Effects of Aging on the Lymphatic System and Immunity
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Lymphatic System and Immunity
Stem cells used in immunity originate in the liver and spleen during the first nine weeks of embryonic development.
Effects
of Aging on the Lymphatic System and Immunity
Stem cells used in immunity originate in the liver and
spleen during the first nine weeks of embryonic development. Later, the bone
marrow becomes the main source of stem cells, which it continues to supply into
adulthood. Lymphocyte precursors become immuno-competent in the thymus and bone
marrow, later pop-ulating other lymphoid tissues. A newborn’s immune system
relies mostly on antibodies and helper T lym-phocytes. As the body encounters
harmful and harm-less microbes, the helper T cells “learn” and become stronger.
When these encounters do not occur, the immune system is more likely to develop
allergies. Normal immune development can be interfered with by overuse of
antibiotics, which can kill of harmful as well as harmless bacteria.
Over time, the immune system can be impaired by the nervous
system. Factors such as depression, emotional stress, and grief can all be
harmful to its function. Diet even plays a part. For example, vitamin D is
needed for CD8 cells to activate and become cytotoxic T cells. Deficiency of
vitamin D is linked to multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases.
The lymphatic system becomes less effective at fighting
disease as we age, resulting in lowered immu-nity. T cells weaken, and fewer of
them can respond to infections. As the thymus shrinks with age, there are lower
circulating levels of thymic hormones. The number of helper T cells is reduced,
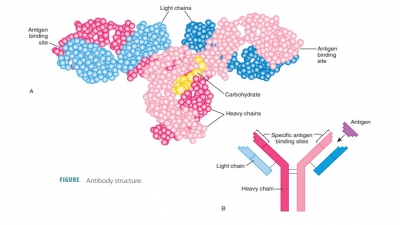
B cells are less responsive, and antibody levels do not rise after expo-sure to
antigens with the same speed they used to. Viral and bacterial infections are
able to proliferate more. This is why vaccinations for diseases such as
influenza and pneumococcal pneumonia are recommended for elderly patients. With
decreased immunity, tumor cells are not eliminated as effectively, and cancer
rates increase with age. In many older people, the immune system develops
chronic low-grade inflammation because of increased production of inflammatory
agents. Chronic inflammation may cause or promote many age-related diseases, including
Alzheimer’s dis-ease and atherosclerosis.