Pharynx
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Respiratory System
1. Which part of the nose is the nasal vestibule? 2. Where are posterior nasal apertures located? 3. Which part of the pharynx houses the pharyngeal tonsil?
Organization of the Respiratory System
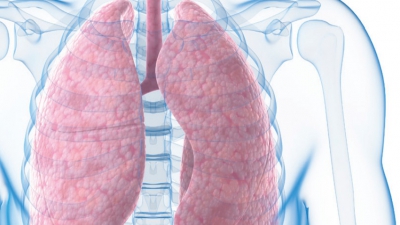
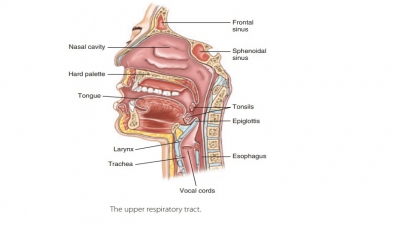
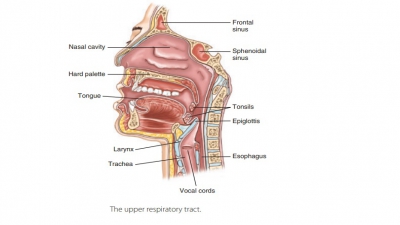
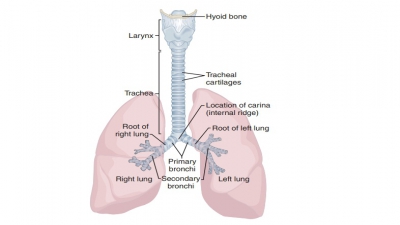
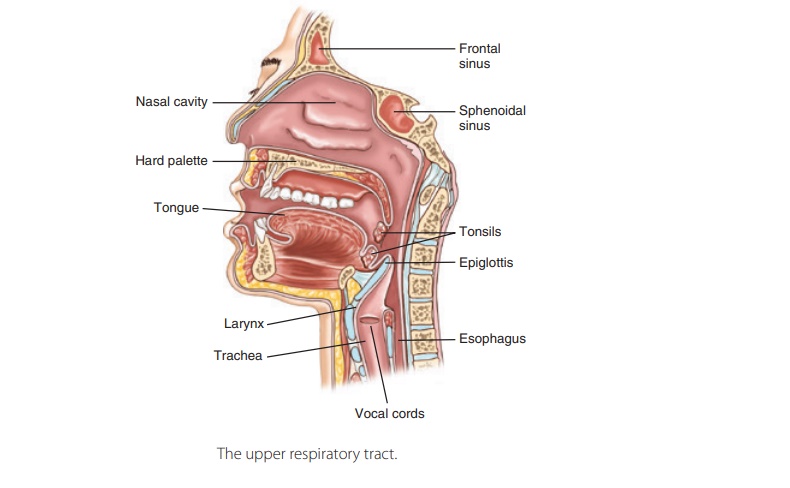
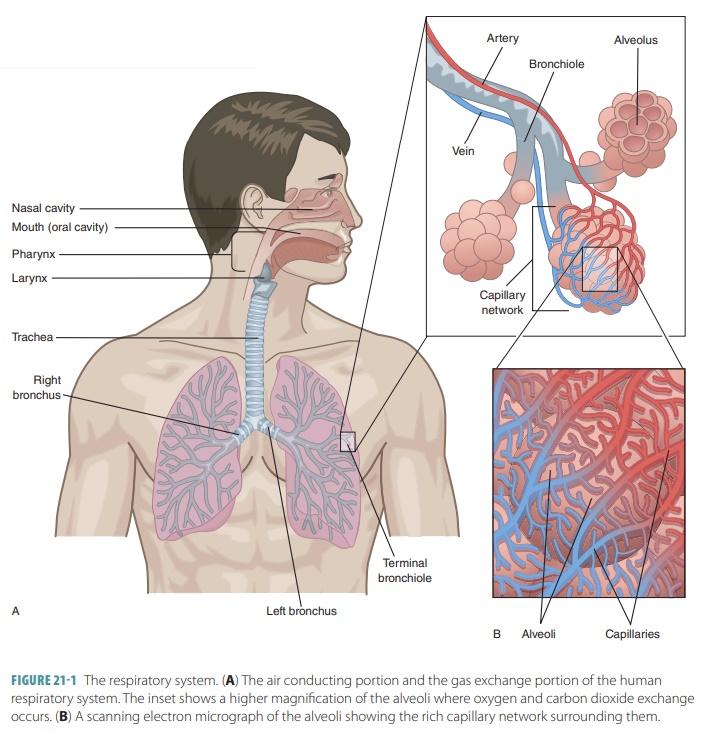
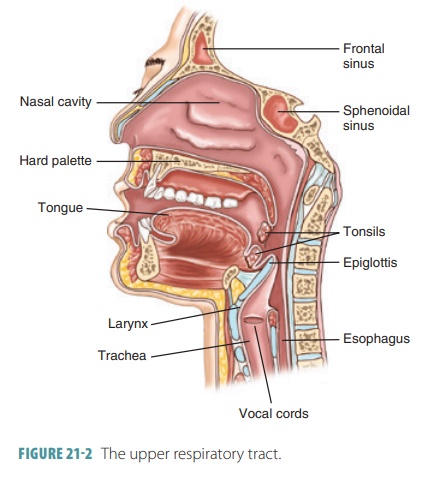
The upper respiratory tract includes the nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and pharynx. The lowerrespiratory tract includes the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The lungs contain the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. FIGURE 21-1 shows the structures of the respiratory system.
Pharynx
The funnel-shaped pharynx, commonly called the throat, is behind the oral cavity and
connects the nasal cavity to the larynx. The pharynx extends for about 13 cm or
5 inches from the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical
vertebra. Food travels from the oral cavity through the pharynx to the
esophagus. Also, air passes through the nasal cavity through the pharynx into
the larynx. The pharynx helps to pro-duce the sounds of speech (Figure 21-2).
Nasopharynx
Posterior to the nasal cavity is the nasopharynx, which also lies inferior to the
sphenoid bone but superior to the soft palate’s level. The nasopharynx is a
passageway for air only, because it is located above the mouth. It is
continuous with the nasal cavity via the posterior nasal apertures and is lined
with pseudostratified cil-iated epithelium, which assists the efforts of the
nasal mucosa to transport mucus. The pharyngeal tonsil, also called the adenoids, is located very high up on the
posterior wall of the nasopharynx. This tonsil traps pathogens from the
incoming air and destroys them.
Oropharynx
The oropharynx is
continuous with the oral cavity via an archway known as the isthmus of the fauces. The oropharynx
lies posterior to the oral cavity. Both air and food pass through the
oropharynx because it extends inferiorly from the level of the soft palate to
the epiglottis. The oropharynx contains two palatinetonsils as well as the lingual tonsil.
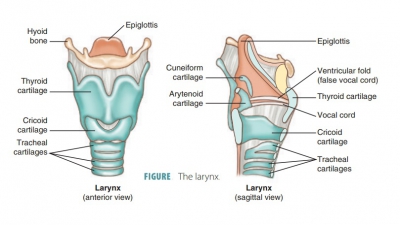
Laryngopharynx
The laryngopharynx also
allows air and food to pass and is also lined with a stratified squamous
epithelium and lies directly posterior to the epiglottis. The laryn-gopharynx
extends to the larynx, at which point respi-ratory and digestive paths
separate. The esophagus is the tube-like structure that allows food and fluids
to pass to the stomach. Air enters the larynx anteriorly. When we swallow,
passage of air temporarily stops so food can pass.
1. Which part of the nose is the nasal vestibule?
2. Where are posterior nasal apertures located?
3. Which part of the pharynx houses the pharyngeal tonsil?