Folic acid and Amino acid Metabolism
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Amino Acid Degradation and Synthesis
Some synthetic pathways require the addition of single carbon groups that exist in a variety of oxidation states, including formyl, methenyl, methylene, and methyl.
FOLIC ACID AND AMINO ACID METABOLISM
Some synthetic pathways
require the addition of single carbon groups that exist in a variety of
oxidation states, including formyl, methenyl, methylene, and methyl. These
single carbon groups can be transferred from carrier compounds such as THF and
SAM to specific structures that are being synthesized or modified. The
“one-carbon pool” refers to the single carbon units attached to this group of
carriers. [Note: CO2, the dehydrated form of carbonic acid, is
carried by the vitamin biotin, which is a prosthetic group for most
carboxylation reactions but is not considered a member of the one-carbon pool.
Defects in the ability to add or remove biotin from carboxylases result in
multiple carboxylase deficiency. Treatment is supplementation with biotin.]
A. Folic acid and one-carbon metabolism
The active form of
folic acid, THF, is produced from folate by dihydrofolate reductase in a
two-step reaction requiring two nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphates
(NADPH). The one-carbon unit carried by THF is bound to nitrogen N5
or N10 or to both N5 and N10. Figure 20.11
shows the structures of the various members of the THF family and their
interconversions and indicates the sources of the one-carbon units and the
synthetic reactions in which the specific members participate. [Note: Folate
deficiency presents as a megaloblastic anemia due to decreased availability of
the purines and of the thymidine monophosphate needed for DNA synthesis.]
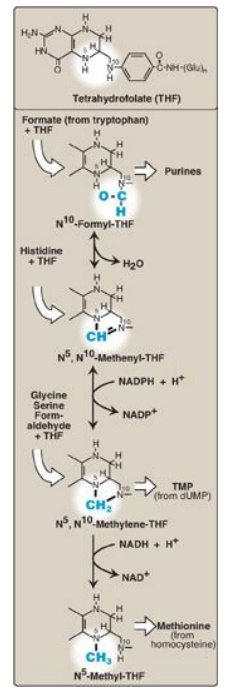
Figure 20.11 Summary of the
interconversions and uses of the carrier tetrahydrofolate. [Note: N5,
N10-Methenyl-THF also arises from N5-formimino-THF (see
Figure 20.4).] NADP(H) = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NAD(H) =
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; TMP = thymidine monophosphate; dUMP = deoxyuridine
monophosphate.
Related Topics
