Chapter Summary, Questions Answers - Amino Acid Degradation and Synthesis
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Amino Acid Degradation and Synthesis
Amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the tricarboxylic acid cycle are termed glucogenic.
CHAPTER SUMMARY
Amino acids whose
catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the tricarboxylic
acid cycle are termed glucogenic (Figure 20.23). They can give rise to the net
formation of glucose in the liver and the kidney. The solely glucogenic amino
acids are glutamine, glutamate, proline, arginine, histidine, alanine, serine,
glycine, cysteine, methionine, valine, threonine, aspartate, and asparagine.
Amino acids whose catabolism yields either acetoacetate or one of its
precursors, acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) or acetoacetyl CoA, are termed ketogenic.
Leucine and lysine are solely ketogenic. Tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan,
and isoleucine are both ketogenic and glucogenic. Nonessential amino acids can
be synthesized from metabolic intermediates or from the carbon skeletons of
essential amino acids. Essential amino acids need to be obtained from the diet.
They include histidine, methionine, threonine, valine, isoleucine,
phenylalanine, tryptophan, leucine, and lysine. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is caused
by a deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), the enzyme that converts
phenylalanine to tyrosine. Hyperphenylalaninemia may also be caused by
deficiencies in the enzymes that synthesize or regenerate the coenzyme for PAH,
tetrahydrobiopterin. Untreated patients with PKU suffer from severe
intellectual disability, developmental delay, microcephaly, seizures and a
characteristic mousey smell of the urine. Treatment involves controlling
dietary phenylalanine. Tyrosine becomes an essential dietary component for
people with PKU. Maple syrup urine disease is caused by a partial or complete
deficiency in branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase, the enzyme that
decarboxylates leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Symptoms include feeding
problems, vomiting, ketoacidosis, changes in muscle tone, and a characteristic
sweet smell of the urine. If untreated, the disease leads to neurologic
problems that result in death. Treatment involves controlling dietary leucine,
isoleucine, and valine. Other important genetic diseases associated with amino
acid metabolism include albinism, homocystinuria, methylmalonyl CoA mutase
deficiency, alkaptonuria, histidinemia, tyrosinemia, and cystathioninuria.
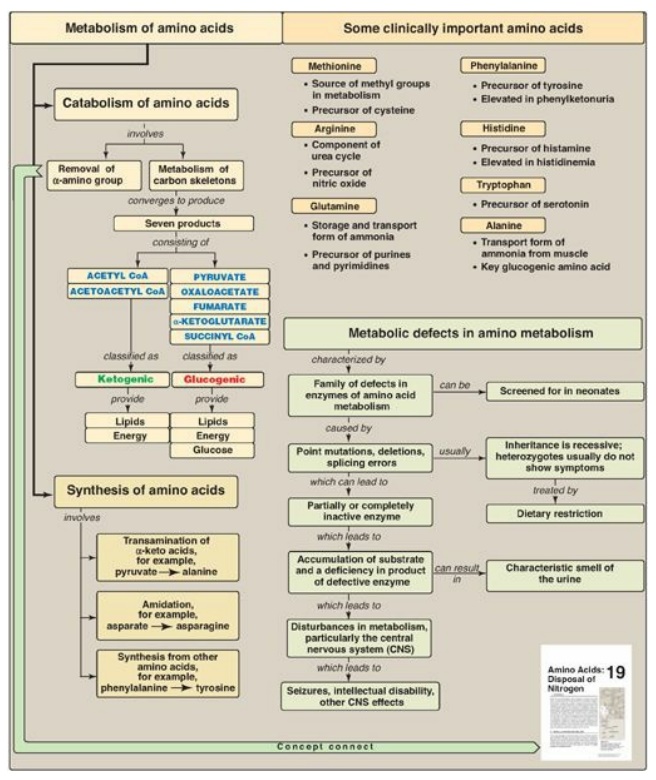
Figure 20.23 Key concept map
for amino acid metabolism. CoA = coenzyme A.
Study Questions:
Choose the ONE best answer.
For Questions 20.1–20.3, match the deficient enzyme
with the associated clinical sign or laboratory finding in urine.
A. Black pigmentation of cartilage
B. Cabbage-like odor of fluids
C. Cystine crystals in urine
D. White hair, red eye color
E. Increased branched-chain amino acids
F. Increased homocysteine
G. Increased methionine
H. Increased phenylalanine
20.1 Cystathionine β-synthase
20.2 Homogentisic acid oxidase
20.3 Tyrosinase
Correct answers = F, A, D. A deficiency in cystathionine
β-synthase of methionine degradation results in a rise in homocysteine. A
deficiency in homogentisic acid oxidase of tyrosine degradation results in a
rise in homogentisic acid, which forms a black pigment that is deposited in
connective tissue. A deficiency in tyrosinase results in decreased formation of
melanin from tyrosine in skin, hair, and eyes. A cabbage-like odor is characteristic
of isovaleryl coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. Cystine crystals in urine
are seen with cystinuria, a defect in intestinal and renal cystine absorption.
Increased branched-chain amino acids are seen in maple syrup urine disease,
increased methionine is seen in defects in homocysteine metabolism, and
increased phenylalanine is seen in phenylketonuria.
20.4 A 1-week-old infant, who was born at home in a
rural area, has undetected classic phenylketonuria. Which statement about this
baby and/or her treatment is correct?
A. A diet devoid of
phenylalanine should be initiated immediately.
B. Dietary treatment
will be recommended to be discontinued in adulthood.
C. Supplementation with
vitamin B6 is required.
D. Tyrosine is an essential amino acid.
Correct answer = D. In patients with phenylketonuria,
tyrosine cannot be synthesized from phenylalanine and, hence, becomes essential
and must be supplied in the diet. Phenylanine in the diet must be controlled
but cannot be eliminated entirely because it is an essential amino acid.
Dietary treatment must begin during the first 7–10 days of life to prevent
intellectual disability, and life-long restriction of phenylalanine is
recommended to prevent cognitive decline. Additionally, elevated levels of phenylalanine
are teratogenic to a developing fetus.
20.5 Which one of the following statements
concerning amino acids is correct?
A. Alanine is
ketogenic.
B. Amino acids that are
catabolized to acetyl coenzyme A are glucogenic.
C. Branched-chain amino
acids are catabolized primarily in liver.
D. Cysteine is essential for individuals consuming
a diet severely limited in methionine.
Correct answer = D. Methionine is the precursor of
cysteine, which becomes essential if methionine is severely restricted. Alanine
is the primary glucogenic amino acid. Acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) cannot be used
for the net synthesis of glucose. Amino acids catabolized to acetyl CoA are
ketogenic. Branched-chain amino acids are catabolized primarily in skeletal
muscle.
20.6 In an individual with the Enzyme 3–deficient
form of maple syrup urine disease, why would lactic acidosis be an expected
finding?
The three α-keto acid
dehydrogenase complexes (pyruvate dehydrogenase [PDH], α-ketoglutarate
dehydrogenase, and branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase [BCKD]) have a
common Enzyme 3 (E3) (dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase). In E3-deficient maple syrup
urine disease, in addition to the branched-chain amino acids and their α-keto
acid derivatives accumulating as a result of decreased activity of BCKD,
lactate will also be increased because of decreased activity of PDH.
20.7 In contrast to the vitamin B6-derived pyridoxal
phosphate required in most enzymic reactions involving amino acids, what
coenzyme is required by the aromatic amino acid hydroxylases?
Tetrahydrobiopterin, made from guanosine triphosphate, is the required coenzyme
Related Topics
