Overview of Nucleotide Metabolism
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Nucleotide Metabolism
Ribonucleoside and deoxyribonucleoside phosphates (nucleotides) are essential for all cells. Without them, neither ribonucleic acid (RNA) nor deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) can be produced, and, therefore, proteins cannot be synthesized or cells proliferate.
Nucleotide Metabolism
OVERVIEW
Ribonucleoside and
deoxyribonucleoside phosphates (nucleotides) are essential for all cells.
Without them, neither ribonucleic acid (RNA) nor deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
can be produced, and, therefore, proteins cannot be synthesized or cells
proliferate. Nucleotides also serve as carriers of activated intermediates in
the synthesis of some carbohydrates, lipids, and conjugated proteins (for
example, uridine diphosphate [UDP]-glucose and cytidine diphosphate
[CDP]-choline) and are structural components of several essential coenzymes,
such as coenzyme A, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD[H2]),
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD[H]), and nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide phosphate (NADP[H]). Nucleotides, such as cyclic adenosine
monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), serve as second
messengers in signal transduction pathways. In addition, nucleotides play an
important role as “energy currency” in the cell. Finally, nucleotides are important
regulatory compounds for many of the pathways of intermediary metabolism,
inhibiting or activating key enzymes. The purine and pyrimidine bases found in
nucleotides can be synthesized de novo or can be obtained through salvage
pathways that allow the reuse of the preformed bases resulting from normal cell
turnover. [Note: Little of the purines and pyrimidines supplied by diet are
utilized and are degraded instead.]
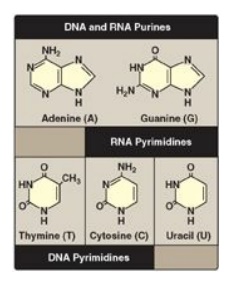
Figure 22.1 Purines and
pyrimidines commonly found in DNA and RNA.
Related Topics
