Chapter Summary, Study Questions
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Fibrous Proteins
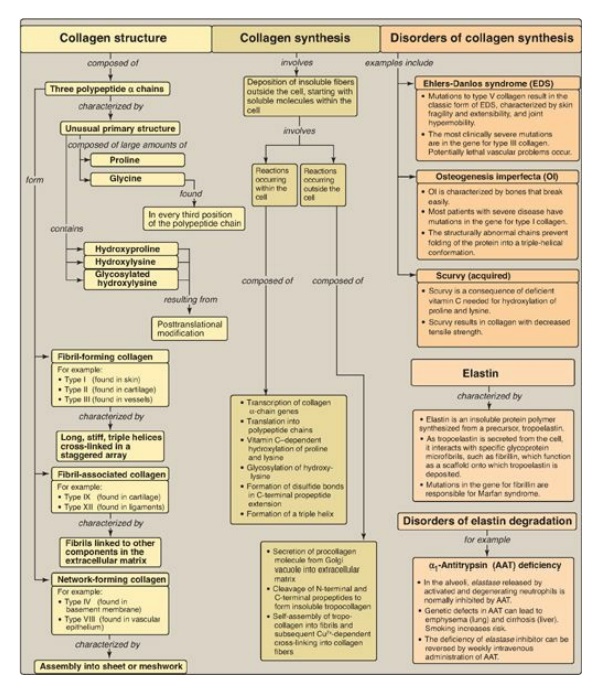
Collagen and elastin are fibrous proteins. Collagen molecules contain an abundance of proline, lysine, and glycine, the latter occurring at every third position in the primary structure.
CHAPTER SUMMARY
Collagen and elastin are fibrous proteins (Figure 4.15). Collagen molecules contain an abundance of proline, lysine, and glycine, the latter occurring at every third position in the primary structure. Collagen also contains hydroxyproline, hydroxylysine, and glycosylated hydroxylysine, each formed by posttranslational modification. Collagen molecules typically form fibrils containing a long, stiff, triple-stranded helical structure, in which three collagen polypeptide chains are wound around one another in a rope-like superhelix (triple helix). Other types of collagen form mesh-like networks. Elastin is a connective tissue protein with rubber-like properties in tissues such as the lung. α1-Antitrypsin (AAT), produced primarily by the liver but also by monocytes and alveolar macrophages, prevents elastase-catalyzed degradation of elastin in the alveolar walls. A deficiency of AAT can cause emphysema and, in some cases, cirrhosis of the liver.
Study Questions
Choose the ONE best answer.
4.1 A 30-year-old woman of Northern European
ancestry presents with progressive dyspnea (shortness of breath). She denies
the use of cigarettes. Family history reveals that her sister also has problems
with her lungs. Which one of the following etiologies most likely explains this
patient’s pulmonary symptoms?
A. Deficiency in
dietary vitamin C
B. Deficiency of α1-antitrypsin
C. Deficiency of prolyl
hydroxylase
D Decreased elastase
activity
E. Increased
collagenase activity
Correct answer = B. α1-Antitrypsin (AAT)
deficiency is a genetic disorder that can cause pulmonary damage and emphysema
even in the absence of cigarette use. A deficiency of AAT permits increased
elastase activity to destroy elastin in the alveolar walls. AAT deficiency
should be suspected when chronic obstructive pulmonary disease develops in a
patient younger than age 45 years who does not have a history of chronic
bronchitis or tobacco use or when multiple family members develop obstructive
lung disease at an early age. Choices A, C, and E refer to collagen, not
elastin.
4.2 What is the differential basis of the liver and
lung pathology seen in α1-antitrypsin deficiency?
With α1-antitrypsin
(AAT) deficiency, the cirrhosis that can result is due to polymerization and
retention of AAT in the liver, its site of synthesis. The alveolar damage is
due to the retention-based deficiency of AAT (a protease inhibitor) in the lung
such that elastase (a protease) is unopposed.
4.3 A 7-month-old child “fell over” while crawling
and now presents with a swollen leg. Imaging reveals a fracture of a bowed
femur, secondary to minor trauma, and thin bones (see x-ray at right). Blue
sclerae are also noted. At age 1 month, the infant had multiple fractures in
various states of healing (right clavicle, right humerus, and right radius). A
careful family history has ruled out nonaccidental trauma (child abuse) as a
cause of the bone fractures. Which pairing of a defective (or deficient)
molecule and the resulting pathology best fits this clinical description?
A. Elastin and
emphysema
B. Fibrillin and Marfan
disease
C. Type I collagen and osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)
D. Type V collagen and
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS)
E. Vitamin C and scurvy
Correct answer = C. The child most likely has
osteogenesis imperfecta. Most cases arise from a defect in the genes encoding
type I collagen. Bones in affected patients are thin, osteoporotic, often
bowed, and extremely prone to fracture. Pulmonary problems are not seen in this
child. Individuals with Marfan syndrome have impaired structural integrity of
the skeleton, eyes, and cardiovascular system. Defects in type V collagen cause
the classic form of EDS characterized by skin extensibility and fragility and
joint hypermobility. Vitamin C deficiency is characterized by capillary
fragility.
4.4 How and why is proline hydroxylated in
collagen?
Proline is hydroxlyated
by prolyl hydroxylase, an enzyme of the rough endoplasmic reticulum that
requires O2, Fe2+, and vitamin C. Hydroxylation increases
interchain hydrogen bond formation, strengthening the triple helix of collagen.
Vitamin C deficiency impairs hydroxylation.
