Mucopolysaccharidoses
| Home | | Biochemistry |Chapter: Biochemistry : Glycosaminoglycans, Proteoglycans, and Glycoproteins
The mucopolysaccharidoses are hereditary diseases (1:25,000 live births) caused by a deficiency of any one of the lysosomal hydrolases normally involved in the degradation of heparan sulfate and/or dermatan sulfate.
MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSES
The
mucopolysaccharidoses are hereditary diseases (1:25,000 live births) caused by
a deficiency of any one of the lysosomal hydrolases normally involved in the
degradation of heparan sulfate and/or dermatan sulfate (see Figure 14.12). They
are progressive disorders characterized by lysosomal accumulation of GAGs in
various tissues, causing a range of symptoms, such as skeletal and
extracellular matrix deformities, and intellectual disability. All are
autosomal recessive disorders except Hunter syndrome, which is X linked.
Children who are homozygous for any one of these diseases are apparently normal
at birth and then gradually deteriorate. In severe cases, death occurs in
childhood. There currently is no cure. Incomplete lysosomal degradation of GAGs
results in the presence of oligosaccharides in the urine. These fragments can
be used to diagnose the specific mucopolysaccharidosis by identifying the
structure present on the nonreducing end of the oligosaccharide, because that
residue would have been the substrate for the missing enzyme. Diagnosis is
confirmed by measuring the patient’s cellular level of the lysosomal
hydrolases. Bone marrow and cord blood transplants, in which transplanted
macrophages produce the enzymes that degrade GAGs, have been used to treat
Hurler and Hunter syndromes, with limited success. Enzyme replacement therapy
is available for both syndromes but does not prevent neurologic damage.
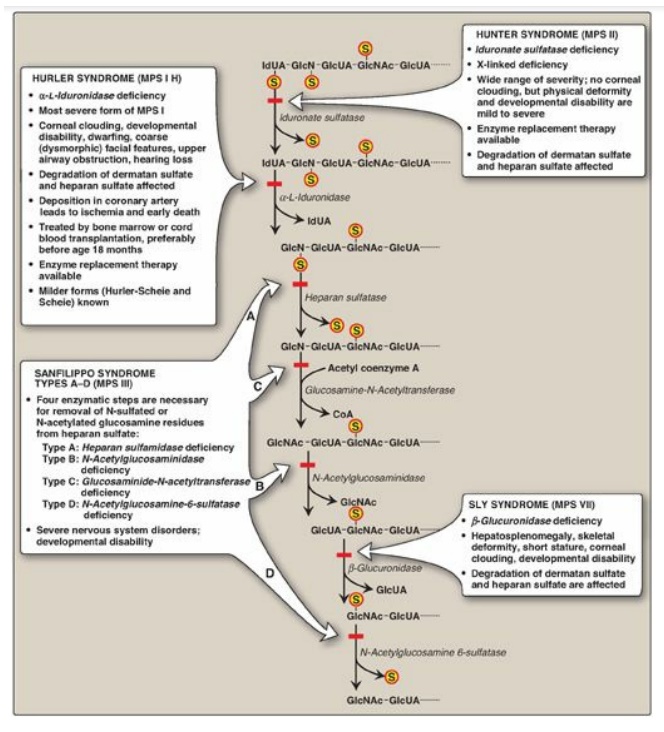
Figure 14.12 Degradation of the glycosaminoglycan heparan sulfate by lysosomal enzymes, indicating sites of enzyme deficiencies in some representative mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs). [Note: Deficiencies in the degradation of keratan sulfate result in Morquio syndrome, A and B. Deficiencies in the degradation of dermatan sulfate result in Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome.] GlcUA = glucuronic acid; IdUA = iduronic acid; GalNAc = N-acetylgalactosamine; GlcNAc = N-acetylglucosamine; GlcN = glucosamine; S = sulfate.
Related Topics
