Respiratory System Functions
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Respiratory System
Respiration is the process of gas exchange between the atmosphere and cells.
Respiratory
System Functions
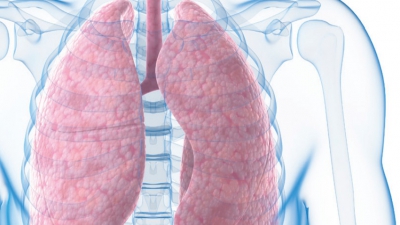
The functions of the respiratory system include the intake of oxygen and
the removal of CO2. Cells need oxygen to break down nutrients to
release energy and produce adenosine triphosphate. CO2 results from
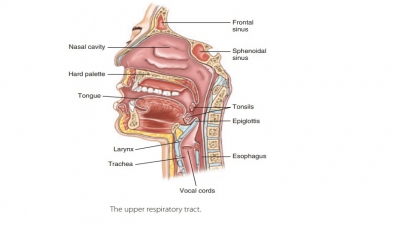
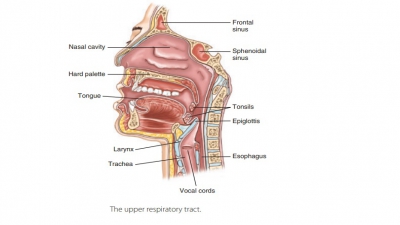
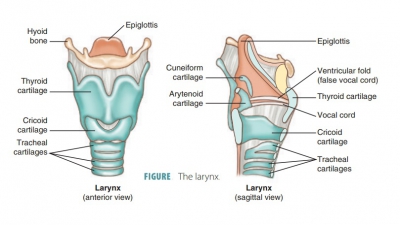
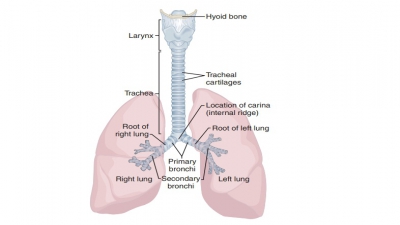
this process and it must be excreted. The respiratory system includes tubes
that filter incoming air while transporting it into and out of the lungs. Gases
are exchanged in microscopic air sacs. Respiratory organs entrap incoming air
particles, control temperature and water (H2O) content in the air,
produce vocal sounds, regulate blood pH, and are essential for the sense of
smell.
Respiration
is the process of gas exchange between the atmosphere and cells.
Four major events are involved in respiration, with the first two handled by
the respiratory system and the last two handled by the cardiovascular or
circulatory system:
■■ Movement of air into and out of the lungs
called pulmonary ventilation or breathing, involving inward movement or
inspiration and outward movement or expiration, in which gases are changed and
refreshed continuously.
■■ Gas exchange between air in the lungs and the
blood or external respiration; oxygen diffuses from the lungs to the blood,
whereas CO2 diffuses from the blood to the lungs.
■■ Gas transport in blood between the lungs and
body cells, accomplished by the cardiovascular system, using blood as the
transporting fluid; oxygen is transported from the lungs to the body’s tissue
cells, whereas CO2 is transported from the tissue cells to the lungs.
■■ Gas exchange between the blood and the cells
or internal respiration; oxygen diffuses from the blood to the body’s tissue
cells, whereas CO2 dif-fuses from the tissue cells to the blood.
All four processes must occur for the
respiratory system to obtain oxygen and eliminate CO 2. Both sys-tems are
closely linked, and if either fails, the cells of the body die from lack of
oxygen. The process of using oxygen and CO2 at the cellular level is called
cellular respiration. It is the basis of all chemical reactions in the body
that produce energy. Cellular respiration is a circulatory function, not a respiratory
function.
Related Topics