Functions of Bones
| Home | | Anatomy and Physiology | | Anatomy and Physiology Health Education (APHE) |Chapter: Anatomy and Physiology for Health Professionals: Support and Movement: Bone Tissues and the Skeletal System
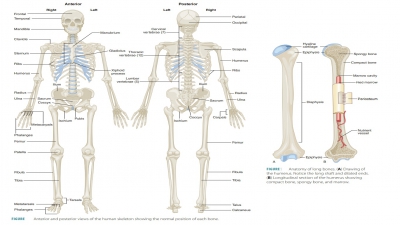
Bone is a connective tissue that performs several basic functions: hemopoiesis, movement, support and protection, and storage of minerals and lipids.
Functions of
Bones
Bone is a connective
tissue that performs several basic functions: hemopoiesis, movement, support
and protection, and storage of minerals and lipids.
■■ Hemopoiesis: This
is the process in which blood cell production begins in the yolk sac of the
developing embryo, which is also referred to as hematopoiesis. Later, this
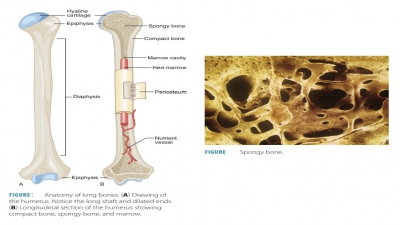
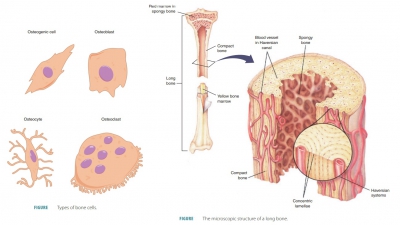
process occurs in the red bone marrow, which contains stem cells that form all
blood cell types. Its color is derived from hemoglobin, which is the
oxygen-carrying pigment of the red blood cells. The locations of red bone
marrow differ between children and adults. In children, red bone marrow is in
the spongy bone inside most of the bones of the body. As children mature into
adults, much of the red bone marrow degenerates into a fatty tissue called
yellow bone marrow. As a result, adults have red bone marrow only in certain
portions of the axial skeleton such as the flat bones of the skull, the
vertebrae, the sternum, the ribs, and the hip bones. Adults also have red bone
marrow in the proximal epiphyses of the femur and humerus.
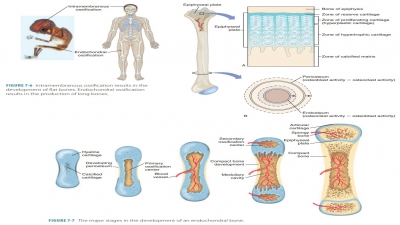
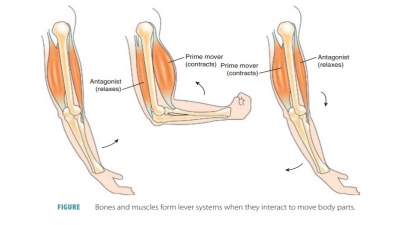
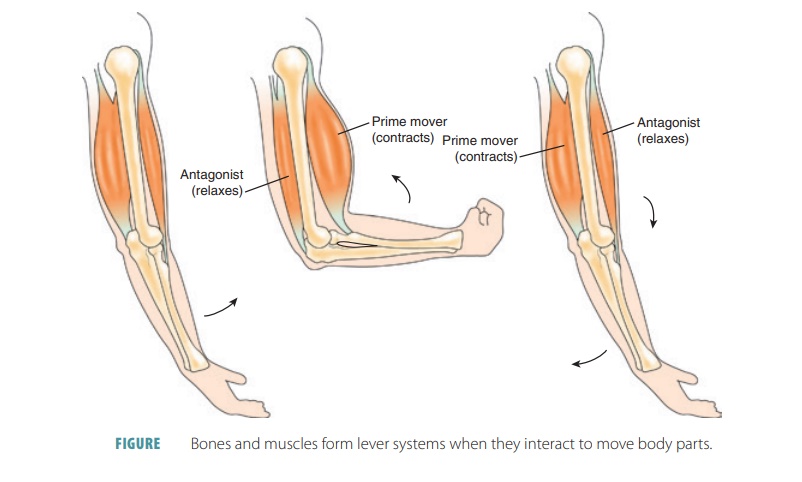
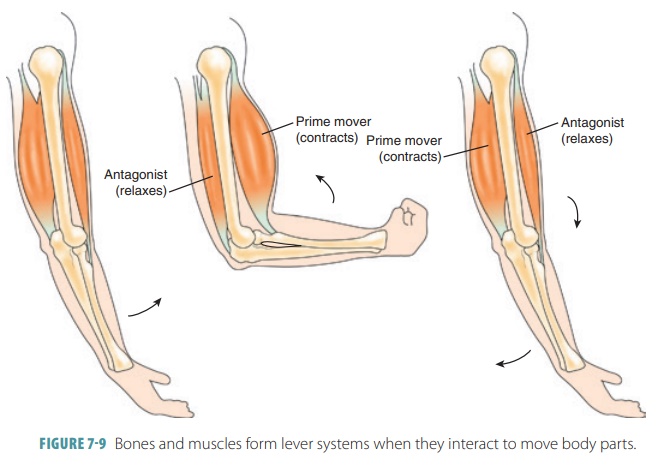
■■ Movement: The bones assist in body movement by providing attachments for skeletal muscles that pull on the bones, causing the bones to act as levers (FIGURE 7-9). For example, when the arm is bent and then straightened at the elbow, the bones and muscles are functioning together in a lever like way. When the arm bends, the hand is moved against resistance provided by the weight of the arm, and the muscles on the anterior side of the arm (including the biceps brachii) supply force. When the arm is straightened, the triceps brachii muscle on the posterior side of the arm supplies the force. The types of movements that are possible depend on the type of joints involved.
■■ Support and
protection: The bones support and protect vital organs of the body such as the
brain, spinal cord, lungs, and heart. They also protect other soft tissues of
the body. The bones of the lower limbs support the trunk of the body during
standing, whereas the rib cage supports the thoracic wall.
■■ Storage of
minerals and growth factor: The bones store more than 90% of the
minerals—calcium and phosphorus—which are essential for many body processes.
When these minerals are needed, some connective bone tissue is broken down, so
they can be released into the bloodstream. Phosphorus is important for the
creation of organic phosphate, which provides adenosine triphosphate. Important
growth factors are stored in the mineralized bone matrix.
■■ Fat storage: In
fat, triglyceride is an energy source stored in bone cavities.
■■ Hormone
production: The hormone osteocalcin is produced by bones. It helps to regulate
bone formation and also protects against glucose intolerance, diabetes
mellitus, and obesity.
1. What is
the function of red bone marrow?
2. What
chemical substances are stored in the bones?
Related Topics