -AAGCTT-3 I.
33.2 An Ashkenazi Jewish couple brings their
6-month-old son to you for evaluation of listlessness, poor head control, and a
fixed gaze. You determine that he has Tay-Sachs disease, an autosomal recessive
disorder. The couple also has a daughter. The family’s pedigree is shown to the
right, along with Southern blots of a restriction fragment length polymorphism
very closely linked to the gene for hexosaminidase A, which is defective in
Tay-Sachs. Which of the statements below is most accurate with respect to the
daughter?
A. She has a 25% chance
of having Tay-Sachs disease.
B. She has a 50% chance
of having Tay-Sachs disease.
C. She has Tay-Sachs
disease.
D. She is a carrier for
Tay-Sachs disease.
E. She is homozygous normal.
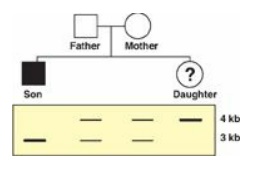
Correct answer = E. Because they have an affected son,
both the biological father and mother must be carriers for this disease. The
affected son must have inherited a mutant allele from each parent. Because he
shows only the 3-kilobase (kb) band on the Southern blot, the mutant allele for
this disease must be linked to the 3-kb band. The normal allele must be linked
to the 4-kb band, and, because the daughter inherited only the 4-kb band, she
must be homozygous normal for the hexosaminidase A gene.
33.3 A physician would like to determine the global
patterns of gene expression in two different types of tumor cells in order to
develop the most appropriate form of chemotherapy for each patient. Which of
the following techniques would be most appropriate for this purpose?
A. Enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay
B. Microarray
C. Northern blot
D. Southern blot
E. Western blot
Correct answer = B. Microarray analysis allows the
determination of messenger RNA (mRNA) production (gene expression) from
thousands of genes at once. A Northern blot only measures mRNA production from
one gene at a time. Western blots and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay measure
protein production (also gene expression) but only from one gene at a time.
Southern blots are used to analyze DNA, not DNA expression.
33.4 A 2-week-old infant is diagnosed with a urea
cycle defect. Enzymic analysis showed no activity for ornithine
transcarbamoylase (OTC), an enzyme of the cycle. Molecular analysis revealed
that the messenger RNA (mRNA) product of the gene for OTC was identical to that
of a control. Which of the techniques listed below was most likely used to
analyze mRNA?
A. Dideoxy chain
termination
B. Northern blot
C. Polymerase chain
reaction
D. Southern blot
E. Western blot
Correct answer = B. Northern blot allows analysis of
the messenger RNA present (expressed) in a particular cell or tissue. Southern
blot is used for DNA analysis, whereas Western blot is used for protein
analysis. Dideoxy chain termination is used to sequence DNA. Polymerase chain
reaction is used to generate multiple, identical copies of a DNA sequence in
vitro.
33.5 For the patient above, which phase of the
central dogma was most likely affected?
Correct answer = Translation. The gene is present and is able to
be expressed as evidenced by messenger RNA production. The lack of enzymic
activity means that some aspect of protein synthesis is affected.
Related Topics
